Abstract
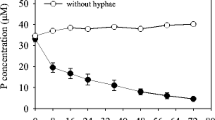
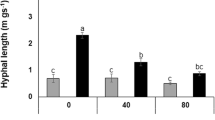
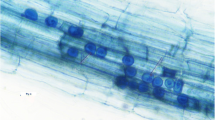
Arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi increase phosphate (P) uptake by plants. Organic phosphate comprises 30–80% of total P in most agricultural soils. Some plants can utilize organic phosphate by secreting acid phosphatase (ACP) from their roots, especially under low P conditions. Although secretion of ACP from extraradical hyphae of AM fungi has been reported, the specific factors that affect the secretion of ACP are unknown. The objective of the present study was to investigate whether secretion of ACP from extraradical hyphae is induced by low P conditions. First, specimens of Allium fistulosum were either inoculated with the AM fungus Rhizophagus clarus strain CK001 or remained uninoculated and were grown in soil with 0.5 g P2O5 kg−1 soil or without P fertilization using two-compartment pots. Soil solution was collected using mullite ceramic tubes 45 days after sowing. The soil solution was analyzed for ACP activity by using p-nitrophenylphosphate. Second, Ri T-DNA transformed roots (i.e., hairy roots) of Linum usitatissimum inoculated with R. clarus were grown on solid minimal media with two P levels applied (3 and 30 μM P) using two-compartment Petri dishes under in vitro conditions. Hyphal exudates, extraradical hyphae, and hairy roots were collected and analyzed for ACP activity. ACP activity in the soil solution of the hyphal compartment in the A. fistulosum inoculation treatment was higher without P fertilization than with P fertilization. AM colonization also was higher without P fertilization than with P fertilization. In the in vitro two-compartment culture, ACP activity of hyphal exudates and extraradical hyphae were higher under the 3-μM treatment than under the 30-μM treatment. These findings suggest that the secretion of ACP from the extraradical hyphae of R. clarus into the hyphosphere is promoted under low P conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez M, Gieseke A, Godoy R, Hartel S (2006) Surface-bound phosphatase activity in ectomycorrhizal fungi: a comparative study between a colorimetric and a microscope-based method. Biol Fert Soils 42:561–568
Bernard M et al (2002) Characterization of a cell-wall acid phosphatase (PhoAp) in Aspergillus fumigatus. Microbiol-Sgm 148:2819–2829. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-148-9-2819
Chabot S, Becard G, Piche Y (1992) Life cycle of Glomus intraradix in root organ culture. Mycologia 84:315–321
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change-Human and Policy Dimensions 19:292–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.Gloenvcha.2008.10.009
Dalal RC (1977) Soil organic phosphorus. Adv Agron 29:83–117
Declerck S, Strullu DG, Plenchette C (1998) Monoxenic culture of the intraradical forms of Glomus sp. isolated from a tropical ecosystem: a proposed methodology for germplasm collection. Mycologia 90:579–585. https://doi.org/10.2307/3761216
Doner L, Becard G (1991) Solubilization of gellan gels by chelation of cations. Biotechnology Techniques 5:25–28
Ehrlich KC, Montalbano BG, Mullaney EJ, Dischinger HC, Ullah AHJ (1994) An acid-phosphatase from Aspergillus ficuum has homology to Penicillium chrysogenum Phoa. Biochem Bioph Res Co 204:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1994.2426
Ezawa T, Yoshida T (1994) Characterization of phosphatase in marigold roots infected with vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 40:255–264
Ezawa T, Saito K (2018) How do arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi handlephosphate? New insight into fine-tuning of phosphate metabolism. New Phytol 220:1116–1121. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15187
Feng G, Song YC, Li XL, Christie P (2003) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to utilization of organic sources of phosphorus by red clover in a calcareous soil. Appl Soil Ecol 22:139–148
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol 84:489–500
Haas H, Redl B, Friedlin E, Stoffler G (1992) Isolation and analysis of the Penicillium chrysogenum Phoa gene encoding a secreted phosphate-repressible acid-phosphatase. Gene 113:129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(92)90680-N
Joner EJ, Johansen A (2000) Phosphatase activity of external hyphae of two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycological Research 104(Part 1):81–86
Joner EJ, Ravnskov S, Jakobsen I (2000) Arbuscular mycorrhizal phosphate transport under monoxenic conditions using radio-labelled inorganic and organic phosphate. Biotechnology Letters 22:1705–1708
Koide RT, Kabir Z (2000) Extraradical hyphae of the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices can hydrolyse organic phosphate. New Phytol 148:511–517
