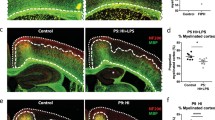
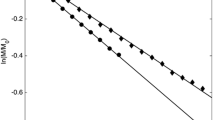
Abstract
Brain white matter is the means of efficient signal propagation in brain and its dysfunction is associated with many neurological disorders. We studied the effect of hyaluronan deficiency on the integrity of myelin in murine corpus callosum. Conditional knockout mice lacking the hyaluronan synthase 2 were compared with control mice. Ultrastructural analysis by electron microscopy revealed a higher proportion of myelin lamellae intruding into axons of knockout mice, along with significantly slimmer axons (excluding myelin sheath thickness), lower g-ratios, and frequent loosening of the myelin wrappings, even though the myelin thickness was similar across the genotypes. Analysis of extracellular diffusion of a small marker molecule tetramethylammonium (74 MW) in brain slices prepared from corpus callosum showed that the extracellular space volume increased significantly in the knockout animals. Despite this vastly enlarged volume, extracellular diffusion rates were significantly reduced, indicating that the compromised myelin wrappings expose more complex geometric structure than the healthy ones. This finding was confirmed in vivo by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy suggested that water was released from within the myelin sheaths. Our results indicate that hyaluronan is essential for the correct formation of tight myelin wrappings around the axons in white matter.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengtsson SL, Nagy Z, Skare S, Forsman L, Forssberg H, Ullen F (2005) Extensive piano practicing has regionally specific effect on white matter development. Nat Neurosci 8:1148–1150
Scholz J, Klein MC, Behrens TEJ, Johansen-Berg H (2009) Training induces changes in white-matter architecture. Nat Neurosci 12:1370–1371
Lassmann H, Brück W, Lucchinetti C (2007) The immunopathology of multiple sclerosis: an overview. Brain Pathol 17:210–218
Marret S, Vanhulle C, Laquerriere A (2013) Pathophysiology of cerebral palsy. Handb Clin Neurol 111:169–176
Armstrong RD, Mierzwa AJ, Marion CM, Sullivan GM (2016) White matter involvement after TBI: clues to axon and myelin repair capacity. Exp Neurol 275:328–333
Fields RD (2008) White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci 31:361–370
Filley CM, Fields RD (2016) White matter and cognition: making the connection. J Neurophysiol 116:2093–2104
Bekku Y, Vargova L, Goto Y, Vorisek I, Dmytrenko L, Narasaki M, Ohtsuka A, Fassler R, Ninomiya Y, Sykova E, Oohashi T (2010) Bral1: its role in diffusion barrier formation and conduction velocity in the CNS. J Neurosci 30:3113–3123
Yamaguchi Y (2000) Lecticans: organizers of the brain extracellular matrix. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:276–289
Dityatev A, Seidenbecher CI, Schachner M (2010) Compartmentalization from the outside: the extracellular matrix and functional microdomains in the brain. Trends Neurosci 33:503–512
Smith PD, Coulson-Thomas VJ, Foscarin S, Kwok JC, Fawcett JW (2015) “GAG-ing with neurons”: the role of glycosaminoglycans patterning in the central nervous system. Exp Neurol 274:100–114
Toole BP (2004) Hyaluronan: from extracellular glue to pericellular cue. Nat Rev Cancer 4:528–539
Toole BP (2000) Hyaluronan is not just a goo! J Clin Invest 106:335–336
Delpech B, Delpech A, Bruckner G, Girard N, Maingonnat C (1989) Hyaluronan and hyaluronectin in the nervous system. Ciba Found Symp 143:208–220; (discussion 21–32, 81–85).
Girard N, Courel MN, Delpech A, Bruckner G, Delpech B (1992) Staining of hyaluronan in rat cerebellum with a hyaluronectin-antihyaluronectin immune complex. Histochem J 24:21–24
Eggli PS, Lucocq Ott P, Graber W, van der Zypen E (1992) Ultrastructural localization of hyaluronan in myelin sheaths of the rat central and rat and human peripheral nervous systems using hyaluronan-binding protein-gold and link protein-gold. Neuroscience 48:137–744
Arranz A, Perkins KL, Irie F, Lewis DP, Hrabe J, Xiao F, Itano N, Kimata K, Hrabetova S, Yamaguchi Y (2014) Hyaluronan deficiency due to Has3 knock-out causes altered neuronal activity and seizures via reduction in brain extracellular space. J Neurosci 34:6164–6176
Sykova E, Nicholson C (2008) Diffusion in brain extracellular space. Physiol Rev 88:1277–1340
Sykova E, Vorisek I, Mazel T, Antonova T, Schachner M (2005) Reduced extracellular space in the brain of tenascin-R- and HNK-1-sulphotransferase deficient mice. Eur J Neurosci 22:1873–1880
Nicholson C (2001) Diffusion and related transport mechanisms in brain tissue. Rep Prog Phys 64:815–884
Hrabe J, Hrabetova S, Segeth K (2004) A model of effective diffusion and tortuosity in the extracellular space of the brain. Biophys J 87:1606–1617
Nicholson C, Phillips JM (1981) Ion diffusion modified by tortuosity and volume fraction in the extracellular microenvironment of the rat cerebellum. J Physiol 321:225–257
Odackal J, Colbourn R, Odackal NJ, Tao L, Nicholson C, Hrabetova S (2017) Real-time iontophoresis with tetramethylammonium to quantify volume fraction and tortuosity of brain extracellular space. J Vis Exp 125:e55755
Rice ME, Okada YC, Nicholson C (1993) Anisotropic and heterogeneous diffusion in the turtle cerebellum: implications for volume transmission. J Neurophysiol 70:2035–2044
Vorisek I, Sykova E (1997) Evolution of anisotropic diffusion in the developing rat corpus callosum. J Neurophysiol 78:912–919
Aoki C, Rodrigues S, Kurose H (2000) Use of electron microscopy in the detection of adrenergic receptors. In: Machida C (ed) Methods in molecular biology: adrenergic receptor protocols, Humana, pp. 535–563.
