Abstract
Background
Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging helps to determine abnormal brain tissue conditions by evaluating metabolite concentrations. Although a powerful technique, it is underutilized in routine clinical studies because of its long scan times.
Objective
In this study, we evaluated the feasibility of scan time reduction in metabolic imaging using compressed-sensing-based MR spectroscopic imaging in pediatric patients undergoing routine brain exams.
Materials and methods
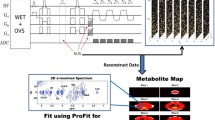
We retrospectively evaluated compressed-sensing reconstructions in MR spectroscopic imaging datasets from 20 pediatric patients (11 males, 9 females; average age: 5.4±4.5 years; age range: 3 days to 16 years). We performed retrospective under-sampling of the MR spectroscopic imaging datasets to simulate accelerations of 2-, 3-, 4-, 5-, 7- and 10-fold, with subsequent reconstructions in MATLAB. Metabolite maps of N-acetylaspartate, creatine, choline and lactate (where applicable) were quantitatively evaluated in terms of the root-mean-square error (RMSE), peak amplitudes and total scan time. We used the two-tailed paired t-test along with linear regression analysis to statistically compare the compressed-sensing reconstructions at each acceleration with the fully sampled reference dataset.
Results
High fidelity was maintained in the compressed-sensing MR spectroscopic imaging reconstructions from 50% to 80% under-sampling, with the RMSE not exceeding 3% in any dataset. Metabolite intensities and ratios evaluated on a voxel-by-voxel basis showed no statistically significant differences and mean metabolite intensities showed high correlation compared to the fully sampled reference dataset up to an acceleration factor of 5.
Conclusion
Compressed-sensing MR spectroscopic imaging has the potential to reduce MR spectroscopic imaging scan times for pediatric patients, with negligible information loss.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panigrahy A, Nelson MD Jr, Bluml S (2010) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in pediatric neuroradiology: clinical and research applications. Pediatr Radiol 40:3–30
Xu D, Vigneron D (2010) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging of the newborn brain — a technical review. Semin Perinatol 34:20–27
Astrakas LG, Zurakowski D, Tzika AA et al (2004) Noninvasive magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging biomarkers to predict the clinical grade of pediatric brain tumors. Clin Cancer Res 10:8220–8228
Gonen O, Wang ZJ, Viswanathan AK et al (1999) Three-dimensional multivoxel proton MR spectroscopy of the brain in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1333–1341
Hourani R, Horska A, Albayram S et al (2006) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging to differentiate between nonneoplastic lesions and brain tumors in children. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:99–107
Laprie A, Pirzkall A, Haas-Kogan DA et al (2005) Longitudinal multivoxel MR spectroscopy study of pediatric diffuse brainstem gliomas treated with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62:20–31
Marcus KJ, Astrakas LG, Zurakowski D et al (2007) Predicting survival of children with CNS tumors using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging biomarkers. Int J Oncol 30:651–657
Moore GJ (1998) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in pediatric neuroradiology. Pediatr Radiol 28:805–814
Tafazoli S, O'Neill J, Bejjani A et al (2013) 1H MRSI of middle frontal gyrus in pediatric ADHD. J Psychiatr Res 47:505–512
Thakur SB, Karimi S, Dunkel IJ et al (2006) Longitudinal MR spectroscopic imaging of pediatric diffuse pontine tumors to assess tumor aggression and progression. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:806–809
Tzika AA (2008) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging as a cancer biomarker for pediatric brain tumors. Int J Oncol 32:517–526
Wu WE, Kirov II, Tal A et al (2013) Brain MR spectroscopic abnormalities in "MRI-negative" tuberous sclerosis complex patients. Epilepsy Behav 27:319–325
Howe FA, Opstad KS (2003) 1H MR spectroscopy of brain tumours and masses. NMR Biomed 16:123–131
Skoch A, Jiru F, Bunke J (2008) Spectroscopic imaging: basic principles. Eur J Radiol 67:230–239
