Abstract
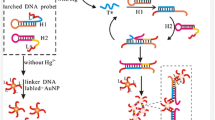
This work describes an aptamer based method for highly sensitive determination of Hg(II). A Hg(II)-binding ssDNA aptamer was linked to silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles (magNPs). Then, a conjugate composed of graphene and CdS quantum dots (Gr-CdS) was linked to the complementary ssDNA. On mixing the two components, a duplex of type magNP-dsNNA-Gr/CdS is generated. If Hg(II) is added, it wills capturing the aptamer, and this leads to the release of Gr/CdS because of the formation of a stable thymine-Hg2+-thymine link. External magnetic force is used to remove the remaining complex. The released graphene-CdS is decomposed by HNO3 and injected into a graphite furnace AAS. The detectable amount of Cd is proportional to the concentration of Hg(II) in the sample. Under the optimal conditions, the method has a linear response in the 2.50 aM to 0.25 nM Hg(II) concentration range, and the detection limit is as low as 7.6 aM (at S/N = 3). It has high selectivity for Hg(II) over other metal ions.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Driscoll CT, Mason RP, Chan HM, Jacob DJ, Pirrone N (2013) Mercury as a global pollutant: sources, pathways, and effects. Environ Sci Technol 47:4967–4983
EPA US (2001) Mercury Update: Impact on Fish Advisories. EPA Fact Sheet EPA-823-F-01-011
Domínguez MA, Grünhut M, Pistonesi MF et al (2012) Automatic flow-batch system for cold vapor atomic absorption spectroscopy determination of mercury in honey from Argentina using online sample treatment. J Agric Food Chem 60:4812–4817
Liu Z, Zhu Z, Wu Q et al (2011) Dielectric barrier discharge-plasma induced vaporization and its application to the determination of mercury by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Analyst 136:4539–4544
Wang M, Feng W, Shi J et al (2007) Development of a mild mercaptoethanol extraction method for determination of mercury species in biological samples by HPLC–ICP-MS. Talanta 71:2034–2039
Kodamatani H, Matsuyama A, Saito K et al (2012) Sensitive determination method for mercury ion, methyl-, ethyl-, and phenyl-mercury in water and biological samples using high-performance liquid chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. Anal Sci 28:959–965
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249(80):505–510
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818
Kim YS, Raston NHA, Gu MB (2016) Aptamer-based nanobiosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 76:2–19
Palecek E, Bartosik M (2012) Electrochemistry of nucleic acids. Chem Rev 112:3427–3481
Wang L, Liu F, Sui N et al (2016) A colorimetric assay for Hg(II) based on the use of a magnetic aptamer and a hybridization chain reaction. Microchim Acta 183:2855–2860
Xue X, Wang F, Liu X (2008) One-step, room temperature, colorimetric detection of mercury (Hg2+) using DNA/nanoparticle conjugates. J Am Chem Soc 130:3244–3245
Srinivasan K, Subramanian K, Murugan K, Dinakaran K (2016) Sensitive fluorescence detection of mercury(II) in aqueous solution by the fluorescence quenching effect of MoS2 with DNA functionalized carbon dots. Analyst 141:6344–6352
Zhang H, Yang L, Zhou B, Liu W, Ge J, Wu J, Wang Y, Wang P (2013) Ultrasensitive and selective gold film-based detection of mercury(II) in tap water using a laser scanning confocal imaging-surface plasmon resonance system in real time. Biosens Bioelectron 47:391–395
Pelossof G, Tel-Vered R, Liu X, Willner I (2011) Amplified surface Plasmon resonance based DNA biosensors, Aptasensors, and Hg2+ sensors using Hemin/G-Quadruplexes and au nanoparticles. Chem Eur J 17:8904–8912
Zhang H, Harpster MH, Park HJ et al (2010) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of DNA derived from the West Nile virus genome using magnetic capture of Raman-active gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 83:254–260
Salimi A, Alizadeh V, Hallaj R (2006) Amperometric detection of ultra trace amounts of Hg(I) at the surface boron doped diamond electrode modified with iridium oxide. Talanta 68:1610–1616
Mor-Piperberg G, Tel-Vered R, Elbaz J, Willner I (2010) Nanoengineered electrically contacted enzymes on DNA scaffolds: functional assemblies for the selective analysis of Hg2+ ions. J Am Chem Soc 132:6878–6879
