Abstract
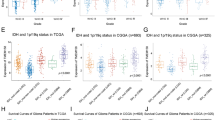
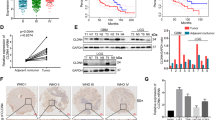
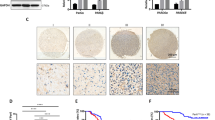
Glioma is the most aggressive primary brain tumor. We have previously provided evidence that IFITM3 promoted glioma cells migration. However, the mechanism of how IFITM3 regulates glioma cells invasion and whether IFITM3 participates in TGF-β-mediated glioma invasion are still unknown. In this paper, we proved that IFITM3 was notably up-regulated in glioma tissues. Knockdown of IFITM3 suppressed STAT3 phosphorylation in vitro, and a specific STAT3 inhibitor AG490 reversed IFITM3-induced invasion of glioma cells. Furthermore, IFITM3 expression was induced by TGF-β in glioma and IFITM3 knockdown abolished TGF-β-mediated glioma cells invasion. Collectively, the results indicate that IFITM3/STAT3 axis may promote TGF-β-induced glioma cells invasion. This study provided some suggestions for the clinical treatment of the brain tumor.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IFITM3:
-
Interferon induced transmembrane protein 3
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription3
- NBTs:
-
Normal brain tissues
- TCGA:
-
The cancer genome atlas
- CGGA:
-
Chinese glioma genome atlas
- RT–qPCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
References
Schwartzbaum JA, Fisher JL, Aldape KD et al (2006) Epidemiology and molecular pathology of glioma. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:494–503 (quiz 1 p following 516)
Liu BL, Cheng JX, Zhang X et al (2010) Controversies concerning the application of brachytherapy in central nervous system tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:173–185
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD et al (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 60:166–193
Lin L, Cai J, Jiang C (2017) Recent advances in targeted therapy for glioma. Curr Med Chem 24:1365–1381
Hickford D, Frankenberg S, Shaw G et al (2012) Evolution of vertebrate interferon inducible transmembrane proteins. BMC Genom 13:155
Sallman Almen M, Bringeland N, Fredriksson R et al (2012) The dispanins: a novel gene family of ancient origin that contains 14 human members. PLoS ONE 7:e31961
Schoggins JW, Wilson SJ, Panis M et al (2011) A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 472:481–485
Brass AL, Huang IC, Benita Y et al (2009) The IFITM proteins mediate cellular resistance to influenza A H1N1 virus, West Nile virus, and dengue virus. Cell 139:1243–1254
Shapira SD, Gat-Viks I, Shum BO et al (2009) A physical and regulatory map of host-influenza interactions reveals pathways in H1N1 infection. Cell 139:1255–1267
Bailey CC, Huang IC, Kam C et al (2012) Ifitm3 limits the severity of acute influenza in mice. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002909
Lewin AR, Reid LE, McMahon M et al (1991) Molecular analysis of a human interferon-inducible gene family. Eur J Biochem 199:417–423
Friedman RL, Manly SP, McMahon M et al (1984) Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell 38:745–755
Desai TM, Marin M, Chin CR et al (2014) IFITM3 restricts influenza A virus entry by blocking the formation of fusion pores following virus-endosome hemifusion. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004048
Jia Y, Xiao Z, Jiang W et al (2017) Overexpression of IFITM3 predicts poor prognosis in stage IIA esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after Ivor Lewis esophagectomy. Thorac Cancer 8:592–599
Li D, Peng Z, Tang H et al (2011) KLF4-mediated negative regulation of IFITM3 expression plays a critical role in colon cancer pathogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 17:3558–3568
Wu RS, Wu LQ, Li KH et al (2016) Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 knock-down inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells in vitro. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 36:244–249
Zhao B, Wang HL, Zong G et al (2013) The role of IFITM3 in the growth and migration of human glioma cells. BMC Neurol 13:210
Darnell JE Jr. (1997) STATs and gene regulation. Science 277:1630–1635
Shuai K, Ziemiecki A, Wilks AF et al (1993) Polypeptide signalling to the nucleus through tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak and Stat proteins. Nature 366:580–583
Chai EZ, Shanmugam MK, Arfuso F et al (2016) Targeting transcription factor STAT3 for cancer prevention and therapy. Pharmacol Ther 162:86–97
de la Iglesia N, Puram SV, Bonni A (2009) STAT3 regulation of glioblastoma pathogenesis. Curr Mol Med 9:580–590
Schindler C, Darnell JE Jr. (1995) Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem 64:621–651
Liu Q, Li G, Li R et al (2010) IL-6 promotion of glioblastoma cell invasion and angiogenesis in U251 and T98G cell lines. J Neurooncol 100:165–176
Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z et al (2014) JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol 44:1643–1651
Wang Y, Wu C, Zhang C et al (2018) TGF-β-induced STAT3 overexpression promotes human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis through malat1/miR-30a interactions. Cancer Lett 436:52–62
