Abstract
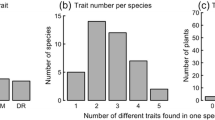
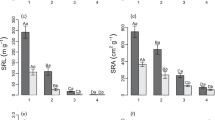
Understanding the differences in fine-root traits among different species is essential to gain a detailed understanding of resource conservation and acquisition strategies of plants. We aimed to explore whether certain root traits are consistent among subsets of species and characterize species together into meaningful community groups. We selected 11 woody species from different microbial symbiotic groups (ectomycorrhiza, arbuscular mycorrhiza, and rhizobia) and phylogenetic groups (broad-leaved angiosperms and coniferous gymnosperms) from the cool temperate forests of Nagano, Japan. We measured root architectural (branching intensity), morphological (root tissue density and specific root length), chemical (N and K concentrations), and anatomical (total stele and total cortex) traits. Significant differences were observed in all root traits, although many species did not differ from one another. Branching intensity was found to be the greatest variation in the measured root traits across the 11 woody species. The results of a principal component analysis of root traits showed a distinct separation between angiosperms and gymnosperms. We identified clusters of species based on their multidimensional root traits that were consistent with the different phylogenetic microbial association groups. Gymnosperm roots may be more resource conservative, while angiosperm roots may be more acquisitive for water and nutrients. We consider that the advances in root traits combination will make a breakthrough in our ability to differentiate the community groups rather than individual root trait.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Chapin IIIFS (1999) The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and pattern. Ecol Res 30:1–67
Assefa D, Godbold DL, Belay B, Abiyu A, Rewald B (2018) Fine root morphology, biochemistry and litter quality indices of fast- and slow-growing woody species in Ethiopian highland forest. Ecosystems 21:482–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-017-0163-7
Bardgett RD, Van Der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 515:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13855
Bardgett RD, Mommer L, De Vries FT (2014) Going underground: root traits as drivers of ecosystem processes. Trends Ecol Evol 29:692–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2014.10.006
Burton AJ, Jarvey JC, Jarvi MP, Zak DR, Pregizer KS (2012) Chronic N deposition alters root respiration-tissue N relationship in northern hardwood forests. Glob Change Biol 18:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02527.x
Clemmesen KE, Bahr A, Ovaskainen O, Dahlberg A, Ekblad A, Wallander H, Stenlid J, Finlay RD, Wardle DA, Lindahl BD (2013) Roots and associated fungi drive long-term carbon sequestration in boreal forest. Science 339:1615–1619
Comas LH, Eissenstat DM (2004) Linking fine root traits to maximum potential growth rate among 11 mature temperate tree species. Funct Ecol 18:388–397
Comas LH, Eissenstat DM (2009) Patterns in root trait variation among 25 co-existing North American forest species. New Phytol 182:919–928. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02799.x
Comas LH, Mueller KE, Taylor LL, Midford PE, Callahan HS, Beerling DJ (2012) Evolutionary patterns and biogeochemical significance of angiosperm root traits. Int J Plant Sci 173:584–595. https://doi.org/10.1086/665823
Comas LH, Callahan HS, Midford PE (2014) Patterns in root traits of woody species hosting arbuscular and ectomycorrhizas: implications for the evolution of belowground strategies. Ecol Evol 4:2979–2990. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1147
de Kroon H, Visser EJW (2003) Root ecology. Springer, Berlin
Development Core Team R (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Eissenstat DM (1992) Costs and benefits of constructing roots of small diameter. J Plant Nutr 15:6–7
Esau K (1977) Anatomy of seed plants, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 215–255
Fitter AH (1991) The ecological significance of root system architecture: an economic approach. In: Atkinson D (ed) Plant and root growth: an ecological perspective. Blackwell Science, London, pp 229–243
Freschet GT, Cornwell WK, Wardle DA, Elumeeva TG, Liu W, Jackson BG, Onipchenko VG, Soudzilovskaia NA, Tao J, Cornelissen JHC (2013) Linking litter decomposition of above- and below-ground organs to plant–soil feedbacks worldwide. J Ecol 101:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12092
Guo D, Xia M, Wei X, Chang W, Liu Y, Wang Z (2008) Anatomical traits associated with absorption and mycorrhizal colonization are linked to root branch order in twenty-three Chinese temperate tree species. New Phytol 180:673–683. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02573.x
Hobbie SE (2015) Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol Evol 30:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.03.015
Hodge A (2004) The plastic plant: root responses to heterogeneous supplies of nutrients. New Phytol 162:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01015.x
Iversen CM (2010) Digging deeper: fine-root responses to rising atmospheric CO2 concentration in forested ecosystems. New Phytol 186:346–357
Johnson SN, Benefer CM, Frew A, Griffiths BS, Hartley SE, Karley AJ, Rasmann S, Schumann M, Sonnemann I, Robert CAM (2016) New frontiers in belowground ecology for plant protection from root-feeding insects. Soil Ecol 108:96–107
Kong D, Ma C, Zhang Q, Li L, Chen X, Zeng H, Guo D (2014) Leading dimensions in absorptive root trait variation across 96 subtropical forest species. New Phytol 203:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12842
Kramer-Walter KR, Bellingham PJ, Millar TR, Smissen RD, Richardson SJ, Laughlin DC (2016) Root traits are multidimensional: specific root length is independent from root tissue density and the plant economic spectrum. J Ecol 104:1299–1310. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12562
Lambers H, Mougel C, Jaillard B, Hinsinger P (2009) Plant–microbe–soil interactions in the rhizosphere: an evolutionary perspective. Plant Soil 321:83–115
