Abstract
Background
The later-line treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) has been drastically changing by the development of immune-oncology drugs and molecular targeted treatment in recent years. Although the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) model is useful for second-line setting, this model has the problem that over 50% patients are classified as intermediate risk group. The aim of this study is to evaluate whether the serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels prior to second-line treatment could divide intermediate risk group patients.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 82 consequent intermediate-risk mRCC patients who received second-line molecular targeted therapy. We classified patients who had serum CRP higher than 0.5 mg/dl in elevated CRP group because the median baseline serum CRP level before second-line treatment was 0.51 mg/dl. We assessed the prognostic impact of serum CRP levels prior to second-line treatment initiation to predict overall survival (OS).
Results
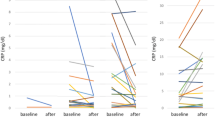
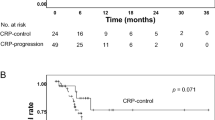
Thirty-three out of 82 (40%) patients demonstrated elevated baseline CRP levels. The median OS of elevated and non-elevated CRP group was 11.5 (95% CI 5.4–17.5) and 29.4 (95% CI 25.5–33.5) months, respectively (p = 0.001). The serum CRP elevation could predict prognosis in intermediate risk patients treated with second-line treatment (HR 2.5, 95% CI 1.4–4.2, p = 0.001).
Conclusions
The serum CRP levels after first-line treatment termination could divide intermediate risk group mRCC patients into two prognostic subgroups in second-line targeted treatment setting.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM et al (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:125–134
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P et al (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:115–124
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P et al (2007) Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:2271–2281
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D et al (2013) Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 369:722–731
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF et al (2015) Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373:1803–1813
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF et al (2018) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 378:1277–1290
Powles T, Staehler M, Ljungberg B et al (2016) Updated EAU guidelines for clear cell renal cancer patients who fail VEGF targeted therapy. Eur Urol 69:4–6
https://www.nccn.org/. Accessed 7 Jan 2019
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM et al (2013) External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 14:141–148
Zeng F, Wei H, Yeoh E et al (2016) Inflammatory markers of CRP, IL6, TNFalpha, and soluble TNFR2 and the risk of ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 25:1231–1239
Zhou B, Shu B, Yang J et al (2014) C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 25:1397–1405
Takamatsu K, Mizuno R, Omura M et al (2018) Prognostic value of baseline serum C-reactive protein level in intermediate-risk group patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma treated by first-line vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Clin Genitourin Cancer 16:e927–e933
Ko JJ, Xie W, Kroeger N et al (2015) The International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium model as a prognostic tool in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma previously treated with first-line targeted therapy: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 16:293–300
Takagi T, Kondo T, Kennoki T et al (2013) Comparison of survival rates in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma according to treatment era including cytokine and targeted therapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 43:439–443
Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA et al (2013) Inflammation-induced cancer: crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer 13:759–771
Fujita T, Nishi M, Tabata K et al (2016) Overall prognostic impact of C-reactive protein level in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Anticancer Drugs 27:1028–1032
Johnson TV, Abbasi A, Owen-Smith A et al (2010) Absolute preoperative C-reactive protein predicts metastasis and mortality in the first year following potentially curative nephrectomy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 183:480–485
Ishihara H, Kondo T, Yoshida K et al (2017) Effect of systemic inflammation on survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving second-line molecular-targeted therapy. Clin Genitourin Cancer 15:495–501
Yasuda Y, Saito K, Yuasa T et al (2013) Prognostic impact of pretreatment C-reactive protein for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Int J Clin Oncol 18:884–889
Teishima J, Kobatake K, Kitano H et al (2016) The impact of change in serum C-reactive protein level on the prediction of effects of molecular targeted therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 117:E67–74
Escudier B, Sharma P, McDermott DF et al (2017) CheckMate 025 Randomized Phase 3 Study: outcomes by key baseline factors and prior therapy for nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 72:962–971
Mizuno R, Mikami S, Takamatsu K et al (2017) Baseline risk stratification or duration of prior therapy predicts prognosis in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with axitinib. Jpn J Clin Oncol 47:1170–1174
Acknowledgements
Supported in part by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan (17K11159 to R.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ryuichi Mizuno MD has received honoraria from Bristol, Novartis, and Pfizer. Mototsugu Oya MD has received honoraria from Bayer, Bristol, Novartis, and Pfizer. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Takamatsu, K., Mizuno, R., Tanaka, N. et al. Prognostic value of serum C-reactive protein level prior to second-line treatment in intermediate risk metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Int J Clin Oncol 24, 1069–1074 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01459-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01459-1