Abstract
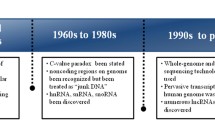
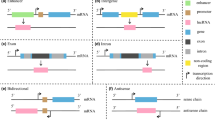
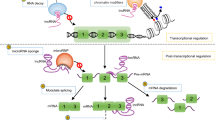
Ischemic stroke is an acute brain injury with high mortality and disability rates worldwide. The pathophysiological effects of ischemic stroke are driven by a multitude of complex molecular and cellular interactions that ultimately result in brain damage and neurological dysfunction. The Human Genome Project revealed that the vast majority of the human genome (and mammalian genome in general) is transcribed into noncoding RNAs. These RNAs have several important roles in the molecular biology of the cell. Of these, the long noncoding RNAs are gaining particular importance in stroke biology. High-throughput analysis of gene expression using methodologies such as RNA-seq and microarrays have identified a number of aberrantly expressed lncRNAs in the post-stroke brain and blood in experimental models as well as in clinical samples. These expression changes exhibited distinct temporal and cell-type-dependent patterns. Many of these lncRNAs were shown to modulate molecular pathways that resulted in deleterious as well as neuroprotective outcomes in the post-stroke brain. In this review, we consolidate the latest data from the literature that elucidate the roles and functions of lncRNAs in ischemic stroke. We also summarize clinical studies identifying differential lncRNA expression changes between stroke patients and healthy individuals, and genetic variations in lncRNA loci that are correlated with an increased risk of stroke development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnall, R. D., Roberts, R. G., Mirza, M. M., Torigoe, T., Prescott, N. J., & Mathew, C. G. (2008). Novel isoforms of the CARD8 (TUCAN) gene evade a nonsense mutation. European Journal of Human Genetics: EJHG,16(5), 619–625. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201996.
Bai, Y., Nie, S., Jiang, G., Zhou, Y., Zhou, M., Zhao, Y., et al. (2014). Regulation of CARD8 expression by ANRIL and association of CARD8 single nucleotide polymorphism rs2043211 (p.C10X) with ischemic stroke. Stroke,45(2), 383–388. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.003393.
Bao, M.-H., Szeto, V., Yang, B. B., Zhu, S., Sun, H.-S., & Feng, Z.-P. (2018). Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death & Disease,9(3), 281. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0282-x.
Beltran, M., Puig, I., Peña, C., García, J. M., Álvarez, A. B., Peña, R., et al. (2008). A natural antisense transcript regulates Zeb2/Sip1 gene expression during Snail1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Genes & Development,22(6), 756–769. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.455708.
Bhattarai, S., Pontarelli, F., Prendergast, E., & Dharap, A. (2017). Discovery of novel stroke-responsive lncRNAs in the mouse cortex using genome-wide RNA-seq. Neurobiology of Disease,108(June), 204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.08.016.
Bhattarai, S., Aly, A., Garcia, K., Ruiz, D., Pontarelli, F., & Dharap, A. (2019). Deep sequencing reveals uncharted isoform heterogeneity of the protein-coding transcriptome in cerebral ischemia. Molecular Neurobiology,56(2), 1035–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1147-0.
Burnett, J. C., & Rossi, J. J. (2012). RNA-based therapeutics: Current progress and future prospects. Chemistry & Biology,19(1), 60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.12.008.
Cabili, M., Trapnell, C., Goff, L., Koziol, M., Tazon-Vega, B., Regev, A., et al. (2011). Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes & Development,25(18), 1915–1927. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.17446611.
Carninci, P., Kasukawa, T., Katayama, S., Gough, J., Frith, M. C., Maeda, N., et al. (2005). Molecular biology: The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science,309(5740), 1559–1563. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1112014.
Chen, S., Wang, M., Yang, H., Mao, L., He, Q., Jin, H., et al. (2017). LncRNA TUG1 sponges microRNA-9 to promote neurons apoptosis by up-regulated Bcl2l11 under ischemia. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,485(1), 167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.043.
Chen, C., Chu, S. F., Liu, D. D., Zhang, Z., Kong, L. L., Zhou, X., et al. (2018a). Chemokines play complex roles in cerebral ischemia. Neurochemistry International,112, 146–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.06.008.
Chen, F., Zhang, L., Wang, E., Zhang, C., & Li, X. (2018b). LncRNA GAS5 regulates ischemic stroke as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-137 to regulate the Notch1 signaling pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,496(1), 184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.022.
Derrien, T., Johnson, R., Bussotti, G., Tanzer, A., Djebali, S., Tilgner, H., et al. (2012). The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Research,22(9), 1775–1789. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.132159.111.
