Abstract
Summary
In aged population, the association of thyroid hormones on physical performance, especially within their normal range, has yet to be elucidated. In this study, individuals with low serum free T3/free T4 were likely to have low muscle mass and impaired physical performance.
Purpose
We aimed to evaluate the associations of muscle mass, strength, and physical performance with thyroid hormone in an aged euthyroid population from a community-based cohort.
Methods
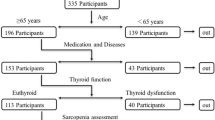
We examined 918 men aged over 60 years and 1215 postmenopausal women from the Ansung cohort study. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass divided by square of height (ASM/ht2) was used as the muscle mass index. Hand grip strength was measured using a hydraulic dynamometer. Physical performance was assessed using the short physical performance battery (SPPB).
Results
Participants with higher tertiles of free T3 and free T3/free T4 were younger and had higher ASM/ht2, stronger hand grip strength, and higher SPPB scores than those in the lower tertiles. In adjusted models, men within higher tertiles of free T3 had higher ASM/ht2 compared with those within lower tertiles (p = 0.033), whereas subjects with higher tertiles of free T4 had lower ASM/ht2 compared with those within lower tertiles (p = 0.043). Subjects within higher tertiles of free T3/free T4 had higher ASM/ht2 (p < 0.001) and better physical performance (p = 0.048) than those within lower tertiles after adjustments. However, free T3, free T4, or free T3/free T4 was not related to hand grip strength after adjustment for covariates.
Conclusion
Our results thus indicate that in an aged euthyroid population, low serum free T3/free T4 was a better index for low muscle mass and impaired physical performance than serum free T3 or free T4 alone.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acree LS, Longfors J, Fjeldstad AS, Fjeldstad C, Schank B, Nickel KJ, Montgomery PS, Gardner AW (2006) Physical activity is related to quality of life in older adults. Health Qual Life Outcomes 4(1):37
Rolland Y, Lauwers-Cances V, Cesari M, Vellas B, Pahor M, Grandjean H (2006) Physical performance measures as predictors of mortality in a cohort of community-dwelling older French women. Eur J Epidemiol 21(2):113–122
Ceresini G, Lauretani F, Maggio M, Ceda GP, Morganti S, Usberti E, Chezzi C, Valcavi R, Bandinelli S, Guralnik JM (2009) Thyroid function abnormalities and cognitive impairment in elderly people: results of the Invecchiare in Chianti study. J Am Geriatr Soc 57(1):89–93
Janssen I, Heymsfield SB, Ross R (2002) Low relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is associated with functional impairment and physical disability. J Am Geriatr Soc 50(5):889–896
Chen L-K, Liu L-K, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung T-W, Bahyah KS, Chou M-Y, Chen L-Y, Hsu P-S, Krairit O (2014) Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc 15(2):95–101
Salvatore D, Simonides WS, Dentice M, Zavacki AM, Larsen PR (2014) Thyroid hormones and skeletal muscle—new insights and potential implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10(4):206–214
Monzani F, Caraccio N, Siciliano G, Manca L, Murri L, Ferrannini E (1997) Clinical and biochemical features of muscle dysfunction in subclinical hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82(10):3315–3318. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.10.4296
Argov Z, Arnold DL (2000) MR spectroscopy and imaging in metabolic myopathies. Neurol Clin 18(1):35–52
Kazakov V, Katinas G, Skorometz A (1986) Pathogenesis of experimental thyrotoxic myopathy. Eur Neurol 25(3):212–224
Dentice M, Marsili A, Ambrosio R, Guardiola O, Sibilio A, Paik J-H, Minchiotti G, DePinho RA, Fenzi G, Larsen PR (2010) The FoxO3/type 2 deiodinase pathway is required for normal mouse myogenesis and muscle regeneration. J Clin Invest 120(11):4021–4030
Hennemann G, Docter R, Krenning E (1988) Causes and effects of the low T3 syndrome during caloric deprivation and non-thyroidal illness: an overview. Acta Med Austriaca 15:42–45
Peeters RP, Wouters PJ, Kaptein E, Van Toor H, Visser TJ, Van den Berghe G (2003) Reduced activation and increased inactivation of thyroid hormone in tissues of critically ill patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(7):3202–3211
Ceresini G, Marina M, Lauretani F, Maggio M, Serra MF, Meschi T, Bandinelli S, Ceda GP, Ferrucci L (2018) Physical performance across the thyroid function values within the normal range in adult and older persons. Aging Clin Exp Res:1–7
Oto Y, Muroya K, Hanakawa J, Asakura Y, Adachi M (2015) The ratio of serum free triiodothyronine to free thyroxine in children: a retrospective database survey of healthy short individuals and patients with severe thyroid hypoplasia or central hypothyroidism. Thyroid Res 8:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13044-015-0023-5
