Abstract
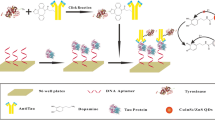
Neurodegeneration currently remains without a differential diagnosis or cure. Tau protein is one of the biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases commonly known as tauopathies. Tau protein plays an integral role in stabilizing microtubules and cell structure; however, due to post-translational modifications, tau protein undergoes self-assembly into cytotoxic structures and is co-localized intra- and extracellularly. Hence, tau protein is a viable biomarker associated with protein pathogenesis and neurodegeneration. The novel optical biosensor for tau441 protein is based on the aptamer recognition probe and the biolayer interferometry (BLI) method for detection. The current biotin-aptasensor in combination with the streptavidin surface provides real-time monitoring of tau441 protein in the nanomolar range, with the limit of detection at 6.7 nM in vitro. The tau441 detection is achieved with high selectivity over other neurodegeneration biomarkers which include amyloid-β and α-synuclein. The aptasensor also allows for tau441 protein detection in a complex matrix such as fetal bovine serum, indicating its utility in other biological fluids for diagnostic applications. The optical method is simple, rapid and highly selective for point-of-care application which is critical for achieving the early and differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases and identifying their treatments.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wingarten MD, Lockwood AH, Hwo SY, Kirschner MW. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;72:1858–62.
Alonso AD, Clerico JD, Li B, Corbo CP, Alaniz ME, Grundke-Iqbal I, et al. Phosphorylation of tau at Thr212, Thr231, and Ser262 combined causes neurodegeneration. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:30851–60.
Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowsk JQ. Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:1121–59.
De Calignon A, Polydoro M, Suarez-Calvet M, William C, Adamowicz DH, Kopeikina KJ, et al. Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 2012;73:685–97.
Kfoury N, Holmes BB, Jiang H, Holtzman DM, Diamond MI. Trans-cellular propagation of tau aggregation by fibrillar species. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:19440–51.
Babić M, Vogrinc Ž, Diana A, Klepac N, Borovečki F, Hof P, et al. Comparison of two commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for cerebrospinal fluid measurement of amyloid β1-42 and total tau. Transl Neurosci. 2013;4:234–40.
Carlin N, Martic-Milne S. Anti-tau antibodies based electrochemical sensor for detection of tau protein biomarkers. J Electrochem Soc. 2018;165:G3018–25.
Kim S, Wark AW, Lee HJ. Femtomolar detection of tau proteins in undiluted plasma using surface plasmon resonance. Anal Chem. 2016;88:7793–9.
Derkus B, Bozkurt PA, Tulu M, Emergul KC, Yucesan C. Simultaneous quantification of myelin basic protein and tau proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of multiple sclerosis patients using nanoimmunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;89:781–8.
Wang SX, Acha D, Shah AJ, Hills F, Roitt I, Demosthenous A, et al. Detection of the tau protein in human serum by a sensitive four-electrode electrochemical biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:482–8.
Nehmé H, Chantepie S, Defert J, Morin P, Papy-Garcia D, Nehmé R. New methods based on capillary electrophoresis for in vitro evaluation of protein tau phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase 3-β. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407:2821–8.
Rissin DM, Kan CW, Campbell TG, Howes SC, Fournier DR, Song L, et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:595–600.
Kontsekova E, Zilka N, Kovacech B, Skrabana R, Novak M. Identification of structural determinants on tau protein essential for its pathological function: novel therapeutic target for tau immunotherapy in Alzheimer's disease. Alz Res Ther. 2014;6:45.
Camero S, Benitez MJ, Cuadros R, Hernandez F, Avila J, Jimenez JS. Thermodynamics of the interaction between Alzheimer's disease related tau protein and DNA. PLoS One. 2014;9:e104690.
Yanamandra K, Kfoury N, Jiang H, Mahan TE, Ma S, Maloney SE, et al. Anti-tau antibodies that block tau aggregate seeding in vitro markedly decrease pathology and improve cognition in vivo. Neuron. 2013;80:402–14.
Vestergaard M, Kerman K, Kim D, Hip HM, Tamiya E. Detection of Alzheimer's tau protein using localised surface plasmon resonance-based immunochip. Talanta. 2008;74:1038–42.
Neely A, Perry C, Varisli B, Singh AK, Arbneshi T, Senapati D, et al. C. Ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of Alzheimer's disease biomarker using two-photon Rayleigh scattering properties of gold nanoparticle. ACS Nano. 2009;3:2834–40.
Zengin A, Tamer U, Caykara T. A SERS-based sandwich assay for ultrasensitive and selective detection of Alzheimer's tau protein. Biomacromolecules. 2013;14:3001–9.
Jayasena SD. Aptamers: an emerging class of molecules that rival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin Chem. 1999;45:1628–50.
Ellington AD, Szostak JW. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990;346:818–22.
Tuerk C, Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990;249:505–10.
Gao S, Zheng X, Jiao B, Wang L. Post-SELEX optimization of aptamers. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:4567–73.
Tan W, Donovan MJ, Jiang J. Aptamers from cell-based selection for bioanalytical applications. Chem Rev. 2013;113:2842–62.