Dharap, A., Nakka, V. P., & Vemuganti, R. (2012). Effect of focal ischemia on long noncoding RNAs. Stroke,43(10), 2800–2802. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.669465.
Dharap, A., Pokrzywa, C., & Vemuganti, R. (2013). Increased binding of stroke-induced long non-coding RNAs to the transcriptional corepressors Sin3A and coREST. ASN Neuro,5(4), 283–289. https://doi.org/10.1042/AN20130029.
Djebali, S., Davis, C. A., Merkel, A., Dobin, A., Lassmann, T., Mortazavi, A., et al. (2012). Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature,489(7414), 101–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11233.
Dykstra-Aiello, C., Jickling, G. C., Ander, B. P., Shroff, N., Zhan, X., Liu, D., et al. (2016). Altered expression of long noncoding RNAs in blood following ischemic stroke and proximity to putative stroke risk Loci. Stroke,47(12), 2896–2903. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013869.
ENCODE Project Consortium. (2012). An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature,489(7414), 57–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11247.
Feng, L., Guo, J., & Ai, F. (2019). Circulating long noncoding RNA ANRIL downregulation correlates with increased risk, higher disease severity and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis,33(1), e22629. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.22629.
Guo, D., Ma, J., Yan, L., Li, T., Li, Z., Han, X., et al. (2017). Down-regulation of Lncrna MALAT1 attenuates neuronal cell death through suppressing Beclin1-dependent autophagy by regulating Mir-30a in cerebral ischemic stroke. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry: International Journal of Experimental Cellular Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology,43(1), 182–194. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480337.
Guo, X., Yang, J., Liang, B., Shen, T., Yan, Y., Huang, S., et al. (2018). Identification of novel LncRNA biomarkers and construction of LncRNA-related networks in Han Chinese patients with ischemic stroke. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry: International Journal of Experimental Cellular Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology,50(6), 2157–2175. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495058.
Guttman, M., Amit, I., Garber, M., French, C., Lin, M. F., Feldser, D., et al. (2009). Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature,458(7235), 223–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07672.
Guttman, M., Garber, M., Levin, J. Z., Donaghey, J., Robinson, J., Adiconis, X., et al. (2010). Ab initio reconstruction of cell type-specific transcriptomes in mouse reveals the conserved multi-exonic structure of lincRNAs. Nature Biotechnology,28(5), 503–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1633.
Han, X., Zheng, Z., Wang, C., & Wang, L. (2018). Association between MEG3/miR-181b polymorphisms and risk of ischemic stroke. Lipids in Health and Disease,17(1), 292. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0941-z.
Holdt, L. M., & Teupser, D. (2018). Long Noncoding RNA ANRIL: Lnc-ing Genetic Variation at the Chromosome 9p21 Locus to Molecular Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine,5, 145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2018.00145.
Hou, X.-X., & Cheng, H. (2018). Long non-coding RNA RMST silencing protects against middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced ischemic stroke. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,495(4), 2602–2608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.087.
Hutchinson, J. N., Ensminger, A. W., Clemson, C. M., Lynch, C. R., Lawrence, J. B., & Chess, A. (2007). A screen for nuclear transcripts identifies two linked noncoding RNAs associated with SC35 splicing domains. BMC Genomics,8, 39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-8-39.
Kim, J., Kang, S.-W., Mallilankaraman, K., Baik, S.-H., Lim, J. C., Balaganapathy, P., et al. (2018). Transcriptome analysis reveals intermittent fasting-induced genetic changes in ischemic stroke. Human Molecular Genetics,27(9), 1497–1513. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy057.
Kopp, F., & Mendell, J. T. (2018). Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell,172(3), 393–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.011.
Li, Z., Li, J., & Tang, N. (2017). Long noncoding RNA Malat1 is a potent autophagy inducer protecting brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by sponging miR-26b and upregulating ULK2 expression. Neuroscience,354, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.04.017.
Liu, X., Hou, L., Huang, W., Gao, Y., Lv, X., & Tang, J. (2016). The mechanism of long non-coding RNA MEG3 for neurons apoptosis caused by Hypoxia: Mediated by miR-181b-12/15-LOX Signaling Pathway. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience,10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00201.
Liu, J., Li, Q., Zhang, K.-S., Hu, B., Niu, X., Zhou, S.-M., et al. (2017). Downregulation of the long non-coding RNA Meg3 promotes angiogenesis after ischemic brain injury by activating notch signaling. Molecular Neurobiology,54(10), 8179–8190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0270-z.
Liu, C., Yang, J., Zhang, C., Liu, M., Geng, X., Ji, X., et al. (2018). Analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Neuroscience Letters,665, 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.11.058.