Donoho DL (2006) Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52:18
Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly JM (2007) Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 58:1182–1195
Bhave S, Lingala SG, Newell JD et al (2016) Blind compressed sensing enables 3-dimensional dynamic free breathing magnetic resonance imaging of lung volumes and diaphragm motion. Investig Radiol 51:387–399
Dyvorne H, Knight-Greenfield A, Jajamovich G et al (2015) Abdominal 4D flow MR imaging in a breath hold: combination of spiral sampling and dynamic compressed sensing for highly accelerated acquisition. Radiology 275:245–254
Jung H, Sung K, Nayak KS et al (2009) K-t FOCUSS: a general compressed sensing framework for high resolution dynamic MRI. Magn Reson Med 61:103–116
Zhang T, Cheng JY, Potnick AG et al (2015) Fast pediatric 3D free-breathing abdominal dynamic contrast enhanced MRI with high spatiotemporal resolution. J Magn Reson Imaging 41:460–473
Hu S, Lustig M, Balakrishnan A et al (2010) 3D compressed sensing for highly accelerated hyperpolarized (13)C MRSI with in vivo applications to transgenic mouse models of cancer. Magn Reson Med 63:312–321
Geethanath S, Baek HM, Ganji SK et al (2012) Compressive sensing could accelerate 1H MR metabolic imaging in the clinic. Radiology 262:985–994
Furuyama JK, Wilson NE, Burns BL et al (2012) Application of compressed sensing to multidimensional spectroscopic imaging in human prostate. Magn Reson Med 67:1499–1505
Maguire ML, Geethanath S, Lygate CA et al (2015) Compressed sensing to accelerate magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging: evaluation and application to 23Na-imaging of mouse hearts. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 17:45
Cao P, Wu EX (2015) Accelerating phase-encoded proton MR spectroscopic imaging by compressed sensing. J Magn Reson Imaging 41:487–495
Wilson NE, Iqbal Z, Burns BL et al (2016) Accelerated five-dimensional echo planar J-resolved spectroscopic imaging: implementation and pilot validation in human brain. Magn Reson Med 75:42–51
Hsiao A, Lustig M, Alley MT et al (2012) Rapid pediatric cardiac assessment of flow and ventricular volume with compressed sensing parallel imaging volumetric cine phase-contrast MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198:W250–W259
Kim DH, Gu M, Cunningham C et al (2009) Fast 3D (1)H MRSI of the corticospinal tract in pediatric brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:1–6
Vasanawala SS, Alley MT, Hargreaves BA et al (2010) Improved pediatric MR imaging with compressed sensing. Radiology 256:607–616
Zhang T, Chowdhury S, Lustig M et al (2014) Clinical performance of contrast enhanced abdominal pediatric MRI with fast combined parallel imaging compressed sensing reconstruction. J Magn Reson Imaging 40:13–25
Naressi A, Couturier C, Castang I et al (2001) Java-based graphical user interface for MRUI, a software package for quantitation of in vivo/medical magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals. Comput Biol Med 31:269–286
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P et al (2013) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006-2010. Neuro Oncol 15:ii1–i56
Knoll F, Clason C, Diwoky C, Stollberger R (2011) Adapted random sampling patterns for accelerated MRI. MAGMA 24:43–50
Zijlstra F, Viergever MA, Seevinck PR (2015) Evaluation of variable density and data-driven k-space undersampling for compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging. Investig Radiol 51:410–419
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Luke Lammers (Arizona State University), Jeffrey Miller, MD, John Curran, MD, and the team of MR technologists at Phoenix Children’s Hospital for their support, as well as Kathy Zeblisky for reference assistance. The project was partly funded by research awards from the Phoenix Children’s Hospital Foundation and the Banner Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidya Shankar, R., Hu, H.H., Bikkamane Jayadev, N. et al. 2-D magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of the pediatric brain using compressed sensing. Pediatr Radiol 49, 1798–1808 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04495-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04495-1