Abstract
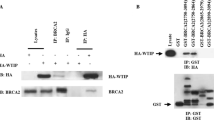
BRD7 is a potential nuclear transcription regulation factor related to nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). BRD2, a putative BRD7-interacting protein, has been screened from human fetal brain cDNA library by yeast two-hybrid system. This study was to further identify the interaction between BRD7 and BRD2 in mammalian cells, and to investigate the subcellular localization of BRD2, as well as the effect on the functions of cell biology. Both immunoprecipitation and subcellular colocalization were performed together to identify the interaction of BRD7 with full-length BRD2, as well as C-terminal truncated BRD2 or N-terminal truncated BRD2. GFP direct fluorescence and Hochest 33258 staining were used to investigate the cellular localization pattern of BRD2 and the roles in initiating cell apoptosis in COS7 and HNE1. The results showed that BRD7 could interact with BRD2 and the region from amino acid 430 to 798 of BRD2 was critical for the interaction of BRD2 with BRD7. BRD2 mainly localizes in nucleus in two distribution patterns, diffused and dotted, and BRD2 has distinct roles in initiating apoptosis, and the dotted distribution pattern of BRD2 in nucleus may be a morphologic marker of cell apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu Ying, Zhang Bi-cheng, Xie Yi, ZHU Shiguo, ZHOU Ming, LI Guiyuan: Analysis and molecular cloning of differentially expressing genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin J Cancer 32(4): 327–332, 2000
YU Ying, ZHU Shiguo, ZHANG Bicheng, ZHOU Ming, Xiang Juanjuan, LI Xiaoling, LI Guiyuan: Growth suppression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line through transfection of BRD7 gene. Chin J Cancer 20(6): 569–574, 2001
Jie Zhou, Jian Ma, Bi-cheng Zhang, Xio-ling Li, Shou-rong Shen, Shi-guo Zhu, Wei Xiong, Hua-ying Liu, He Huang, Ming Zhou, Gui-yuan Li: BRD7, A novel bromodomain gene, inhibits G1-S progression by transcriptionally regulating some important molecular involved in Ras/MEK/ERK and E2F Pathways. Journal of cellular physiology 200: 89–98, 2004
Ada S, Enserink JM, Stein JL, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ: Molecular characterization of celtix-1, a bromodomain protein interacting with the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 2. J Cell Physiol 185(2): 269–79, 2000
Kzhyshkowska J, Rusch A, Wolf H, Dobner T: Regulation of transcription by the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein E1B-AP5 is mediated by complex formation with the novel bromodomain-containing protein BRD7. Biochen J 371: 385–393, 2003
Tamkun JW, Deuring R, Scott MP, Kissinger M, Pattatucci AM, Kaufman TC, Kennison JA: Brahma: A regulator of Drosophila homeotic genes structurally related to the yeast transcriptional activator SNF2/SWI2. Cell 68: 561–572, 1992
Jeanmougin F, Wurtz JM, Le Douarin B, Chambon P, Losson R: The bromodomain revisited. Trends Biochem Sci 22(5): 151–153, 1997
Horn PJ, Peterson CL: The bromodomain: A regulator of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. Front Biosci 6: D1019–1023, 2001
Patrizia F, Ornghi P, Paola B: The bromodomain: A chromatin brower. Frontiers in Bioscience 1: 866–876, 2001
French CA, Miyoshi I, Aster JC, Kubonishi I, Kroll TG, Dal Cin P, Vargas SO, Perez-Atayde AR, Fletcher JA: BRD4 bromodomain gene rearrangement in aggressive carcinoma with translocation t (15; 19). Am J Pathol 159(6): 1987–1992, 2001
Ohshima T, Suganuma T, Ikeda M: A novel mutation lacking the bromodomain of the transcriptional coactivator p300 in the SiHa cervical carcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281(2): 569–575, 2001
YU Ying, ZHU Shiguo, ZHANG Bicheng, ZHOU Ming, LI Xiaoling, LI Guiyuan: Screening of BRD7 interacting proteins by yeast two-hybrid system, Science in China 32 (2): 153–158, 2002
Denis. GV, Green MR: A novel, mitogen-activated nuclear kinaes is related to a Drosophila development regulator. Genes Dev 10: 261–271, 1996
Deb K. Pal, Oleg V. Evgrafov, Paula Tabares, Fengli Zhang, Martina Durner, David A. Greenberg: BRD2 (RING3) Is a Probable Major Susceptibility Gene for Common Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy. Am J Hum Genet 73(2): 261–270, 2003
Guo N, Faller DV, Denis GV: Activation-induced nuclear translocation of RING3. J Cell Sci 113: 3085–3091, 2000
Crowley TE, Kaine EM, Yoshida M, Nandi A, Wolgemuth DJ: Reproductive cycle regulation of nuclear import, euchromatic localization, and association with components of Pol II mediator of a mammalian double-bromodomain protein, Mol. Endocrinol 16: 1727–1737, 2002
Kelly A. Robinson, Jay I. Koepke, Murtaza Kharodawala, John M. Lopes: A network of yeast basic helix—loop—helix interactions. Nucleic Acids Research 28(22): 4460–4466, 2000
Marcela Del Rio, Abubakr Imam, Maryely Deleon, Gary Gomez, Jaya Mishra, Qing Ma, Samir Parikh, Prasad Devarajan: The Death Domain of Kidney Ankyrin Interacts with Fas and Promotes Fas-Mediated Cell Death in Renal Epithelia. J Am Soc Nephro 115: 41–51, 2004
Chikashi Obuse, Osamu Iwasaki, Tomomi Kiyomitsu, Gohta Goshima, Yusuke Toyoda, Mitsuhiro Yanagida: A conserved Mis12 centromere complex is linked to heterochromatic HP1 and outer kinetochore protein Zwint-1. Nature Cell Biology 6: 1135–1141, 2004
Takashi Ito, Tomoko Chiba, Ritsuko Ozawa, Mikio Yoshida, Masahira Hattori, Yoshiyuki Sakaki: A comprehensive two-hybrid analysis to explore the yeast protein interactome. PNAS 98 (8): 4569–4574, 2001
Van Criekinge W, Beyaert R: Yeast Two-Hybrid: State of the Art. Biol Proced Online 2: 1–381, 1999
Thomas E. Crowley, Michele Brunoria, Kunsoo Rheea, Xiangyuan Wanga, Debra J. Wolgemuth. Change in nuclear-cytoplasmic localization of a double-bromodomain protein during proliferation and differentiation of mouse spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. Developmental Brain Research 149: 93–101, 2004
Wei JIN, Le-feng QU, Ping MIN, Shan CHEN, Hong LI, He LU, Yong-tai HOU: Identification of genes responsive to apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25(3): 319–326, 2004
Boudreau N, Werb Z, Bissell MJ: Suppression of apoptosis by basement membrane requires three-dimensional tissue organization and withdrawal from the cell cycle, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93: 3509–3513, 1996
Han EK, Begemann M, Sgambato A, Soh JW, Doki Y, Xing WQ, Liu W, Weinstein IB: Increased expression of cyclin D1 in a murine mammary epithelial cell line induces p27kip1, inhibits growth, and enhances apoptosis. Cell Growth Differ 7: 699–710, 1996
Ma J, Ptashne M: A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell 51(1): 113–119, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Xu, XJ., Zhou, HD. et al. BRD2 is one of BRD7-interacting proteins and its over-expression could initiate apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 292, 205–212 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9233-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9233-4