Long, F.-Q., Su, Q.-J., Zhou, J.-X., Wang, D.-S., Li, P.-X., Zeng, C.-S., et al. (2018). LncRNA SNHG12 ameliorates brain microvascular endothelial cell injury by targeting miR-199a. Neural Regeneration Research,13(11), 1919–1926. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.238717.
Ma, L., Bajic, V. B., & Zhang, Z. (2013). On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biology,10(6), 924–933. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.24604.
Massone, S., Vassallo, I., Fiorino, G., Castelnuovo, M., Barbieri, F., Borghi, R., et al. (2011). 17A, a novel non-coding RNA, regulates GABA B alternative splicing and signaling in response to inflammatory stimuli and in Alzheimer disease. Neurobiology of Disease,41(2), 308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.09.019.
Mehta, S. L., Kim, T., & Vemuganti, R. (2015). Long noncoding RNA FosDT promotes ischemic brain injury by interacting with REST-associated chromatin-modifying proteins. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience,35(50), 16443–16449. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2943-15.2015.
Mercer, T. R., Qureshi, I. A., Gokhan, S., Dinger, M. E., Li, G., Mattick, J. S., et al. (2010). Long noncoding RNAs in neuronal-glial fate specification and oligodendrocyte lineage maturation. BMC Neuroscience,11(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-11-14.
Nishimoto, Y., Nakagawa, S., Hirose, T., Okano, H., Takao, M., Shibata, S., et al. (2013). The long non-coding RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1_2 induces paraspeckle formation in the motor neuron during the early phase of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Molecular Brain,6(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-6-31.
Noh, K.-M., Hwang, J.-Y., Follenzi, A., Athanasiadou, R., Miyawaki, T., Greally, J. M., et al. (2012). Repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor (REST)-dependent epigenetic remodeling is critical to ischemia-induced neuronal death. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,109(16), E962–E971. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1121568109.
Ponjavic, J., Ponting, C. P., & Lunter, G. (2007). Functionality or transcriptional noise? Evidence for selection within long noncoding RNAs. Genome Research,17(5), 556–565. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.6036807.
Powell, W. T., Coulson, R. L., Crary, F. K., Wong, S. S., Ach, R. A., Tsang, P., et al. (2013). A Prader-Willi locus lncRNA cloud modulates diurnal genes and energy expenditure. Human Molecular Genetics,22(21), 4318–4328. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt281.
Qi, X., Shao, M., Sun, H., Shen, Y., Meng, D., & Huo, W. (2017). Long non-coding RNA SNHG14 promotes microglia activation by regulating miR-145-5p/PLA2G4A in cerebral infarction. Neuroscience,348, 98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.02.002.
Ren, L., Wei, C., Li, K., & Lu, Z. (2019). LncRNA MALAT1 up-regulates VEGF-A and ANGPT2 to promote angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation via targetting miR-145. Bioscience Reports,39(3), BSR20180226. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20180226.
Rinn, J. L., Kertesz, M., Wang, J. K., Squazzo, S. L., Xu, X., Brugmann, S. A., et al. (2007). Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell,129(7), 1311–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022.
Ruan, W., Li, J., Xu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, F., Yang, X., et al. (2019). MALAT1 up-regulator polydatin protects brain microvascular integrity and ameliorates stroke through C/EBPβ/MALAT1/CREB/PGC-1α/PPARγ pathway. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology,39(2), 265–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-018-00646-4.
Shiekhattar, R., Guigo, R., Lipovich, L., Lassmann, T., Brown, J. B., Bussotti, G., et al. (2012). The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Research,22(9), 1775–1789. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.132159.111.
Wang, X., Arai, S., Song, X., Reichart, D., Du, K., Pascual, G., et al. (2008). Induced ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit transcription. Nature,454(7200), 126–130. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06992.
Wang, J., Cao, B., Han, D., Sun, M., & Feng, J. (2017a). Long non-coding RNA H19 induces cerebral Ischemia reperfusion injury via activation of autophagy. Aging and Disease,8(1), 71–84. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2016.0530.
Wang, J., Zhao, H., Fan, Z., Li, G., Ma, Q., Tao, Z., et al. (2017b). Long Noncoding RNA H19 promotes neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke by driving histone deacetylase 1-dependent M1 microglial polarization. Stroke,48(8), 2211–2221. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017387.
Wang, C., Qu, Y., Suo, R., & Zhu, Y. (2019a). Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates angiogenesis following oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine,23(4), 2970–2983. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14204.
Wang, S., Han, X., Mao, Z., Xin, Y., Maharjan, S., & Zhang, B. (2019b). MALAT1 lncRNA induces autophagy and protects brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation by binding to miR-200c-3p and upregulating SIRT1 expression. Neuroscience,397, 116–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.11.024.