Baik I, Kim J, Abbott RD, Joo S, Jung K, Lee S, Shim J, Kang K, Yoo S, Shin C (2008) Association of snoring with chronic bronchitis. Arch Intern Med 168(2):167–173
Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ, Heo JY, Oh JH, Ban HJ, Yoon D, Lee MH, Kim DJ, Park M, Cha SH, Kim JW, Han BG, Min H, Ahn Y, Park MS, Han HR, Jang HY, Cho EY, Lee JE, Cho NH, Shin C, Park T, Park JW, Lee JK, Cardon L, Clarke G, McCarthy MI, Lee JY, Lee JK, Oh B, Kim HL (2009) A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet 41(5):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.357
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Leon AS, Jacobs DR Jr, Montoye HJ, Sallis JF, Paffenbarger RS Jr (1993) Compendium of physical activities: classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25(1):71–80
Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, Glynn RJ, Berkman LF, Blazer DG, Scherr PA, Wallace RB (1994) A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol 49(2):M85–M94
Moon MK, Lee YJ, Choi SH, Lim S, Yang EJ, Lim J-Y, Paik N-J, Kim KW, Park KS, Jang HC (2010) Subclinical hypothyroidism has little influences on muscle mass or strength in elderly people. J Korean Med Sci 25(8):1176–1181
De Jongh R, Lips P, van Schoor N, Rijs K, Deeg DJ, Comijs H, Kramer M, Vandenbroucke J, Dekkers O (2011) Endogenous subclinical thyroid disorders, physical and cognitive function, depression and mortality in older individuals. European journal of endocrinology:EJE-11-0430
Greenlund LJ, Nair KS, Brennan MD (2008) Changes in body composition in women following treatment of overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism. Endocrine practice : official journal of the American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists 14(8):973–978. https://doi.org/10.4158/ep.14.8.973
Charge SB, Rudnicki MA (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 84(1):209–238
Muscat GE, Mynett-Johnson L, Dowhan D, Downes M, Griggs R (1994) Activation of myoD gene transcription by 3, 5, 3′-triiodo-L-thyronine: a direct role for the thyroid hormone and retinoid X receptors. Nucleic Acids Res 22(4):583–591
Ceresini G, Ceda GP, Lauretani F, Maggio M, Bandinelli S, Guralnik JM, Cappola AR, Usberti E, Morganti S, Valenti G (2011) Mild thyroid hormone excess is associated with a decreased physical function in elderly men. Aging Male 14(4):213–219
Maino F, Cantara S, Forleo R, Pilli T, Castagna MG (2018) Clinical significance of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase polymorphism. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab (just-accepted)
Medici M, Chaker L, Peeters RP (2017) A step forward in understanding the relevance of genetic variation in type 2 deiodinase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102(5):1775–1778
Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR (2002) Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology, and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocr Rev 23(1):38–89
Ng L, Goodyear RJ, Woods CA, Schneider MJ, Diamond E, Richardson GP, Kelley MW, Germain DLS, Galton VA, Forrest D (2004) Hearing loss and retarded cochlear development in mice lacking type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(10):3474–3479
Galton VA, Schneider MJ, Clark AS, St. Germain DL (2009) Life without thyroxine to 3, 5, 3′-triiodothyronine conversion: studies in mice devoid of the 5′-deiodinases. Endocrinology 150(6):2957–2963
Reid KF, Naumova EN, Carabello RJ, Phillips EM, Fielding RA (2008) Lower extremity muscle mass predicts functional performance in mobility-limited elders. J Nutr Health Aging 12(7):493–498
Martin H, Yule V, Syddall H, Dennison E, Cooper C, Sayer AA (2006) Is hand-held dynamometry useful for the measurement of quadriceps strength in older people? A comparison with the gold standard Biodex dynamometry. Gerontology 52(3):154–159
Hughes VA, Frontera WR, Wood M, Evans WJ, Dallal GE, Roubenoff R, Singh MAF (2001) Longitudinal muscle strength changes in older adults: influence of muscle mass, physical activity, and health. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Med Sci 56(5):B209–B217
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare, & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (Grant No. A092077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, S., Kim, J., Park, Y. et al. Low free T3 to free T4 ratio was associated with low muscle mass and impaired physical performance in community-dwelling aged population. Osteoporos Int 31, 525–531 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-05137-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-05137-w