Krylova SM, Musheev M, Nutiu R, Li Y, Lee G, Krylov S. N. tau protein binds single-stranded DNA sequence specifically--the proof obtained in vitro with non-equilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:1371–5.
Mechaly A, Cohen H, Cohen O, Mazor O. A biolayer interferometry-based assay for rapid and highly sensitive detection of biowarfare agents. Anal Biochem. 2016;506:22–7.
Verzijl D, Riedl T, Parren P, Gerritsen A. A novel label-free cell-based assay technology using biolayer interferometry. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;87:388–95.
Zhang M, Jiang X, Le H, Wan P, Ye B. Dip-and-read method for label-free renewable sensing enhanced using complex DNA structures. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:473–8.
Do T, Ho F, Heidecker B, Witte K, Chang L, Lerner L. A rapid method for determining dynamic binding capacity of resins for the purification of proteins. Prot Expr Purif. 2008;60:147–50.
Ciesielski GL, Hytöne VP, Kaguni L. S. Biolayer interferometry: a novel method to elucidate protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions in the mitochondrial DNA Replisome. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2016;1351:223–31.
Auer S, Koho T, Uusi-Kerttula H, Vesikari T, Blazevic V, Hytonen VP. Rapid and sensitive detection of norovirus antibodies in human serum with a biolayer interferometry biosensor. Sens. Act. B Chem. 2015;221:507–14.
Gao S, Zheng X, Wu J. A biolayer interferometry-based competitive biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of saxitoxin. Sens Act B Chem. 2017;246:169–74.
Gao S, Zheng X, Wu J. A biolayer interferometry-based enzyme-linked aptamer sorbent assay for real-time and highly sensitive detection of PDGF-BB. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;102:57–62.
Wu X, Wu D, Lu Z, Chen W, Hu X, Ding YJ. A novel method for high-level production of TEV protease by superfolder GFP tag. Biomed Biotech. 2009;2009:108.
Barghorn S, Nimmrich V, Striebinger A, Krantz C, Keller P, Janson B, et al. Globular amyloid beta-peptide oligomer - a homogenous and stable neuropathological protein in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 2005;95:834–47.
Kim S, Lee HJ. Direct detection of α-1 antitrypsin in serum samples using surface Plasmon resonance with a new Aptamer-antibody Sandwich assay. Anal Chem. 2015;87:7235–40.
Kim S, Lee J, Lee SJ, Lee HJ. Ultra-sensitive detection of IgE using biofunctionalized nanoparticle-enhanced SPR. Talanta. 2010;81:1755–9.
Mocak J, Bond AM, Mitchell S, Scollary G. A statistical overview of standard (IUPAC and ACS) and new procedures for determining the limits of detection and quantification: application to voltammetric and stripping techniques. Pure Appl Chem. 1997;69:297–328.
Li Y, Lim E, Fields T, Wu H, Xu Y, Wang A, et al. Improving sensitivity and specificity of amyloid-β peptides and tau protein detection with antibiofouling magnetic nanoparticles for liquid biopsy of alzheimer’s disease. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5:3595–605.
Chen Z, Mengela D, Keshavanb A, Rissman RA, Billinton A, Perkinton M, et al. Learnings about the complexity of extracellular tau aid development of a blood-based screen for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2019;15:487–96.
Shui B, Tao D, Cheng J, Mei Y, Jaffrezic-Renault N, Guo Z. A novel electrochemical aptamer–antibody sandwich assay for the detection of tau-381 in human serum. Analyst. 2018;143:3549–54.
Li D, Scarano S, Lisi S, Palladino P, Minunni M. Real-time tau protein detection by sandwich-based piezoelectric biosensing: exploring tubulin as a mass enhancer. Sensors. 2018;18:946–56.
Demeritte T, Nellore BPV, Kanchanapally R, Sinha SS, Pramanik A, Chavva SR, et al. Hybrid graphene oxide based plasmonic-magnetic multifunctional nanoplatform for selective separation and label-free identification of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:13693–700.
Lisi S, Scarano S, Fedeli S, Pascale E, Cicchi S, Ravelet C, et al. Toward sensitive immuno-based detection of tau protein by surface plasmon resonance coupled to carbon nanostructures as signal amplifiers. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;93:289–92.
Neely A, Perry C, Varisli B, Singh AK, Arbneshi T, Senapati D, et al. Ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarker using two-photon rayleigh scattering properties of gold nanoparticle. ACS Nano. 2009;3:2834–40.
Nu TTV, Tran NHT, Nam E, Nguyen TT, Yoon WJ, Cho S, et al. Blood-based immunoassay of tau proteins for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease using surface plasmon resonance fiber sensors. RSC Adv. 2018;8:7855–62.
Chen L, Lin J, Yi J, Weng Q, Zhou Y, Han Z, et al. A tyrosinase-induced fluorescence immunoassay for detection of tau protein using dopamine-functionalized CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:5277–85.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Department of Chemistry at Oakland University for support.
Funding
This project was funded in part by the NIH NIGMS R15 to S.M. (2016-2018) and C.W. (2019-2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
A. Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 868 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziu, I., Laryea, E.T., Alashkar, F. et al. A dip-and-read optical aptasensor for detection of tau protein. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 1193–1201 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02350-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02350-8