Abstract
Introduction
Treatment failures of standard regimens and new strains egression are due to the augmented drug resistance conundrum. These confounding factors now became the drug designers spotlight to implement therapeutics against Helicobacter pylori strains and to safeguard infected victims with devoid of adverse drug reactions. Thereby, to navigate the chemical space for medicine, paramount vital drug target opting considerations should be imperative. The study is therefore aimed to develop potent therapeutic variants against an insightful extrapolative, common target LpxC as a follow-up to previous studies.
Methods
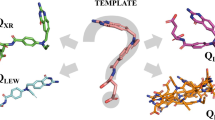
We explored the relationships between existing inhibitors and novel leads at the scaffold level in an appropriate conformational plasticity for lead-optimization campaign. Hierarchical-clustering and shape-based screening against an in-house library of > 21 million compounds resulted in panel of 11,000 compounds. Rigid-receptor docking through virtual screening cascade, quantum-polarized-ligand, induced-fit dockings, post-docking processes and system stability assessments were performed.
Results
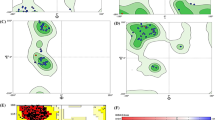
After docking experiments, an enrichment performance unveiled seven ranked actives better binding efficiencies with Zinc-binding potency than substrate and in-actives (decoy-set) with ROC (1.0) and area under accumulation curve (0.90) metrics. Physics-based membrane permeability accompanied ADME/T predictions and long-range dynamic simulations of 250 ns chemical time have depicted good passive diffusion with no toxicity of leads and sustained consistency of lead1-LpxC in the physiological milieu respectively.
Conclusions
In the study, as these static outcomes obtained from this approach competed with the substrate and existing ligands in binding affinity estimations as well as positively correlated from different aspects of predictions, which could facilitate promiscuous new chemical entities against H. pylori.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DOPE:
-
Discrete optimized protein energy
- OPLS_AA:
-
Optimized potential for liquid simulations for all atoms
- VSW:
-
Virtual screening workflow
- RRD:
-
Rigid receptor docking
- QPLD:
-
Quantum polarized ligand docking
- IFD:
-
Induced fit docking
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC)
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- MM/GBSA:
-
Molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area
- RMSD:
-
Root-mean-square deviation
- RMSF:
-
Root mean square fluctuation
- PE:
-
Potential energy
- LBFGS:
-
Limited memory Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno
References
Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410, 1990.
Barb, A. W., T. M. Leavy, L. I. Robins, Z. Guan, D. A. Six, P. Zhou, M. J. Hangauer, C. R. Bertozzi, and C. R. Raetz. Uridine-based inhibitors as new leads for antibiotics targeting Escherichia coli LpxC. Biochemistry. 48(14):3068–3077, 2009.
Buetow, L., A. Dawson, and W. N. Hunter. The nucleotide-binding site of Aquifex aeolicus LpxC. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62(Pt11):1082–1086, 2006.
Castrignanò, T., P. D. De Meo, D. Cozzetto, I. G. Talamo, and A. Tramontano. The PMDB protein model database. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Database issue):D306–D309, 2006.
Cho, A. E., V. Guallar, B. J. Berne, and R. Friesner. Importance of accurate charges in molecular docking: quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) approach. J Comput Chem. 26:915–931, 2005.
Cuny, G. D. A new class of UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxymyristol)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (LpxC) inhibitors for the treatment of Gram-negative infections: PCT application WO 2008027466. Expert Opin Ther Pat 19(6):893–899, 2009.
De Francesco, V., F. Giorgio, C. Hassan, G. Manes, L. Vannella, C. Panella, E. Ierardi, and A. Zullo. Worldwide H. pylori antibiotic resistance: a systematic review. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 19(4):409–414, 2010.
Del Giudice, G., P. Malfertheiner, and R. Rappuoli. Development of vaccines against Helicobacter pylori. Expert Rev Vaccines 8(8):1037–1049, 2009.
Delano, W. L. PYMOL. San Carlos: DeLano Scientific LLC, 2002.
