Abstract
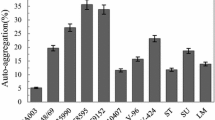
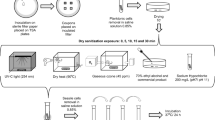
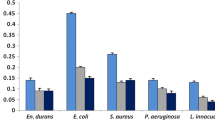
This study aimed to assess the biofilm formation by Bacillus cereus on two novel surfaces namely: aluminum and cold steel in comparison study with stainless steel and polystyrene. Also, it aimed to study the inhibitory effect of a new strain Pediococcus acidilactici against biofilm formation by B. cereus grown on these surfaces. In this study, B. cereus M50 isolated from milky machine surface was selected as the highest biofilm producer. The number of M50 cells adhered to aluminum and stainless steel surfaces were more than that adhered to polystyrene and cold steel, respectively. The antimicrobial, anti-adhesive and SEM studies revealed that the P. acidilactici P12 culture and its cell free filtrate showed a significant potential inhibition of biofilm formation of M50 on all tested surfaces under different conditions. These results demonstrated that P. acidilactici strain are considered a new biotreatment for biofilm destruction of food borne pathogens, food biopreservation and food safety.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonsaglia ECR, Silva NCC, Fernades Junior A, Araujo Junior JP, Tsunemi MH, Rall VLM. Production of biofilm by Listeria monocytogenes in different materials and temperatures. Food Control. 35: 386–391 (2014)
Bulgasem Y, Hassan Z, Abdalsadiq NKA, Yusoff WMM, et al. Anti-adhesion activity of lactic acid bacteria supernatant against human pathogenic Candida species biofilm. Health Sci. J. 9: 1–9 (2015)
Castelijn GA, van der Veen S, Zwietering MH, Moezelaar R, Abee T. Diversity in biofilm formation and production of curlifimbriae and cellulose of Salmonella typhimurium strains of different origin in high and low nutrient medium. Biofouling. 28: 51–63. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2011.648927 (2012)
Cerca N, Pier GB, Vilanova M, Oliveira R, Azeredo J. Quantitative analysis of adhesion and biofilm formation on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Res. Microbiol. 156: 506–514 (2005)
Cibik R, Lepage E, Tailliez P (2000) Molecular diversity of Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Leuconostoc citreum isolated from traditional French cheeses as revealed by RAPD fingerprinting, 16S rDNA sequencing and 16S rDNA fragment amplification. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 23: 267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0723-2020(00)80014
Denkova R, Denkova Z, Yanakieva V, Blazheva D. Antimicrobial activity of probiotic lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and propionic acid bacteria, isolated from different sources. Microb. Path. Stratg. Comb. 857–864 (2013)
Djadouni F, Mebrouk K. Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria and the spectrum of their biopeptides against spoiling germs in foods. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 3: 435–443 (2012)
Donlan RM, Costerton JW. Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 15: 167–193 (2002)
Duary RK, Rajput YS, Batish VK, Grover S. Assessing the adhesion of putative indigenous probiotic lactobacilli to human colonic epithelial cells. Ind. J. Med. Res. 134: 664–671 (2011)
EL-Sayed N, Reda FM, Farag O, Nasrallah D. Surface Analysis of Nitrogen Plasma Treated C60/PS Nanocomposite Films for Antibacterial Activity. J. Biol. Phys. 43: 211–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-017-9447-6 (2017)
Gómez NC, Abriouel H, Grande MJ, Pulido, RP, Gálvez A. Effect of enterocin AS-48 in combination with biocides on planktonic and sessile Listeria monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 30: 51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2011.12.013 (2012)
Gram L, Bagge-Ravn D, Ng YY, Gymoese P, Vogel BF. Influence of food soiling matrix on cleaning and disinfection efficiency on surface attached Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control. 18: 1165–1171 (2007)
Hayrapetyan H. Bacillus cereus Growth and Biofilm Formation: the Impact of Substratum, Iron Sources, and Transcriptional Regulator Sigma 54. Thesis Ph.D. at Wageningen University in the Aula (2017)
Hejda F, Solar P, Kousal J. Surface free energy determination by contact angle measurements–a comparison of various approaches, WDS’10. In: Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 25 (2010)