Tao L, Song C, Sun Y, Li X, Li Y, Jin B, Zhang Z, Yang K (2013) Analytica Chimica Acta a fluorescent and chemiluminescent difunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticle as a label for the ultrasensitive detection of cancer cells. Anal Chim Acta 761:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.11.046
Yu X, Munge B, Patel V, Jensen G, Bhirde A, Gong JD, Kim SN, Gillespie J, Gutkind JS, Papadimitrakopoulos F, Rusling JF (2006) Carbon nanotube amplification strategies for highly sensitive immunodetection of cancer biomarkers. J Am Chem Soc 128:11199–11205
Huang J, Gao X, Jia J, Kim JK, Li Z (2014) Graphene oxide-based amplified fluorescent biosensor for Hg2+ detection through hybridization chain reactions. Anal Chem 86:3209–3215
Qu Z, Xu H, Xu P, Chen K, Mu R, Fu J, Gu H (2014) Ultrasensitive ELISA using enzyme-loaded nanospherical brushes as labels. Anal Chem 86:9367–9371
Mani V, Wasalathanthri DP, Joshi AA et al (2012) Highly efficient binding of paramagnetic beads bioconjugated with 100 000 or more antibodies to protein-coated surfaces. Anal Chem 84:10485–10491
Kim C, Searson PC (2017) Detection of Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase antigen in buffer using Aptamer-modified magnetic microparticles for capture, oligonucleotide-modified quantum dots for detection, and oligonucleotide-modified Gold nanoparticles for signal amplification. Bioconjug Chem 28:2230–2234
Chon H, Lee S, Yoon S-Y et al (2014) SERS-based competitive immunoassay of troponin I and CK-MB markers for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Chem Commun 50:1058–1060
Salimi A, Rahmatpanah R, Hallaj R, Roushani M (2013) Covalent attachment of thionine onto gold electrode modified with cadmium sulfide nanoparticles: improvement of electrocatalytic and photelectrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide. Electrochim Acta 95:60–70
Zhang H, Ma X, Ji Y et al (2003) Single crystalline CdS nanorods fabricated by a novel hydrothermal method. Chem Phys Lett 377:654–657
Liu S-J, Nie H-G, Jiang J-H, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2009) Electrochemical sensor for mercury (II) based on conformational switch mediated by interstrand cooperative coordination. Anal Chem 81:5724–5730
Ma X, Wang Z, He S et al (2019) L-cysteine modified gold nanoparticles for tube-based fluorometric determination of mercury (II) ions. Microchim Acta 186:632
Mao A, Wei C (2019) Cytosine-rich ssDNA-templated fluorescent silver and copper/silver nanoclusters: optical properties and sensitive detection for mercury (II). Microchim Acta 186:541
Zhang Z, Zhang F, He P et al (2019) Fluorometric determination of mercury (II) by using thymine-thymine mismatches as recognition elements, toehold binding, and enzyme-assisted signal amplification. Microchim Acta 186:551
Huang X, Hao Y, Wu H et al (2014) Magnetic beads based colorimetric detection of mercuric ion. Sensors Actuators B Chem 191:600–604
Chen Y, Wu L, Chen Y et al (2012) Determination of mercury (II) by surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy based on thiol-functionalized silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 177:341–348
Huang R-F, Liu H-X, Gai Q-Q, Liu GJ, Wei Z (2015) A facile and sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for Hg2+ analysis based on a dual-function oligonucleotide probe. Biosens Bioelectron 71:194–199
Liu F, Wang S, Zhang M et al (2014) Aptamer based test stripe for ultrasensitive detection of mercury (II) using a phenylene-ethynylene reagent on nanoporous silver as a chemiluminescence reagent. Microchim Acta 181:663–670
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Iranian Nanotechnology Initiative and the Research Office of the University of Kurdistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharifi, A., Hallaj, R., Bahar, S. et al. Indirect determination of mercury(II) by using magnetic nanoparticles, CdS quantum dots and mercury(II)-binding aptamers, and quantitation of released CdS by graphite furnace AAS. Microchim Acta 187, 91 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4029-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4029-x