Abstract
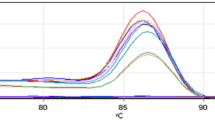
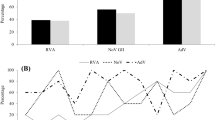
Saffold virus as a newly discovered virus, which seems to be related to acute gastroenteritis as with other enteric viruses and to human airway diseases in children belongs to Cardiovirus genus in picornaviridae family with 11 genotypes. Saffold virus initially was detected in America from infant stool sample. Saffold virus has also been detected in environmental water samples. Until now, two reports have demonstrated that sewage water sources are contaminated with Saffold viruses. Molecular detection of Saffold virus mostly depended on reverse transcription PCR methods and RT-qPCR, which had targeted 5′UTR region of the viral genome. The present study aims to evaluate the molecular detection and quantity of Saffold virus in sewage water and river water specimens by RT-qPCR assay in Karaj, Iran. Fifty samples collected from environmental waters containing treated and untreated sewage water and river water samples were included in this study. After viral RNA extraction, the Real-time PCR was developed to amplify the 5′UTR sequence of Saffold virus genome and viral load was assessed. Out of the 50 samples tested (consisting 28 river water samples and 22 sewage water samples), the Saffold virus genomic RNA was identified in 10/28 (35.7%) of river water samples and in 4/12 (33.3%) of treated and 4/10 (40%) of untreated sewage samples. The maximum viral load was 6.8 × 106 copies/l in untreated sewage water sample in December, and the lower viral load was 1.2 × 106 copies/l related to treated sewage water taken in October. Our results for the first time indicate that Saffold virus has apparently been circulating among Iranian peoples. Also, the viral prevalence of Saffold virus in each of the three sets of tested samples was within moderate to high in range.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed, Y., & Boivin, G. (2008). New Saffold cardioviruses in 3 children, Canada. Emerging Infectious Diseases,14(5), 834.
Adineh, M., Ghaderi, M., & Mousavi-Nasab, S. D. (2019). Occurrence of salivirus in sewage and river water samples in Karaj, Iran. Food and Environmental Virology,11, 193–197.
Azhdar, Z., Ghaderi, M., & Mousavi-Nasab, S. D. (2019). Optimization of RT-qPCR for detection of aichi virus in sewage and river water samples in Karaj, Iran. Archives of Iranian Medicine,22(5), 242–246.
Blinkova, O., Kapoor, A., Victoria, J., Jones, M., Wolfe, N., Naeem, A., et al. (2009a). Cardioviruses are genetically diverse and cause common enteric infections in South Asian children. Journal of Virology,83(9), 4631–4641.
Blinkova, O., Rosario, K., Li, L., Kapoor, A., Slikas, B., Bernardin, F., et al. (2009b). Frequent detection of highly diverse variants of cardiovirus, cosavirus, bocavirus, and circovirus in sewage samples collected in the United States. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,47(11), 3507–3513.
Chiu, C. Y., Greninger, A. L., Kanada, K., Kwok, T., Fischer, K. F., Runckel, C., et al. (2008). Identification of cardioviruses related to Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus in human infections. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,105(37), 14124–14129.
Dennehy, P. H. (2005). Acute diarrheal disease in children: Epidemiology, prevention, and treatment. Infectious Disease Clinics,19(3), 585–602.
Denno, D. M., Klein, E. J., Young, V. B., Fox, J. G., Wang, D., & Tarr, P. I. (2007). Explaining unexplained diarrhea and associating risks and infections. Animal Health Research Reviews,8(1), 69–80.
Drexler, J. F., Baumgarte, S., de Souza Luna, L. K., Stöcker, A., Almeida, P. S., Ribeiro, T. C. M., et al. (2010). Genomic features and evolutionary constraints in Saffold-like cardioviruses. Journal of General Virology,91(6), 1418–1427.
Drexler, J. F., de Souza Luna, L. K., Stöcker, A., Almeida, P. S., Ribeiro, T. C. M., Petersen, N., et al. (2008). Circulation of 3 lineages of a novel Saffold cardiovirus in humans. Emerging Infectious Diseases,14(9), 1398.
Hertzler, S., Liang, Z., Treso, B., & Lipton, H. L. (2011). Adaptation of Saffold virus 2 for high-titer growth in mammalian cells. Journal of Virology,85(14), 7411–7418.
Himeda, T., & Ohara, Y. (2012). Saffold virus, a novel human Cardiovirus with unknown pathogenicity. Journal of Virology,86(3), 1292–1296.
Ibrahim, C., Hammami, S., Mejri, S., Mehri, I., Pothier, P., & Hassen, A. (2017). Detection of Aichi virus genotype B in two lines of wastewater treatment processes. Microbial Pathogenesis,109, 305–312.
Itagaki, T., Abiko, C., Aoki, Y., Ikeda, T., Mizuta, K., Noda, M., et al. (2011). Saffold cardiovirus infection in children associated with respiratory disease and its similarity to coxsackievirus infection. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal,30(8), 680–683.
