Abstract
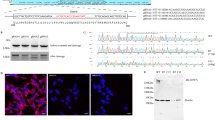
Mouse Nsmce1 gene is the homolog of non-structural maintenance of chromosomes element 1 (NSE1) that is mainly involved in maintenance of genome integrity, DNA damage response, and DNA repair. Defective DNA repair may cause neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). So far, there is no direct evidence for the correlation between Nsmce1 and AD. In order to explore the function of Nsmce1 in the regulation of nervous system, we have overexpressed or knocked down Nsmce1 in the mouse hippocampal neuronal cells (MHNCs) HT-22 and detected its regulation of AD marker genes as well as cell proliferation. The results showed that the expression of App, Bace2, and Mapt could be inhibited by Nsmce1 overexpression and activated by the knockdown of Nsmce1. Moreover, the HT-22 cell proliferation ability could be promoted by Nsmce1 overexpression and inhibited by knockdown of Nsmce1. Furthermore, we performed a transcriptomics study by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) to evaluate and quantify the gene expression profiles in response to the overexpression of Nsmce1 in HT-22 cells. As a result, 224 significantly dysregulated genes including 83 upregulated and 141 downregulated genes were identified by the comparison of Nsmce1 /+ to WT cells, which were significantly enriched in several Gene Ontology (GO) terms and pathways. In addition, the complexity of the alternative splicing (AS) landscape was increased by Nsmce1 overexpression in HT-22 cells. Thousands of AS events were identified to be mainly involved in the pathway of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (UMP) as well as 3 neurodegenerative diseases including AD. The protein-protein interaction network was reconstructed to show top 10 essential genes regulated by Nsmce1. Our sequencing data is available in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database with accession number as GSE113436. These results may provide some evidence of molecular and cellular functions of Nsmce1 in MHNCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann MA, Shriver M, Perry NA, Hu LY, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A (2014) Obscurins: Goliaths and Davids take over non-muscle tissues. PloS One 9:e88162. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088162
Alexandrov PN, Zhao Y, Jaber V, Cong L, Lukiw WJ (2017) Deficits in the proline-rich synapse-associated Shank3 protein in multiple neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Neurol 8:670. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00670
Anthony TE, Heintz N (2007) The folate metabolic enzyme ALDH1L1 is restricted to the midline of the early CNS, suggesting a role in human neural tube defects. J Comp Neurol 500:368–383. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21179
Austin BA, James C, Silverman RH, Carr DJ (2005) Critical role for the oligoadenylate synthetase/RNase L pathway in response to IFN-beta during acute ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 175:1100–1106
Baker M et al (2006) Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature 442:916–919. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05016
Birdwell LD et al (2016) Activation of RNase L by murine coronavirus in myeloid cells is dependent on basal Oas gene expression and independent of virus-induced interferon. J Virol 90:3160–3172. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03036-15
Duan X et al (2009) Architecture of the Smc5/6 Complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a unique interaction between the Nse5-6 subcomplex and the hinge regions of Smc5 and Smc6. J Biol Chem 284:8507–8515. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M809139200
Fragkouli A, Tsilibary EC, Tzinia AK (2014) Neuroprotective role of MMP-9 overexpression in the brain of Alzheimer's 5xFAD mice. Neurobiol Dis 70:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.06.021
Geller LN, Potter H (1999) Chromosome missegregation and trisomy 21 mosaicism in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 6:167–179. https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.1999.0236
Gillardon F, Skutella T, Uhlmann E, Holsboer F, Zimmermann M, Behl C (1996) Activation of c-Fos contributes to amyloid beta-peptide-induced neurotoxicity. Brain Res 706:169–172
Goswami SC, Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J, Mishra S, Hoon MA, Mannes AJ, Iadarola MJ (2014) Itch-associated peptides: RNA-Seq and bioinformatic analysis of natriuretic precursor peptide B and gastrin releasing peptide in dorsal root and trigeminal ganglia, and the spinal cord. Mol Pain 10:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-10-44
