Abstract
Purpose
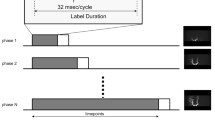
MR angiography using the silent MR angiography algorithm (silent MRA), which combines arterial spin labeling and an ultrashort time echo, has not been used for the evaluation of cerebral arteriovenous malformations (CAVMs). We aimed to determine the usefulness of silent MRA for the evaluation of CAVMs.
Methods
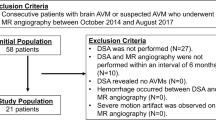
Twenty-nine CAVMs of 28 consecutive patients diagnosed by 4D CT angiography or digital subtraction angiography, who underwent both time-of-flight (TOF) MRA and silent MRA, were enrolled. Two observers independently assessed the TOF-MRA and silent MRA images of CAVMs. Micro AVM was defined as AVM with a nidus diameter less than 10 mm. The detection rate, visualization of the components, and accuracy of Spetzler–Martin grade were evaluated with statistical software R.
Results
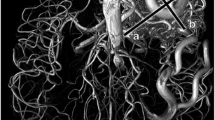
For all 29 CAVMs, 23 (79%) lesions were detected for TOF-MRA and all for silent MRA. Of 10 micro AVMs, only 4 (40%) lesions were detectable on TOF-MRA and all (100%) on silent MRA. The visibility of the nidus and drainer was significantly better for silent MRA than TOF-MRA (p < 0.001), while there was no significant difference in the feeder between the two sequences. The accuracy rates of the Spetzler–Martin grade for the TOF and silent MRA were 38% (11/29) and 79.3% (23/29), respectively (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Silent MRA is useful for evaluating CAVM components and detecting micro AVM.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAVM:
-
Cerebral arteriovenous malformations
- ARUBAA:
-
Randomized trial of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous malformations
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- D:
-
Dimensional
- TOF:
-
Time of flight
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- ASL:
-
Arterial spin labeling
- UTE:
-
Ultrashort time echo
- AV:
-
Arteriovenous
- T:
-
Tesla
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NEX:
-
Number of excitations
- MIP:
-
Maximum intensity projection
- PLD:
-
Post-labeling delay
References
Laakso A, Dashti R, Seppänen J, Juvela S, Väärt K, Niemelä M, Sankila R, Hernesniemi JA (2008) Long-term excess mortality in 623 patients with brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 63(2):244–253
Michalak SM, Rolston JD, Lawton MT (2016) Incidence and predictors of complications and mortality in cerebrovascular surgery: national trends from 2007 to 2012. Neurosurgery 79(2):182–193
Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C, Moquete E, Moy CS, Overbey JR, Al-Shahi Salman R, Vicaut E, Young WL, Houdart E, Cordonnier C, Stefani MA, Hartmann A, von Kummer R, Biondi A, Berkefeld J, Klijn CJ, Harkness K, Libman R, Barreau X, Moskowitz AJ, international ARUBA investigators (2014) Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA) a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 383(9917):614–621
Halim AX, Johnston SC, Singh V, McCulloch CE, Bennett JP, Achrol AS, Sidney S, Young WL (2014) Longitudinal risk of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with arteriovenous malformation of the brain within a defined population. Stroke 35:1697–1702
Hernesniemi JA, Dashti R, Juvela S, Väärt K, Niemelä M, Laakso A (2008) Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: a long-term follow-up study of risk of hemorrhage in 238 patients. Neurosurgery 63(5):823–829 discussion 829-31
Stapf C, Mast H, Sciacca RR, Choi JH, Khaw AV, Connolly ES, Pile-Spellman J, Mohr JP (2006) Predictors of hemorrhage in patients with untreated brain arteriovenous malformation. Neurology 9;66(9):1350–1355
Meisel HJ, Mansmann U, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, Brock M, Lasjaunias P (2000) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations and associated aneurysms:analysis of 305 cases from a series of 662 patients. Neurosurgery 46:793–802
Mast H, Young WL, Koennecke HC, Sciacca RR, Osipov A, Pile-Spellman J, Hacein-Bey L, Duong H, Stein BM, Mohr JP (1997) Risk of spontaneous haemorrhage after diagnosis of cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Lancet 350:1065–1068
Stapf C, Mohr JP, Sciacca RR, Hartmann A, Aagaard BD, Pile-Spellman J, Mast H (2000) Incident hemorrhage risk of brain arteriovenous malformations located in the arterial borderzones. Stroke 31:2365–2368
Thiex R, Norbash AM, Frerichs KU (2010) The safety of dedicated-team catheter-based diagnostic cerebral angiography in the era of advanced noninvasive imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:230–234
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Dawkins AA, Evans AL, Wattam J, Romanowski CA, Connolly DJ, Hodgson TJ, Coley SC (2007) Complications of cerebral angiography: a prospective analysis of 2,924 consecutive procedures. Neuroradiology 49:753–759
Buis DR, Bot JC, Barkhof F, Knol DL, Lagerwaard FJ, Slotman BJ, Vandertop WP, van den Berg R (2012) The predictive value of 3D time-of-flight MR angiography in assessment of brain arteriovenous malformation obliteration after radiosurgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(2):232–238
