Abstract
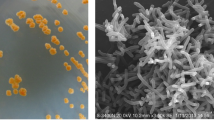
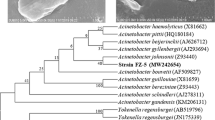
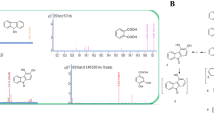
The interest of fluoroanilines in the environment is due to their extensive applications in industry and their low natural biodegradability. A pure bacterial strain capable of degrading 3-fluoroaniline (3-FA) as the sole source of carbon and energy was isolated from a sequencing batch reactor operating for the treatment of 3-FA. The strain (designated as JF-3) was identified by 16S rRNA gene analysis as a member of the genus Rhizobium. When grown in 3-FA medium at concentrations of 100–700 mg/L, strain JF-3 almost completely removed 3-FA within 72 h. However, the obvious cell growth inhibition was observed in cultures treated with 3-FA concentrations greater than 500 mg/L. The degradation kinetics of 3-FA were consistent with Haldane’s model with the maximum degradation rate as 67.66 mg/(g dry cell h). The growth kinetics of strain JF-3 followed Andrew’s model with the maximum growth rate as 30.87 h−1. Also, strain JF-3 was able to degrade 4-fluoroaniline, aniline, and catechol, but hardly grew on 2-fluoroaniline, 2,4-dfluoroaniline, 2,3,4-trifluoroaniline, 3-fluorocatechol, and 4-fluorocatechol. Additionally, it was able to grow over a wide pH range (pH 6–10), and also showed tolerance to salinity with lower than 1.0%. This result, in combination with the enzyme assays and analysis of metabolite intermediates, indicated an unconventional pathway for 3-fluoroaniline metabolism that involved conversion to 3-aminophenol and resorcinol by monooxygenase, and which was subsequently metabolized via the ortho-cleavage pathway. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the utilization of 3-FA as a growth substrate by Rhizobium sp.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebusoye SA (2017) Biological degradation of 4-chlorobenzoic acid by a PCB-metabolizing bacterium through a pathway not involving (chloro)catechol. Biodegradation 28:37–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-016-9776-3
Amorim CL, Carvalho MF, Afonso CMM, Castro PML (2013) Biodegradation of fluoroanilines by the wild strain Labrys portucalensis. Int Biodeter Biodegr 80:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.02.001
Amorim CL, Ferreira ACS, Carvalho MF, Afonso CMM, Castro PML (2014) Mineralization of 4-fluorocinnamic acid by a Rhodococcus strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:1893–1905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5149-6
Arora PK, Mohanta TK, Srivastava A, Bae HH, Singh VP (2014) Metabolic pathway for degradation of 2-chloro-4-aminophenol by Arthrobacter sp SPG. Microb Cell Fact 13:164. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12934-014-0164-6
Bouwman H, Govender D, Underhill L, Polder A (2015) Chlorinated, brominated and fluorinated organic pollutants in African Penguin eggs: 30 years since the previous assessment. Chemosphere 126:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.071
Carvalho MF, Alves CCT, Ferreira MIM, De Marco P, Castro PML (2002) Isolation and initial characterization of a bacterial consortium able to mineralize fluorobenzene. Appl Environ Microb 68:102–105. https://doi.org/10.1128/Aem.68.1.102-105.2002
Carvalho MF, Ferreira MIM, Moreira IS, Castro PML, Janssen DB (2006) Degradation of fluorobenzene by Rhizobiales strain F11 via ortho cleavage of 4-fluorocatechol and catechol. Appl Environ Microb 72:7413–7417. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01162-06
Cho SY et al (2017) Identification of the upstream 4-chlorophenol biodegradation pathway using a recombinant monooxygenase from Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6. Bioresour Technol 245:1800–1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.006
Cui DZ, Shen D, Wu CR, Li C, Leng DJ, Zhao M (2017) Biodegradation of aniline by a novel bacterial mixed culture AC. Int Biodeter Biodegr 125:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.08.010
Dorn E, Knackmuss HJ (1978) Chemical-structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic-compounds—substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of catechol. Biochem J 174:85–94
EEA (2014) Progress in management of contaminated sites (CSI 015/LSI 003)—Assessment published May 2014. http://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/progress-inmanagement-of-contaminated-sites-3/assessment. Accessed 14 May 2015
Farrell A, Quilty B (1999) Degradation of mono-chlorophenols by a mixed microbial community via a meta-cleavage pathway. Biodegradation 10:353–362
Ferreira MIM, Marchesi JR, Janssen DB (2008) Degradation of 4-fluorophenol by Arthrobacter sp. strain IF1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:709–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1343-3
Gosetti F et al (2010) Sun light degradation of 4-chloroaniline in waters and its effect on toxicity. A high performance liquid chromatography—diode array—tandem mass spectrometry study. Environ Pollut 158:592–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.08.012
Groffen T, Wepener V, Malherbe W, Bervoets L (2018) Distribution of perfluorinated compounds (PFASs) in the aquatic environment of the industrially polluted Vaal River, South Africa. Sci Total Environ 627:1334–1344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.023
Hongsawat P, Vangnai AS (2011) Biodegradation pathways of chloroanilines by Acinetobacter baylyi strain GFJ2. J Hazard Mater 186:1300–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.002
Huang X, Shi J, Cui C, Yin H, Zhang R, Ma X, Zhang X (2016) Biodegradation of phenanthrene by Rhizobium petrolearium SL-1. J Appl Microbiol 121:1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13292
Huang Y, Pan YH, Wang WW, Jiang L, Dan Y (2019) Synthesis and properties of partially biodegradable fluorinated polyacrylate: poly(L-lactide)-co-poly(hexafluorobutyl acrylate) copolymer. Mater Des 162:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.11.055
Key BD, Howell RD, Criddle CS (1997) Fluorinated organics in the biosphere. Environ Sci Technol 31:2445–2454. https://doi.org/10.1021/Es961007c
Kiel M, Engesser KH (2015) The biodegradation vs. biotransformation of fluorosubstituted aromatics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:7433–7464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6817-5