Liese R, Alings K, Meier IC (2017) Root branching is a leading root trait of the plant economics spectrum in temperate trees. Front Plant Sci 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00315
Lux A, Luxová M, Abe J, Morita S (2004) Root cortex: structural and functional variability and responses to environmental stress. Root Res 13:117–131
Ma Z, Guo D, Xu X, Lu M, Bardgett RD, Eissenstat DM, McCormack ML, Hedin LO (2018) Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits. Nature 555:94–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25783
Makita N, Hirano Y, Mizoguchi T, Kominami Y, Dannoura M, Ishii H, Finér L, Kanazawa Y (2011) Very fine roots respond to soil depth: biomass allocation, morphology, and physiology in a broad-leaved temperate forest. Ecol Res 26:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-010-0764-5
Makita N, Hirano Y, Sugimoto T, Tanikawa T, Ishii H (2015) Intraspecific variation in fine root respiration and morphology in response to in situ soil nitrogen fertility in a 100-year-old Chamaecyparis obtusa forest. Oecologia 179:959–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-015-3413-4
McCormack ML, Dickie IA, Eissenstat DM, Fahey TJ, Fernandez CW, Guo D, Helmisaari HS, Hobbie EA, Iversen CM, Jackson RB, Leppälammi-Kujansuu J, Norby RJ, Phillips RP, Pregitzer KS, Pritchard SG, Rewald B, Zadworny M (2015) Redefining fine roots improves understanding of below-ground contributions to terrestrial biosphere processes. New Phytol 207:505–518. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13363
McCormack ML, Guo D, Iversen CM, Chen W, Eissenstat DM, Fernandez CW, Li L, Ma C, Ma Z, Poorter H, Reich PB, Zadworny M, Zanne A (2017) Building a better foundation: improving root-trait measurements to understand and model plant and ecosystem processes. New Phytol 215:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14459
Onoda Y, Wright IJ, Evans JR, Hikosaka K, Kitajima K, Niinemets Ü, Poorter H, Tosens T, Westoby M (2017) Physiological and structural tradeoffs underlying the leaf economics spectrum. New Phytol 214:1447–1463. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14496
Ostonen I, Lohmus K (2003) Proportion of fungal mantle, cortex and stele of ectomycorrhizas in Picea abies (L.) Karst. In different soils and site conditions. Plant Soil 257:435–442
Pregitzer KS, Laskowski MJ, Burton AJ, Lessard VC, Zak DR (1998) Variation in sugar maple root respiration with root diameter and soil depth. Tree Physiol 18:665–670
Pregitzer KS, Deforest JL, Burton AJ, Allen MF, Ruess RW, Hendrick RL (2002) Fine root architecture of nine North American trees. Ecol Monogr 72:293–309
Reich PB (2014) The world-wide ‘fast-slow’ plant economics spectrum: a traits manifesto. J Ecol 102:275–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12211
Roumet C, Birouste M, Picon-Cochard C, Ghestem M, Osman N, Vrignon-Brenas S, Cao K, Stokes A (2016) Root structure–function relationships in 74 species: evidence of a root economics spectrum related to carbon economy. New Phytol 210:815–826. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13828
Ryan MG, Hubbard RM, Pongracic S, Raison RJ, McMurtrie RE (1996) Foliage, fine-root, woody-tissue and stand respiration in Pinus radiata in relation to nitrogen status. Tree Physiol 16:333–343
Saleem M, Law AD, Sahib MR, Pervaiz ZH, Zhang Q (2018) Impact of root system architecture on rhizosphere and root microbiome. Rhizosphere 6:47–51
Strand AE, Pritchard SG, McCormack ML, Davis MA, Oren R (2008) Irreconcilable differences: fine-root life spans and soil carbon persistence. Science 319:456–458. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1151382
Taiz L, Zeiger E (2002) Plant physiology. Mineral nutrition, 3rd edn. Sinauer Associates Inc, Sunderland, pp 67–86
Tilman D, Knops J, Wedin D, Reich P, Ritchie M, Siemann E (1997) The influence of functional diversity and composition on ecosystem processes. Science 277:1300–1302
Weemstra M, Mommer L, Visser EJW, van Ruijven J, Kuyper TW, Mohren GMJ, Sterck FJ (2016) Towards a multidimensional root trait framework: a tree root review. New Phytol 211:1159–1169. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14003
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee T, Lee W, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas ML, Niinemets Ü, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov VI, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 428:821–827. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02403
Yanai RD, McFarlane KJ, Lucash MS, Kulpa SE, Wood DM (2009) Similarity of nutrient uptake and root dimensions of Engelmann spruce and subalpine fir at two contrasting sites in Colorado. For Ecol Manag 258:2233–2241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.04.035
Zadworny M, McCormack ML, Mucha J, Reich P, Oleksyn J (2016) Scots pine fine roots adjust along a 2000-km latitudinal climatic gradient. New Phytol 212:389–399
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged Ms. H Umezu, Ms. K Nakazawa, Ms. J Wang, Dr. H Kobayashi, Dr. T Kunito and Dr. H Park of Shinshu University for helpful support in field and laboratory experiments. We also thank two reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions for the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially funded by Grant-in Aid for Japan Society for the Promotion of Science fellows (15K18719, 18K14488) and by the Fujiwara Natural History Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY and NM conceived and designed the experiments. HY, NT, MO and NM performed the experiments and analyzed the data. HY and NM wrote the manuscript and other authors provided editorial advice.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Susana Rodriguez Echeverria.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yahara, H., Tanikawa, N., Okamoto, M. et al. Characterizing fine-root traits by species phylogeny and microbial symbiosis in 11 co-existing woody species. Oecologia 191, 983–993 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-019-04546-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-019-04546-2