Louche J, Ali MA, Cloutier-Hurteau B, Sauvage FX, Quiquampoix H, Plassard C (2010) Efficiency of acid phosphatases secreted from the ectomycorrhizal fungus Hebeloma cylindrosporum to hydrolyse organic phosphorus in podzols. Fems Microbiol Ecol 73:323–335. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1574-6941.2010.00899.X
Maruyama H et al (2012) Effect of exogenous phosphatase and phytase activities on organic phosphate mobilization in soils with different phosphate adsorption capacities. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 58:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2012.656298
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis Part 2 Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 403–430
Olsson PA, van Aarle IM, Allaway WG, Ashford AE, Rouhier H (2002) Phosphorus effects on metabolic processes in monoxenic arbuscular mycorrhiza cultures. Plant Physiol 130:1162–1171. https://doi.org/10.1104/Pp.009639
Oshima Y (1997) The phosphatase system in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Genet Syst 72:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.72.323
Oshima Y, Ogawa N, Harashima S (1996) Regulation of phosphatase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae - a review. Gene 179:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00425-8
Robinson WD et al (2012) The secreted purple acid phosphatase isozymes AtPAP12 and AtPAP26 play a pivotal role in extracellular phosphate-scavenging by Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 63:6531–6542. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers309
Sato T, Ezawa T, Cheng WG, Tawaraya K (2015) Release of acid phosphatase from extraradical hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus clarus. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 61:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2014.993298
Scandalios JG (1969) Genetic control of multiple molecular forms of enzymes in plants: a review. Biochemical Genetics 3:37–79
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis Third Edition. Academic Press, London
Spatafora JW et al (2016) A phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia 108:1028–1046. https://doi.org/10.3852/16-042
St-Arnaud M, Hamel C, Vimard B, Caron M, Fortin JA (1996) Enhanced hyphal growth and spore production of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices in an in vitro system in the absence of host roots. Mycol Res 100:328–332
Tarafdar JC, Marschner H (1994) Phosphatase activity in the rhizosphere and hyphosphere of VA mycorrhizal wheat supplied with inorganic and orgnic phosphorus. Soil Biol Biochem 26:387–395
Tasaki Y, Azwan A, Yazaki J, Hara T, Joh T (2006) Structure and expression of two genes encoding secreted acid phosphatases under phosphate-deficient conditions in Pholiota nameko strain N2. Curr Genet 49:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-006-0058-1
Tawaraya K, Hashimoto K, Wagatsuma T (1998) Effect of root exudate fractions from P-deficient and P-sufficient onion plants on root colonisation by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Gigaspora margarita. Mycorrhiza 8:67–70
Tawaraya K, Naito M, Wagatsuma T (2006) Solubilization of insoluble inorganic phosphate by hyphal exudates of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. J Plant Nutr 29:657–665
van Aarle IM, Plassard C (2010) Spatial distribution of phosphatase activity associated with ectomycorrhizal plants is related to soil type. Soil Biol Biochem 42:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.Soilbio.2009.11.011
Wasaki J et al (2009) Overexpression of the LASAP2 gene for secretory acid phosphatase in white lupin improves the phosphorus uptake and growth of tobacco plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 55:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1747-0765.2008.00329.X
Wu QS, Li Y, Zou YN, He XH (2015) Arbuscular mycorrhiza mediates glomalin-related soil protein production and soil enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of trifoliate orange grown under different P levels. Mycorrhiza 25:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-014-0594-3
Wykoff DD, O’Shea EK (2001) Phosphate transport and sensing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 159:1491–1499
Funding
This study was financially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP15K07332 and JP18K05368.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, T., Hachiya, S., Inamura, N. et al. Secretion of acid phosphatase from extraradical hyphae of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus clarus is regulated in response to phosphate availability. Mycorrhiza 29, 599–605 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-019-00923-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-019-00923-0