Kim EJ, Jeon JR, Kim YM, Murugesan K, Chang YS (2010) Mineralization and transformation of monofluorophenols by Pseudonocardia benzenivorans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1569–1577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2647-7
Kiprono SJ, Ullah MW, Yang G (2018) Encapsulation of E-coli in biomimetic and Fe3O4-doped hydrogel: structural and viability analyses. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:933–944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8625-6
Kodama N, Takenaka S, Murakumi S, Shinke R, Aoki K (1997) Production of methyl, dimethyl, ethyl, chloro-, fluoro-, and hydroxyl derivatives of catechol from thirteen aromatic amines by the transpositional mutant B-9 of the aniline-assimilating Pseudomonas species AW-2. J Ferment Bioeng 84:232–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0922-338x(97)82060-0
Li L, Zheng HY, Wang TY, Cai MH, Wang P (2018) Perfluoroalkyl acids in surface seawater from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean: contamination, distribution and transportation. Environ Pollut 238:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.018
Liu H, Liu H-X, Wang Z-R, Wang L-S (2009) Study on lgKow and –lg1/EC50 relationships for fluorine-contained aromatics by QSPR. Environ Sci Technol 32:1–5 (in Chinese)
Ma R, Shih K (2010) Perfluorochemicals in wastewater treatment plants and sediments in Hong Kong. Environ Pollut 158:1354–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.01.013
Murphy CD (2016) Microbial degradation of fluorinated drugs: biochemical pathways, impacts on the environment and potential applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2617–2627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7304-3
Murphy CD, Sandford G (2015) Recent advances in fluorination techniques and their anticipated impact on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 11:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.2015.1020295
O’Hagan D, Deng H (2015) Enzymatic fluorination and biotechnological developments of the fluorinase. Chem Rev 115(2):634–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500209t
Patel BP, Kumar A (2017) Biodegradation and co-metabolism of monochlorophenols and 2,4-dichlorophenol by microbial consortium. Clean-Soil Air Water 45:1700329. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201700329
Paul AG, Jones KC, Sweetman AJ (2009) A first global production, emission, and environmental inventory for perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ Sci Technol 43:386–392
Sihtmae M, Mortimer M, Kahru A, Blinova I (2010) Toxicity of five anilines to crustaceans, protozoa and bacteria. J Serb Chem Soc 75:1291–1302. https://doi.org/10.2298/Jsc091219103s
Song EX, Wang MZ, Shen DS (2014) Isolation, identification and characterization of a novel Ralstonia sp FD-1, capable of degrading 4-fluoroaniline. Biodegradation 25:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-013-9642-5
Travkin VM, Solyanikova IP, Rietjens IMCM, Vervoort J, van Berkel WJH, Golovleva LA (2003) Degradation of 3,4-dichloro- and 3,4-difluoroaniline by Pseudomonas fluorescens 26-K. J Environ Sci Health B 38:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1081/Pfc-120018443
USEPA (2015) Final national priorities list (NPL) Sites. http://www.epa.gov/superfund/sites/query/queryhtm/nplfin.htm. Accessed 14 May 2015
Wang MZ, Xu JJ, Wang JH, Wang S, Feng HJ, Shentu JL, Shen DS (2013) Differences between 4-fluoroaniline degradation and autoinducer release by Acinetobacter sp TW: implications for operating conditions in bacterial bioaugmentation. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:6201–6209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1660-7
Wei GH, Yu JF, Zhu YH, Chen WM, Wang L (2008) Characterization of phenol degradation by Rhizobium sp. CCNWTB 701 isolated from Astragalus chrysopteru in mining tailing region. J Hazard Mater 151:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.058
Xun LY, Webster CM (2004) A monooxygenase catalyzes sequential dechlorinations of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by oxidative and hydrolytic reactions. J Biol Chem 279:6696–6700. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312072200
Zhang CJ, Zhou Q, Chen L, Yuan Y, Yu H (2007) Degradation of mono-fluorophenols by an acclimated activated sludge. Biodegradation 18:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-9035-5
Zhang LL, He D, Chen JM, Liu Y (2010) Biodegradation of 2-chloroaniline, 3-chloroaniline, and 4-chloroaniline by a novel strain Delftia tsuruhatensis H1. J Hazard Mater 179:875–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.086
Zhang XQ et al (2014) The effect of electricity on 2-fluoroaniline removal in a bioelectrochemically assisted microbial system (BEAMS). Electrochim Acta 135:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.05.033
Zhao ZQ, Tian BH, Zhang X, Ghulam A, Zheng TC, Shen DS (2015) Aerobic degradation study of three fluoroanilines and microbial community analysis: the effects of increased fluorine substitution. Biodegradation 26:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9704-3
Zhao SH et al (2018) General nondestructive passivation by 4-fluoroaniline for perovskite solar cells with improved performance and stability. Small 14:1803350. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201803350
Zhou S et al (2016) Physiological responses of Microcystis aeruginosa against the algicidal bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ecotox Environ Safe 127:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.001
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21607092; 21476127; U1607119); the Public Technology Research Program of Zhejiang Province (Nos. GF18B060002; 2017C33012); the Talent Project of Quzhou University (Nos. XNZQN201506; BSJX201601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, ZQ., Zheng, TC., Zhang, WJ. et al. Degradation of 3-fluoroanilne by Rhizobium sp. JF-3. Biodegradation 30, 433–445 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-019-09885-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-019-09885-8