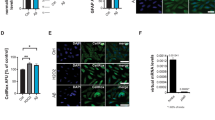
Abstract
Gracilins are diterpenes derivative, isolated from the marine sponge Spongionella gracilis. Natural gracilins and synthetic derivatives have shown antioxidant, immunosuppressive, and neuroprotective capacities related to the affinity for cyclophilins. The aim of this work was to study anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive pathways modulated by gracilin L and two synthetic analogues, compound 1 and 2, on a cellular model of inflammation. In this way, the murine BV2 microglia cell line was used. To carry out the experiments, microglia cells were pre-treated with compounds for 1 h and then stimulated with lipopolysaccharide for 24 h to determine reactive oxygen species production, mitochondrial membrane potential, the release of nitric oxide, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α and the expression of Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2, Nuclear Factor-κB, the inducible nitric oxide synthase, and the cyclophilin A. Finally, a co-culture of neuron SH-SY5Y and microglia BV2 cells was used to check the neuroprotective effect of these compounds. Cyclosporine A was used as a control of effect. The compounds were able to decrease inflammatory mediators, the expression of inflammatory target proteins as well as they activated anti-oxidative mechanism upon inflammatory conditions. For this reason, natural and synthetic gracilins could be interesting for developing anti-inflammatory drugs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasov ME, Alvariño R, Chaheine CM, Alonso E, Sánchez JA, Conner ML et al (2019) Simplified immunosuppressive and neuroprotective agents based on gracilin A. Nat Chem 11(4):342–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-019-0230-0
Alvariño R, Alonso E, Lacret R, Oves-Costales D, Genilloud O, Reyes F et al (2019) Caniferolide A, a macrolide from streptomyces caniferus, attenuates neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, amyloid-beta, and tau pathology in vitro. Mol Pharm 16(4):1456–1466. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b01090
Bi W, Zhu L, Wang C, Liang Y, Liu J, Shi Q et al (2011) Rifampicin inhibits microglial inflammation and improves neuron survival against inflammation. Brain Res 1395:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.04.019
Bozic I, Savic D, Laketa D, Bjelobaba I, Milenkovic I, Pekovic S et al (2015) Benfotiamine attenuates inflammatory response in LPS stimulated BV-2 microglia. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0118372. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118372
Brandt C, Liman P, Bendfeldt H, Mueller K, Reinke P, Radbruch A et al (2010) Whole blood flow cytometric measurement of NFATc1 and IL-2 expression to analyze cyclosporine A-mediated effects in T cells. Cytometry A 77(7):607–613. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20928
Burton JD (2005) The MTT assay to evaluate chemosensitivity. Methods Mol Med 110:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-869-2:069
Chrissobolis S, Miller AA, Drummond GR, Kemp-Harper BK, Sobey CG (2011) Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in cerebrovascular disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 16:1733–1745
Dawar FU, Xiong Y, Khattak MNK, Li J, Lin L, Mei J (2017) Potential role of cyclophilin A in regulating cytokine secretion. J Leukoc Biol 102(4):989–992. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.3RU0317-090RR
Faulkner DJ (2000) Marine pharmacology. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 77(2):135–145
Fleiss B, Chhor V, Rajudin N, Lebon S, Hagberg H, Gressens P et al (2015) The anti-inflammatory effects of the small molecule pifithrin-µ on BV2 microglia. Dev Neurosci 37(4–5):363–375. https://doi.org/10.1159/000370031
Glezer I, Simard AR, Rivest S (2007) Neuroprotective role of the innate immune system by microglia. Neuroscience 147(4):867–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.055
González-Scarano F, Baltuch G (1999) Microglia as mediators of inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:219–240. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.219
Guzik TJ, Korbut R, Adamek-Guzik T (2003) Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J Physiol Pharmacol 54(4):469–487
Haddad JJ (2009) The role of inflammatory cytokines and NF-kappaB/MAPK signaling pathways in the evolution of familial Mediterranean fever: current clinical perspectives and potential therapeutic approaches. Cell Immunol 260(1):6–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2009.08.003
Haefner B (2003) Drugs from the deep: marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov Today 8(12):536–544
Heal JW, Wells SA, Blindauer CA, Freedman RB, Römer RA (2015) Characterization of folding cores in the cyclophilin A-cyclosporin A complex. Biophys J 108(7):1739–1746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2015.02.017
Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J, Rao A (2003) Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes Dev 17(18):2205–2232. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1102703
Hsieh HL, Yang CM (2013) Role of redox signaling in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed Res Int 2013:484613. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/484613
Hunot S, Brugg B, Ricard D, Michel PP, Muriel MP, Ruberg M et al (1997) Nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB is increased in dopaminergic neurons of patients with parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(14):7531–7536
Javadov S, Jang S, Parodi-Rullán R, Khuchua Z, Kuznetsov AV (2017) Mitochondrial permeability transition in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion: whether cyclophilin D is a viable target for cardioprotection? Cell Mol Life Sci 74(15):2795–2813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2502-4
Kumari S, Roy S, Singh P, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2013) Cyclophilins: proteins in search of function. Plant Signal Behav 8(1):e22734. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.22734
Leirós M, Sánchez JA, Alonso E, Rateb ME, Houssen WE, Ebel R et al (2014) Spongionella secondary metabolites protect mitochondrial function in cortical neurons against oxidative stress. Mar Drugs 12(2):700–718. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12020700
Leirós M, Alonso E, Rateb ME, Houssen WE, Ebel R, Jaspars M et al (2015) Gracilins: Spongionella-derived promising compounds for Alzheimer disease. Neuropharmacology 93:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.02.015