Grupe A, Li Y, Rowland C, Nowotny P, Hinrichs AL, Smemo S, Kauwe JS, Maxwell TJ, Cherny S, Doil L, Tacey K, van Luchene R, Myers A, Wavrant-de Vrièze F, Kaleem M, Hollingworth P, Jehu L, Foy C, Archer N, Hamilton G, Holmans P, Morris CM, Catanese J, Sninsky J, White TJ, Powell J, Hardy J, O'Donovan M, Lovestone S, Jones L, Morris JC, Thal L, Owen M, Williams J, Goate A (2006) A scan of chromosome 10 identifies a novel locus showing strong association with late-onset Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet 78:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1086/498851
Guo G, Gui Y, Gao S, Tang A, Hu X, Huang Y, Jia W, Li Z, He M, Sun L, Song P, Sun X, Zhao X, Yang S, Liang C, Wan S, Zhou F, Chen C, Zhu J, Li X, Jian M, Zhou L, Ye R, Huang P, Chen J, Jiang T, Liu X, Wang Y, Zou J, Jiang Z, Wu R, Wu S, Fan F, Zhang Z, Liu L, Yang R, Liu X, Wu H, Yin W, Zhao X, Liu Y, Peng H, Jiang B, Feng Q, Li C, Xie J, Lu J, Kristiansen K, Li Y, Zhang X, Li S, Wang J, Yang H, Cai Z, Wang J (2011) Frequent mutations of genes encoding ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis pathway components in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Genet 44:17–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.1014
Ham S, Kim TK, Lee S, Tang YP, Im HI (2017) MicroRNA profiling in aging brain of PSEN1/PSEN2 double knockout mice. Mol Neurobiol 55:5232–5242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0753-6
He G, Luo W, Li P, Remmers C, Netzer WJ, Hendrick J, Bettayeb K, Flajolet M, Gorelick F, Wennogle LP, Greengard P (2010) Gamma-secretase activating protein is a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 467:95–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09325
Holler CJ et al (2012) BACE2 expression increases in human neurodegenerative disease. Am J Pathol 180:337–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.09.034
Jeppesen DK, Bohr VA, Stevnsner T (2011) DNA repair deficiency in neurodegeneration. Prog Neurobiol 94:166–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.04.013
John Lin CC, Yu K, Hatcher A, Huang TW, Lee HK, Carlson J, Weston MC, Chen F, Zhang Y, Zhu W, Mohila CA, Ahmed N, Patel AJ, Arenkiel BR, Noebels JL, Creighton CJ, Deneen B (2017) Identification of diverse astrocyte populations and their malignant analogs. Nat Neurosci 20:396–405. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4493
Jonsson T, Atwal JK, Steinberg S, Snaedal J, Jonsson PV, Bjornsson S, Stefansson H, Sulem P, Gudbjartsson D, Maloney J, Hoyte K, Gustafson A, Liu Y, Lu Y, Bhangale T, Graham RR, Huttenlocher J, Bjornsdottir G, Andreassen OA, J A.eas EG, Palotie A, Behrens TW, Magnusson OT, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Watts RJ, Stefansson K (2012) A mutation in APP protects against Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline. Nature 488:96–99. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11283
Kang K, Lee D, Hong S, Park SG, Song MR (2013) The E3 ligase Mind bomb-1 (Mib1) modulates Delta-Notch signaling to control neurogenesis and gliogenesis in the developing spinal cord. J Biol Chem 288:2580–2592. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.398263
Kaplan A et al (2014) Neuronal matrix metalloproteinase-9 is a determinant of selective neurodegeneration. Neuron 81:333–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.009
Li J, Xu M, Zhou H, Ma J, Potter H (1997) Alzheimer presenilins in the nuclear membrane, interphase kinetochores, and centrosomes suggest a role in chromosome segregation. Cell 90:917–927
Lin Y, Smith GR (1994) Transient, meiosis-induced expression of the rec6 and rec12 genes of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics 136:769–779
Madabhushi R, Pan L, Tsai LH (2014) DNA damage and its links to neurodegeneration. Neuron 83:266–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.06.034
McDonald WH, Pavlova Y, Yates JR 3rd, Boddy MN (2003) Novel essential DNA repair proteins Nse1 and Nse2 are subunits of the fission yeast Smc5-Smc6 complex. J Biol Chem 278:45460–45467. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M308828200
Merlo S, Sortino MA (2012) Estrogen activates matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 to increase beta amyloid degradation. Mol Cell Neurosci 49:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2012.02.005
Pebernard S, McDonald WH, Pavlova Y, Yates JR 3rd, Boddy MN (2004) Nse1, Nse2, and a novel subunit of the Smc5-Smc6 complex, Nse3, play a crucial role in meiosis. Mol Biol Cell 15:4866–4876. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E04-05-0436
Pebernard S, Perry JJ, Tainer JA, Boddy MN (2008) Nse1 RING-like domain supports functions of the Smc5-Smc6 holocomplex in genome stability. Mol Biol Cell 19:4099–4109. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E08-02-0226