Sun J, Liu SZ, Lin Y et al (2014) TGF-beta promotes glioma cell growth via activating Nodal expression through Smad and ERK1/2 pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443:1066–1072
Kwiatkowski W, Gray PC, Choe S (2014) Engineering TGF-beta superfamily ligands for clinical applications. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35:648–657
Varga J, Pasche B (2009) Transforming growth factor beta as a therapeutic target in systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 5:200–206
Kaminska B, Kocyk M, Kijewska M (2013) TGF beta signaling and its role in glioma pathogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol 986:171–187
Arjaans M, Oude Munnink TH, Timmer-Bosscha H et al (2012) Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta expression and activation mechanisms as potential targets for anti-tumor therapy and tumor imaging. Pharmacol Ther 135:123–132
Lim W-C, Kim H, Kim Y-J et al (2017) Dioscin suppresses TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses A549 lung cancer migration and invasion. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:3342–3348
Gupta S, Hau AM, Al-Ahmadie HA et al (2016) Transforming growth factor-β is an upstream regulator of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2–dependent bladder cancer cell migration and invasion. Am J Pathol 186:1351–1360
Sciumè G, Soriani A, Piccoli M et al (2010) CX3CR33/CX3CL1 axis negatively controls glioma cell invasion and is modulated by transforming growth factor-beta1. Neuro-Oncology 12:701–710
Gan CP, Sam KK, Yee PS et al (2019) IFITM3 knockdown reduces the expression of CCND1 and CDK4 and suppresses the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Oncol (Dordrecht) 42:477–490
Dowlati A, Nethery D, Kern JA (2004) Combined inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor and JAK/STAT pathways results in greater growth inhibition in vitro than single agent therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 3:459–463
Scott R, Siegrist F, Foser S et al (2011) Interferon-alpha induces reversible DNA demethylation of the interferon-induced transmembrane protein-3 core promoter in human melanoma cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31:601–608
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Fulop J et al (2015) CBTRUS Statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro-oncology 17(4):41–462
Komori T, Sasaki H, Yoshida K (2016) Revised WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system: summary of the revision and perspective. Neurol Surg 44:625–635
Miller JJ, Shih HA, Andronesi OC et al (2017) Isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutant glioma: evolving clinical and therapeutic implications. Cancer 123:4535–4546
Jhaveri N, Chen TC, Hofman FM (2016) Tumor vasculature and glioma stem cells: contributions to glioma progression. Cancer Lett 380:545–551
Miller JJ, Wen PY (2016) Emerging targeted therapies for glioma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 21:441–452
Reid LE, Brasnett AH, Gilbert CS et al (1989) A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:840–844
Yang Y, Lee JH, Kim KY et al (2005) The interferon-inducible 9-27 gene modulates the susceptibility to natural killer cells and the invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett 221:191–200
Zhang D, Wang H, He H et al (2017) Interferon induced transmembrane protein 3 regulates the growth and invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac Cancer 8:337–343
Liu H, Su YK, Bamodu O et al (2018) The disruption of the β-catenin/TCF-1/STAT3 signaling axis by 4-acetylantroquinonol b inhibits the tumorigenesis and cancer stem-cell-like properties of glioblastoma cells, vitro and in vivo. Cancers 10:491
Sun XL, Wang JH, Huang M et al (2018) STAT3 promotes tumour progression in glioma by inducing FOXP1 transcription. J Cell Mol Med 22:5629–5638
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H et al (2014) IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Investig 124:1853–1867
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K et al (2006) Activation of STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 15:1445–1451
Seystahl K, Tritschler I, Szabo E et al (2015) Differential regulation of TGF-beta-induced, ALK-5-mediated VEGF release by SMAD2/3 versus SMAD1/5/8 signaling in glioblastoma. Neuro-oncology 17:254–265
Liu S, Sun J, Lan Q (2013) TGF-beta-induced miR10a/b expression promotes human glioma cell migration by targeting PTEN. Mol Med Rep 8:1741–1746
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Central laboratory of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81072066, No. 81502149, No. 81402078), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No. 1608085MH225, No. 1508085MH194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Tang, F., Bian, E. et al. IFITM3/STAT3 axis promotes glioma cells invasion and is modulated by TGF-β. Mol Biol Rep 47, 433–441 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05146-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05146-2