Meda L, Cassatella MA, Szendrei GI, Otvos L, Baron P, Villalba M et al (1995) Activation of microglial cells by beta-amyloid protein and interferon-gamma. Nature 374(6523):647–650. https://doi.org/10.1038/374647a0
Morohashi K, Sahara H, Watashi K, Iwabata K, Sunoki T, Kuramochi K et al (2011) Cyclosporin A associated helicase-like protein facilitates the association of hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase with its cellular cyclophilin B. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18285. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018285
Nigro P, Pompilio G, Capogrossi MC (2013) Cyclophilin A: a key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis 4:e888. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.410
Nualsanit T, Rojanapanthu P, Gritsanapan W, Kwankitpraniti T, Min KW, Baek SJ (2011) Damnacanthal-induced anti-inflammation is associated with inhibition of NF-κB activity. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 10(6):455–463
Park HY, Park C, Hwang HJ, Kim BW, Kim GY, Kim CM et al (2014) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone attenuates the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells through the suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med 33(4):1027–1034. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.1652
Qin X, Li X, Liu C, Chen Z (2017) A novel mechanism of pre-transplant insulin resistance contributing to post-transplant complications: Cyclosporin A-induced O-GlcNAcylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 492(2):172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.08.033
Rateb ME, Houssen WE, Schumacher M, Harrison WT, Diederich M, Ebel R et al (2009) Bioactive diterpene derivatives from the marine sponge Spongionella sp. J Nat Prod 72(8):1471–1476. https://doi.org/10.1021/np900233c
Sánchez JA, Alfonso A, Leirós M, Alonso E, Rateb ME, Jaspars M et al (2015) Spongionella secondary metabolites regulate store operated calcium entry modulating mitochondrial functioning in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 37(2):779–792. https://doi.org/10.1159/000430395
Sánchez JA, Alfonso A, Leirós M, Alonso E, Rateb ME, Jaspars M et al (2016a) Identification of Spongionella compounds as cyclosporine A mimics. Pharmacol Res 107:407–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.029
Sánchez JA, Alfonso A, Rodriguez I, Alonso E, Cifuentes JM, Bermudez R et al (2016b) Spongionella secondary metabolites, promising modulators of immune response through CD147 receptor modulation. Front Immunol 7:452. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00452
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24(10):R453–R462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034
Schmidt HH, Walter U (1994) NO at work. Cell 78(6):919–925
Shah SA, Khan M, Jo MH, Jo MG, Amin FU, Kim MO (2017) Melatonin stimulates the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway counteracting lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress to rescue postnatal rat brain. CNS Neurosci Ther 23(1):33–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12588
Thomas TR, Kavlekar DP, LokaBharathi PA (2010) Marine drugs from sponge-microbe association—a review. Mar Drugs 8(4):1417–1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8041417
Velagapudi R, Aderogba M, Olajide OA (2014) Tiliroside, a dietary glycosidic flavonoid, inhibits TRAF-6/NF-κB/p38-mediated neuroinflammation in activated BV2 microglia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(12):3311–3319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.08.008
von Ungern-Sternberg SNI, Zernecke A, Seizer P (2018) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer EMMPRIN (CD147) in cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020507
White MG, Wang Y, Akay C, Lindl KA, Kolson DL, Jordan-Sciutto KL (2011) Parallel high throughput neuronal toxicity assays demonstrate uncoupling between loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and neuronal damage in a model of HIV-induced neurodegeneration. Neurosci Res 70(2):220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2011.01.013
Wu Y, Shang Y, Sun S, Liu R (2007) Antioxidant effect of erythropoietin on 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 564(1–3):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.020
Yang L, Zhu Q, Gong J, Xie M, Jiao T (2018) CyPA and Emmprin play a role in peri-implantitis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 20(2):102–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12549
Yano I (2008) Pharmacodynamic monitoring of calcineurin phosphatase activity in transplant patients treated with calcineurin inhibitors. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 23(3):150–157
Ziebell JM, Adelson PD, Lifshitz J (2015) Microglia: dismantling and rebuilding circuits after acute neurological injury. Metab Brain Dis 30(2):393–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9539-y
Acknowledgements
This work could not have been done without the invaluable collaboration of Dr. Daniel Romo group from the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Baylor University, TX (United States).
Funding
The research leading to these results has received funding from the following FEDER cofunded-Grants. From Consellería de Cultura, Educación e Ordenación Universitaria, Xunta de Galicia, 2017 GRC GI-1682 (ED431C 2017/01). From CDTI and Technological Funds, supported by Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad, AGL2016-78728-R (AEI/FEDER, UE), ISCIII/PI16/01830 and RTC-2016-5507-2, ITC-20161072. From European Union POCTEP 0161-Nanoeaters -1-E-1, Interreg AlertoxNet EAPA-317-2016, Interreg Agritox EAPA-998-2018, and H2020 778069-EMERTOX. Sandra Gegunde was supported by a fellowship from FIDIS, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Sandra Gegunde and Amparo Alfonso. Methodology and formal analysis: Sandra Gegunde and Rebeca Alvariño. Validation: Eva Alonso. Writing-Original Draft Preparation: Sandra Gegunde. Writing-Review and Editing: Amparo Alfonso and Luis Botana. Supervision: Amparo Alfonso. Funding’s acquisitions: Amparo Alfonso and Luis Botana.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
All authors have read and agreed with the submission of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gegunde, S., Alfonso, A., Alonso, E. et al. Gracilin-Derivatives as Lead Compounds for Anti-inflammatory Effects. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40, 603–615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00758-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00758-5