Itagaki, T., Abiko, C., Ikeda, T., Aoki, Y., Seto, J., Mizuta, K., et al. (2010). Sequence and phylogenetic analyses of Saffold cardiovirus from children with exudative tonsillitis in Yamagata, Japan. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases,42(11–12), 950–952.
Jin, Y., Cheng, W.-X., Yang, X.-M., Jin, M., Zhang, Q., Xu, Z.-Q., et al. (2009). Viral agents associated with acute gastroenteritis in children hospitalized with diarrhea in Lanzhou, China. Journal of Clinical Virology,44(3), 238–241.
Jones, M. S., Lukashov, V. V., Ganac, R. D., & Schnurr, D. P. (2007). Discovery of a novel human picornavirus in a stool sample from a pediatric patient presenting with fever of unknown origin. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,45(7), 2144–2150.
Khamrin, P., Thongprachum, A., Kikuta, H., Yamamoto, A., Nishimura, S., Sugita, K., et al. (2013). Three clusters of Saffold viruses circulating in children with diarrhea in Japan. Infection, Genetics and Evolution,13, 339–343.
Leguia, M., Loyola, S., Rios, J., Juarez, D., Guevara, C., Silva, M., et al. (2015). Full genomic characterization of a Saffold virus isolated in Peru. Pathogens,4(4), 816–825.
Menage, L., Yodmeeklin, A., Khamrin, P., Kumthip, K., & Maneekarn, N. (2017). Prevalence of human cosavirus and saffold virus with an emergence of saffold virus genotype 6 in patients hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis in Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2014–2016. Infection, Genetics and Evolution,53, 1–6.
Mullapudi, E., Nováček, J., Pálková, L., Kulich, P., Lindberg, A. M., van Kuppeveld, F. J., et al. (2016). Structure and genome release mechanism of the human cardiovirus Saffold virus 3. Journal of Virology,90(17), 7628–7639.
Naeem, A., Hosomi, T., Nishimura, Y., Alam, M. M., Oka, T., Zaidi, S. S. Z., et al. (2014). Genetic diversity of circulating Saffold viruses in Pakistan and Afghanistan. Journal of General Virology,95(9), 1945–1957.
Nielsen, A. C. Y., Böttiger, B., Banner, J., Hoffmann, T., & Nielsen, L. P. (2012). Serious invasive Saffold virus infections in children, 2009. Emerging Infectious Diseases,18(1), 7.
Nielsen, A. C. Y., Gyhrs, M. L., Nielsen, L. P., Pedersen, C., & Böttiger, B. (2013). Gastroenteritis and the novel picornaviruses aichi virus, cosavirus, saffold virus, and salivirus in young children. Journal of Clinical Virology,57(3), 239–242.
Ren, L., Gonzalez, R., Xiao, Y., Xu, X., Chen, L., Vernet, G., et al. (2009). Saffold cardiovirus in children with acute gastroenteritis, Beijing, China. Emerging Infectious Diseases,15(9), 1509.
Ren, L., Xiao, Y., Li, J., Chen, L., Zhang, J., Vernet, G., et al. (2013). Multiple genomic recombination events in the evolution of saffold cardiovirus. PLoS ONE,8(9), e74947.
Thongprachum, A., Fujimoto, T., Takanashi, S., Saito, H., Okitsu, S., Shimizu, H., et al. (2018). Detection of nineteen enteric viruses in raw sewage in Japan. Infection, Genetics and Evolution,63, 17–23.
Wang, C., Greer, R., Delwart, E., Sloots, T., & Mackay, I. (2012). A newly designed real-time RT-PCR for SAFV detects SAFV-2 and SAFV-3 in the respiratory tracts of ill children during 2011. Journal of Clinical Virology,55(2), 173–176.
Xu, Z.-Q., Cheng, W.-X., Qi, H.-M., Cui, S.-X., Jin, Y., & Duan, Z.-J. (2009). New Saffold cardiovirus in children. China. Emerging infectious diseases,15(6), 993.
Xu, Y., Victorio, C. B. L., Ng, Q., Tan, Y. J., & Chua, K. B. (2014). Saffold virus is able to productively infect primate and rodent cell lines and induces apoptosis in these cells. Emerging microbes & infections,3(1), 1–8.
Zoll, J., Hulshof, S. E., Lanke, K., Lunel, F. V., Melchers, W. J., Schoondermark-van de Ven, E., et al. (2009). Saffold virus, a human Theiler’s-like cardiovirus, is ubiquitous and causes infection early in life. PLoS Pathogens,5(5), e1000416.
Acknowledgements
This work was performed as part of Mona Aminipour’s MSc thesis in Microbiology at Karaj Islamic Azad University. We would like to thank the office of applied research of Karaj Islamic Azad University for their support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aminipour, M., Ghaderi, M. & Harzandi, N. First Occurrence of Saffold Virus in Sewage and River Water Samples in Karaj, Iran. Food Environ Virol 12, 75–80 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-019-09415-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-019-09415-y