Ridnour LA, Dhanapal S, Hoos M, Wilson J, Lee J, Cheng RY, Brueggemann EE, Hines HB, Wilcock DM, Vitek MP, Wink DA, Colton CA (2012) Nitric oxide-mediated regulation of beta-amyloid clearance via alterations of MMP-9/TIMP-1. J Neurochem 123:736–749. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12028
Santa Maria SR, Gangavarapu V, Johnson RE, Prakash L, Prakash S (2007) Requirement of Nse1, a subunit of the Smc5-Smc6 complex, for Rad52-dependent postreplication repair of UV-damaged DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 27:8409–8418. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01543-07
Simpson JE, Ince PG, Shaw PJ, Heath PR, Raman R, Garwood CJ, Gelsthorpe C, Baxter L, Forster G, Matthews FE, Brayne C, Wharton SB, MRC Cognitive Function and Ageing Neuropathology Study Group (2011) Microarray analysis of the astrocyte transcriptome in the aging brain: relationship to Alzheimer’s pathology and APOE genotype. Neurobiol Aging 32:1795–1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.04.013
Suberbielle E et al (2015) DNA repair factor BRCA1 depletion occurs in Alzheimer brains and impairs cognitive function in mice. Nat Commun 6:8897. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9897
Tapia-Alveal C, O'Connell MJ (2011) Nse1-dependent recruitment of Smc5/6 to lesion-containing loci contributes to the repair defects of mutant complexes. Mol Biol Cell 22:4669–4682. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-03-0272
Welty S, Teng Y, Liang Z, Zhao W, Sanders LH, Greenamyre JT, Rubio ME, Thathiah A, Kodali R, Wetzel R, Levine AS, Lan L (2018) RAD52 is required for RNA-templated recombination repair in post-mitotic neurons. J Biol Chem 293:1353–1362. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.808402
Funding
This study received financial supports by the Natural Science Foundation Project of Anhui Province (1508085QC63 and 1908085MC87), Key University Science Research Project of Anhui Province (KJ2017A021), and the Scientific Research Foundation and Academic & Technology Leaders Introduction Project, and 211 Project of Anhui University (10117700023), and the Student Research Training Program of Anhui University (J10118516042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KH conceived and designed the study. MG, YL, WZ, and WXL performed the experiments and data analysis. MG and KH wrote the paper. SY, JZ, HZ, and JW reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1.
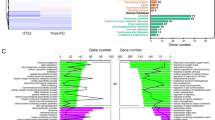
The full information of DEGs in response to the overexpression ofNsmce1in the hippocampus neuron HT22 cells. Based on the analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs), we have identified 224 significantly dysregulated genes with FC more than 2 and p value less than 0.05, including 83 up-regulated (in red) and 141 down-regulated (in green) genes by the comparison of Nsmce1 /+ group to WT group. The full information of each DEG contains Ensembl ID, Gene symbol, gene expression profiles in each sample, average expression value in the WT group (G1), average expression value in the Nsmce1 /+ group (G2), log2 of Fold change by the comparison of Nsmce1 /+ group to WT group, significance level p value, false discovery rate (FDR), involved Gene Ontology (GO) terms including three categories of biological process (BP), cellular component (CC) and molecular function (MF) as well as KEGG pathways. (XLS 808 kb).
Table S2.
The enriched GO terms in response to the overexpression ofNsmce1in HT22 cells. There were totally 320 GO terms for BP, 24 GO terms for CC as well as 98 GO terms for MF significantly enriched in the regulation of Nsmce1 in HT-22 cells.The information of each GO term contains ID in Gene Ontology database, the name of GO terms, the category, the number of involved genes (annotated), the number of identified DEGs (significant), the gene symbol of involved DEGs and the significance. (XLS 142 kb).
Table S3.
The enriched KEGG pathways in response to the overexpression ofNsmce1in HT22 cells. There were 17 KEGG pathways were identified to be significantly enriched in the regulation of Nsmce1 in HT-22 cells. The information of each KEGG pathway contains ID in KEGG database, the name of KEGG pathway, the pathway class, the number of involved genes (annotated), the number of identified DEGs (significant), the gene symbol of involved DEGs and the significance. (XLS 23 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, M., Wang, Z., Liu, Y. et al. A transcriptomic analysis of Nsmce1 overexpression in mouse hippocampal neuronal cell by RNA sequencing. Funct Integr Genomics 20, 459–470 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00728-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00728-6