Wu, Z., Wu, P., Zuo, X., Yu, N., Qin, Y., Xu, Q., et al. (2017). LncRNA-N1LR enhances neuroprotection against ischemic stroke probably by inhibiting p53 phosphorylation. Molecular Neurobiology,54(10), 7670–7685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0246-z.
Xu, Q., Deng, F., Xing, Z., Wu, Z., Cen, B., Xu, S., et al. (2016). Long non-coding RNA C2dat1 regulates CaMKIIδ expression to promote neuronal survival through the NF-κB signaling pathway following cerebral ischemia. Cell Death & Disease,7(3), e2173. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.57.
Yan, H., Yuan, J., Gao, L., Rao, J., & Hu, J. (2016). Long noncoding RNA MEG3 activation of p53 mediates ischemic neuronal death in stroke. Neuroscience,337, 191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.09.017.
Yan, H., Rao, J., Yuan, J., Gao, L., Huang, W., Zhao, L., et al. (2017). Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate ischemic neuronal death by targeting miR-21/PDCD4 signaling pathway. Cell Death & Disease,8(12), 3211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0047-y.
Yang, H., Xi, X., Zhao, B., Su, Z., & Wang, Z. (2018a). KLF4 protects brain microvascular endothelial cells from ischemic stroke induced apoptosis by transcriptionally activating MALAT1. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,495(3), 2376–2382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.205.
Yang, J., Gu, L., Guo, X., Huang, J., Chen, Z., Huang, G., et al. (2018b). LncRNA ANRIL expression and ANRIL gene polymorphisms contribute to the risk of ischemic stroke in the chinese han population. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology,38(6), 1253–1269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-018-0593-6.
Yin, W.-L., Yin, W.-G., Huang, B.-S., & Wu, L.-X. (2019). LncRNA SNHG12 inhibits miR-199a to upregulate SIRT1 to attenuate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through activating AMPK signaling pathway. Neuroscience Letters,690, 188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.08.026.
Zhang, J., Yuan, L., Zhang, X., Hamblin, M. H., Zhu, T., Meng, F., et al. (2016). Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia. Experimental Neurology,277, 162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.12.014.
Zhang, B., Wang, D., Ji, T.-F., Shi, L., & Yu, J.-L. (2017a). Overexpression of lncRNA ANRIL up-regulates VEGF expression and promotes angiogenesis of diabetes mellitus combined with cerebral infarction by activating NF-κB signaling pathway in a rat model. Oncotarget,8(10), 17347–17359. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14468.
Zhang, X., Tang, X., Liu, K., Hamblin, M. H., & Yin, K.-J. (2017b). Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience,37(7), 1797–1806. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3389-16.2017.
Zhang, T., Wang, H., Li, Q., Fu, J., Huang, J., & Zhao, Y. (2018). MALAT1 Activates the P53 Signaling Pathway by Regulating MDM2 to Promote Ischemic Stroke. Cellular Physiology and biochemistry: International Journal of Experimental Cellular Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology,50(6), 2216–2228. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495083.
Zhao, M., Wang, J., Xi, X., Tan, N., & Zhang, L. (2018). SNHG12 promotes angiogenesis following ischemic stroke via regulating miR-150/VEGF pathway. Neuroscience,390, 231–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.08.029.
Zheng, Z., Liu, S., Wang, C., & Han, X. (2018). A Functional Polymorphism rs145204276 in the Promoter of Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Ischemic Stroke. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases: The Official Journal of National Stroke Association,27(12), 3535–3541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.08.016.
Zhong, J., Jiang, L., Cheng, C., Huang, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, H., et al. (2016). Altered expression of long non-coding RNA and mRNA in mouse cortex after traumatic brain injury. Brain Research,1646, 589–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.07.002.
Zhou, X., Han, X., Wittfeldt, A., Sun, J., Liu, C., Wang, X., et al. (2016). Long non-coding RNA ANRIL regulates inflammatory responses as a novel component of NF-κB pathway. RNA Biology,13(1), 98–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1122164.
Zhu, R., Liu, X., & He, Z. (2018). Long non-coding RNA H19 and MALAT1 gene variants in patients with ischemic stroke in a northern Chinese Han population. Molecular Brain,11(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-018-0402-7.
Zhu, W., Tian, L., Yue, X., Liu, J., Fu, Y., & Yan, Y. (2019). LncRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke during the transition from the acute to subacute stage. Frontiers in Neurology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00036.
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the JFK Neuroscience Institute, HackensackMeridian Health JFK Medical Center in Edison, NJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human and Animal Participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akella, A., Bhattarai, S. & Dharap, A. Long Noncoding RNAs in the Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke. Neuromol Med 21, 474–483 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08542-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08542-w