Hooshmand MJ, Anderson AJ, Cummings BJ (2014) Improved pre-embedded immuno-electron microscopy procedures to preserve myelin integrity in mammalian central nervous tissue. In: Mendex-Vilas A (eds) Microscopy: advances in scientific research and education. pp. 59–65.
West KL, Kelm ND, Carson RP, Does MD (2015) Quantitative analysis of mouse corpus callosum from electron microscopy images. Data Brief 5:124–128
Xiao F, Hrabetova S (2009) Enlarged extracellular space of aquaporin-4-deficient mice does not enhance diffusion of Alexa Fluor 488 or dextran polymers. Neuroscience 161:39–45
Nicholson C (1993) Ion-selective microelectrodes and diffusion measurements as tools to explore the brain cell microenvironment. J Neurosci Methods 48:199–213
Hrabetova S (2005) Extracellular diffusion is fast and isotropic in the stratum radiatum of hippocampal CA1 region in rat brain slices. Hippocampus 15:441–450
Hrabetova S, Nicholson C (2007) Biophysical properties of brain extracellular space explored with ion-selective microelectrodes, integrative optical imaging and related techniques. In: Michael AC, Borland LM (eds) Electrochemical methods for neuroscience. CRC, Florida, pp 167–204
Sykova E, Mazel T, Hasenohrl RU, Harvey AR, Simonova Z, Mulders WHAM, Huston JP (2002) Learning deficits in aged rats related to decrease in extracellular volume and loss of diffusion anisotropy in hippocampus. Hippocampus 12:269–279
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 103:247–254
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructral and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative diffusion tensor MRI. J Magn Reson 111:209–219
Callaghan PT (1991) Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance microscopy. Oxford University Press, New York
Hrabe J, Kaur G, Guilfoyle DN (2007) Principles and limitations of NMR diffusion measurements. J Med Phys 32:34–42
Mansfied P (1977) Multi-planar image formation using NMR spin echoes. J Phys C 10:L55–L58
Bottomley PA (1987) Spatial localization in NMR spectroscopy in vivo. Ann NY Acad Sci USA 508:333–348
Gruetter R (1993) Automatic, localized in vivo adjustment of all first- and second-order shim coils. Magn Reson Med 29:804–811
Tkac I, Starcuk Z, Choi IY, Gruetter R (1999) In vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy of rat brain at 1 ms echo time. Magn Reson Med 41:649–656
Provencher SW (1993) Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 30:672–679
Ernst T, Kreis R, Ross BD (1993) Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the human brain. I. Compartments and water. J Magn Reson B 102:1–8
Sturrock RR (1980) Myelination of the mouse corpus callosum. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 6:415–420
Lehman DM, Hale DE, Cody JT, Harrison JM, Leach RJ (1999) Molecular, morphometric and functional analyses demonstrate that the growth hormone deficient little mouse is not hypomyelinated. Dev Brain Res 116:191–199
Sykova E, Mazel T, Simonova Z (1998) Diffusion constrains and neuron-glia interaction during aging. Exp Gerontol 33:837–851
Oohashi T, Hirakawa S, Bekku Y, Rauch U, Zimmermann DR, Su WD, Ohtsuka A, Murakami T, Ninomiya Y (2002) Bral1, a brain-specific link protein, colocalizing with the versican V2 isoform at the nodes of Ranvier in developing and adult mouse central nervous systems. Mol Cell Neurosci 19:43–57
Xiao F, Hrabe J, Hrabetova S (2015) Anomalous extracellular diffusion in rat cerebellum. Biophys J 108:2384–2395
Menon RS, Allen PS (1991) Application of continuous relaxation time distributions to the fitting of data from model systems and excised tissue. Magn Reson Med 20:214–227
MacKay AL, Laule C (2016) Magnetic resonance of myelin water: An in vivo marker for myelin. Brain Plast 2:71–91
Orije J, Kara F, Guglielmetti C, Praet J, Van der Linden A, Ponsaerts P, Verhoye M (2015) Longitudinal monitoring of metabolic alterations in cuprizone mouse model of multiple sclerosis using 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuroimage 114:128–135
Matsushima GK, Morell P (2001) The neurotoxicant, cuprizone, as a model to study demyelination and remyelination in the central nervous system. Brain Pathol 11:107–116
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke grant R01 NS047557 to SH and CA, National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke grant R01 NS066019 to CA, National Institutes of Health National Institute of General Medical Sciences grant R25 GM097634 to CA, National Institutes of Health National Institute of Aging grant RF1 AG057579 to YY, National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute Core grant EY13079 to the Center for Neural Science, New York University, and National Institutes of Health National Center for Research Resources shared instrumentation grant S10 RR023534 to Nathan S. Kline Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All protocols for animal use were in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guidelines and approved by the local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute, State University of New York Downstate, and Nathan S. Kline Institute. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Special Issue: In honor of Prof Eva Sykova.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherpa, A.D., Guilfoyle, D.N., Naik, A.A. et al. Integrity of White Matter is Compromised in Mice with Hyaluronan Deficiency. Neurochem Res 45, 53–67 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02819-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02819-z