Farb RI, McGregor C, Kim JK, Laliberte M, Derbyshire JA, Willinsky RA, Cooper PW, Westman DG, Cheung G, Schwartz ML, Stainsby JA, Wright GA (2001) Intracranial arteriovenous malformations: real-time auto-triggered elliptic centric-ordered 3D gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography--initial assessment. Radiology 220(1):244–251
Willemse RB, Mager JJ, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, Mauser H, Wolbers JG (2000) Bleeding risk of cerebrovascular malformations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Neurosurg 92(5):779–784
Meybodi AT, Kim H, Nelson J, Hetts SW, Krings T, ter Brugge KG, Faughnan ME, Lawton MT, On Behalf Of The Brain Vascular Malformation Consortium HHT Investigator Group (2018) Surgical treatment vs nonsurgical treatment for brain arteriovenous malformations in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: a retrospective multicenter consortium study. Neurosurgery 82(1):35–47
Alibek S, Vogel M, Sun W, Winkler D, Baker CA, Burke M, Gloger H (2014) Acoustic noise reduction in MRI using silent scan: an initial experience. Diagn Interv Radiol 20(4):360–363
Iryo Y, Hirai T, Nakamura M, Kawano T, Kaku Y, Ohmori Y, Kai Y, Azuma M, Nishimura S, Shigematsu Y, Kitajima M, Yamashita Y (2016) Evaluation of intracranial arteriovenous malformations with four-dimensional arterial-spin labeling-based 3-T magnetic resonance angiography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 40:290–296
Xu J, Shi D, Chen C, Li Y, Wang M, Han X, Jin L, Bi X (2011) Noncontrast-enhanced four-dimensional MR angiography for the evaluation of cerebral arteriovenous malformation: a preliminary trial. J Magn Reson Imaging 34:1199–1205
Raoult H, Bannier E, Robert B, Barillot C, Schmitt P, Gauvrit JY (2014) Time-resolved spin-labeled MR angiography for the depiction of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a comparison of techniques. Radiology 271:524–533
Wolf RL, Wang J, Detre JA, Zager EL, Hurst RW (2008) Arteriovenous shunt visualization in arteriovenous malformations with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:681–687
Yu S, Yan L, Yao Y, Wang S, Yang M, Wang B, Zhuo Y, Ai L, Miao X, Zhao J, Wang DJ (2012) Noncontrast dynamic MRA in intracranial arteriovenous malformation (AVM), comparison with time of flight (TOF) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Magn Reson Imaging 30(6):869–877
Amukotuwa SA, Heit JJ, Marks MP, Fischbein N, Bammer R (2016) Detection of cortical venous drainage and determination of the Borden type of dural arteriovenous fistula by means of 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 207:163–169
Le TT, Fischbein NJ, André JB, Wijman C, Rosenberg J, Zaharchuk G (2012) Identification of venous signal on arterial spin labeling improves diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistulas and small arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:61–68
Schubert T, Clark Z, Sandoval-Garcia C, Zea R, Wieben O, Wu H, Turski PA, Johnson KM (2018) Non contrast, pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling and accelerated 3-dimensional radial acquisition intracranial 3-dimensional magnetic resonance angiography for the detection and classification of intracranial arteriovenous shunts. Investig Radiol 53(2):80–86
Kukuk GM, Hadizadeh DR, Boström A, Gieseke J, Bergener J, Nelles M, Mürtz P, Urbach H, Schild HH, Willinek WA (2010) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations at 3.0 T: intraindividual comparative study of 4D-MRA in combination with selective arterial spin labeling and digital subtraction angiography. Investig Radiol 45:126–132
Takano N, Suzuki M, Irie R, Yamamoto M, Teranishi K, Yatomi K, Hamasaki N, Kumamaru KK, Hori M, Oishi H, Aoki S (2017) Non-contrast-enhanced silent scan MR angiography of intracranial anterior circulation aneurysms treated with a low-profile visualized intraluminal support device. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38(8):1610–1616
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
The Comprehensive R Archive Network. The R Project for Statistical Computing. https://cran.r-project.org/ Published 2017. Accessed December 13, 2018
Mukherji SK, Quisling RG, Kubilis PS, Finn JP, Friedman WA (1995) Intracranial arteriovenous malformations: quantitative analysis of magnitude contrast MR angiography versus gradient-echo MR imaging versus conventional angiography. Radiology 196(1):187–193
Matsubara S, Mandzia JL, terBrugge K, Willinsky RA, Faughnan ME (2000) Angiographic and clinical characteristics of patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformations associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21(6):1016–1020
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Our hospital IRB deemed informed consent unnecessary for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, N., Akiyama, T., Fujiwara, K. et al. Silent MRA: arterial spin labeling magnetic resonant angiography with ultra-short time echo assessing cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Neuroradiology 62, 455–461 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02345-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02345-3