Henriques AO, Moran CP. Structure, assembly, and function of the spore surface layers. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 61: 555–588 (2007)
Hibbing ME, Fuqua C, Parsek MR, Peterson SB. Bacterial competition: surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8: 15–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2259 (2010)
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 9th ed. The Williams & Wilkins Co USA, Baltimore (1994)
Houry A, Briandet R, Aymerlch S, Gohar M. Involvement of motility and flagella in Bacillus cereus biofilm formation. Microbiology. 156(4): 1009–1018 (2010)
Hussain MS, Oh DH. Impact of the Isolation Source on the Biofilm Formation Characteristics of Bacillus cereus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28: 77–86 (2018)
Hyde FW, Alberg M, Smith K. Comparison of fluorinated polymers against stain steel, glass and polypropylene in microbial biofilm adherence and removal. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19: 142–149 (1997)
Karunakaran E, Biggs CA. Mechanisms of Bacillus cereus biofilm formation: An investigation of the physicochemical characteristics of cell surfaces and extracellular proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechol. 89: 1161–1175 (2011)
Li S, Huang R, Shah NP, Tao X, Xiong Y. Antioxidant and anti-bacterial activities of exopolysaccharides from Bifidobacterium bifidum WBIN03 and Lactobacillus plantarum R315. J. Dairy Sci. 97: 7334–7343 (2014)
Majed R, Faille C, Kallassy M, Gohar M. Bacillus cereus biofilms-same, only different. Front. Microbiol. 7:1054. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01054 (2016)
Reda FM. Detoxification of enterotoxigenic Bacillus cereus (JX455159) isolated from meat by local strain of Lactobacillus plantarum (JX282192). Ann. Microbiol. 64: 287–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0662-5 (2014)
Ribeiro M.C, Fernandes M.S, Kuaye A.Y, Jimenez-Flores R, Gigante M. Preconditioning of the stainless steel surface affects the adhesion of Bacillus cereus spores. Int. Dairy J. 66: 108–114 (2017)
Salustiano VC, Andrade NJ, Ribeiro Junior JI, Fernandes PE, Lopes JP, Bernardes PC, Portugal JG. Controlling Bacillus cereus adherence to stainless steel with different cleaning and sanitizing procedures used in dairy plants. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 62(6): 1478–1483 (2010)
Sharma V, Harjai K, Shukla G. Effect of bacteriocin and exopolysaccharides isolated from probiotic on P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm. Folia Microbiol. 63: 181–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0545-4 (2018)
Shukla G, Devi P, Seghal R. Effect of Lactobacillus casei as a probiotic on modulation of giardiasis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53: 2671–2679 (2008)
Simões M, LC Simões, MJ Vieira. A review of current and emergent biofilm control strategies. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 43: 573–583 (2010)
Soleimani NA, Kasra Kermanshahi R, Yakhchali B, Sattari TN. Antagonistic activity of probiotic lactobacilli against Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 420: 2169–2173 (2010)
Suga H, Smith K. Molecular mechanisms of bacterial quorum sensing as a new drug target. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 7: 586–591 (2003)
Tesfaye A. Antagonism and primary in vitro probiotic evaluation of lactic acid bacteria recovered from Ergo. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 7: 240–245 (2014)
van der Voort, M, Abee T. Sporulation environment of emetic toxin-producing Bacillus cereus strains determines spore size, heat resistance and germination capacity. J. Appl. Microbiol. 114: 1201–1210 (2013)
Yong CC, Khoo BY, Sasidharan S. Activity of crude and fractionated extracts by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from local dairy, meat and fermented products against Staphylococcus aureus. Ann. Microbiol. 65:1037–1047 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Dr. Naglaa EL-Sayed for her guidance for studying hydrophobicity/hydrophylicity of surfaces.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reda, F.M. Antibacterial and anti-adhesive efficiency of Pediococcus acidilactici against foodborne biofilm producer Bacillus cereus attached on different food processing surfaces. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 841–850 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0518-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0518-7