Du, J., H. Sun, L. Xi, J. Li, Y. Yang, H. Liu, and X. Yao. Molecular modeling study of checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors by multiple docking strategies and Prime/ MMGBSA calculation. J Comput Chem. 13:2800–2809, 2011.
Eisenberg, D., R. Lüthy, and J. U. Bowie. VERIFY3D: assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Methods Enzymol. 277:396–404, 1997.
Farid, R., T. Day, R. A. Friesner, and R. A. Pearlstein. New insights about HERG blockade obtained from protein modeling potential energy mapping and docking studies. Bioorg Med Chem. 14(9):3160–3173, 2006.
Friesner, R. A., J. L. Banks, R. B. Murphy, T. A. Halgren, J. J. Klicic, D. T. Mainz, M. P. Repasky, E. H. Knoll, M. Shelley, J. K. Perry, D. E. Shaw, P. Francis, and P. S. Shenkin. Glide: a new approach for rapid accurate docking and scoring 1 Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem. 47(7):1739–1749, 2004.
Gerrits, M. M., A. H. van Vliet, E. J. Kuipers, and J. G. Kusters. Helicobacter pylori and antimicrobial resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Infect Dis 6(11):699–709, 2006.
Ghotaslou, R., H. E. Leylabadlo, and Y. M. Asl. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: a recent literature review. World J Methodol. 5(3):164–174, 2015.
Graham, D. Y. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: implications for therapy. Gastroenterology 115(5):1272–1277, 1998.
Huang, N., B. K. Shoichet, and J. J. Irwin. Benchmarking sets for molecular docking. J Med Chem. 49:6789–6801, 2006.
Jackman, J. E., C. R. Raetz, and C. A. Fierke. UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase of Escherichia coli is a zinc metalloenzyme. Biochemistry. 38(6):1902–1911, 1999.
Jorgensen, W. L., and E. M. Duffy. Prediction of drug solubility from structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 54:355–366, 2002.
Kalinin, D. V., and R. Holl. Insights into the zinc-dependent deacetylase LpxC: biochemical properties and inhibitor design. Curr Top Med Chem 16(21):2379–2430, 2016.
Kalinin, D. V., and R. Holl. LpxC inhibitors: a patent review (2010-2016). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 27(11):1227–1250, 2017.
Kelley, L. A., S. P. Gardner, and M. J. Sutcliffe. An automated approach for clustering an ensemble of NMR-derived protein structures into conformationally related subfamilies. Protein Eng. 9(11):1063–1065, 1996.
Laskowski, R. A., M. W. MacArthur, D. S. Moss, and J. M. Thornton. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Cryst 26:283–291, 1993.
Lee, C. J., X. Liang, Q. Wu, J. Najeeb, J. Zhao, R. Gopalaswamy, M. Titecat, F. Sebbane, N. Lemaitre, E. J. Toone, and P. Zhou. Drug design from the cryptic inhibitor envelope. Nat Commun. 7:10638, 2016.
Lipinski, C. A., and A. Hopkins. Navigating chemical space for biology and medicine. Nature. 432:855–861, 2004.
Lipinski, C. A., F. Lombardo, B. W. Dominy, and P. J. Feeney. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 46:3–26, 2001.
Liu, F., and S. Ma. Recent process in the inhibitors of UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxyacyl)-nacetylglucosamine deacetylase (LpxC) against gram-negative bacteria. Mini Rev Med Chem. 18(4):310–323, 2018.
Mochalkin, I., J. D. Knafels, and S. Lightle. Crystal structure of LpxC from Pseudomonas aeruginosa complexed with the potent BB-78485 inhibitor. Protein Sci. 17(3):450–457, 2008.
Morgan, D. R., J. Torres, R. Sexton, R. Herrero, E. Salazar-Martínez, E. R. Greenberg, L. E. Bravo, R. L. Dominguez, C. Ferreccio, E. C. Lazcano-Ponce, M. M. Meza-Montenegro, E. M. Peña, R. Peña, P. Correa, M. E. Martínez, W. D. Chey, M. Valdivieso, G. L. Anderson, G. E. Goodman, J. J. Crowley, and L. H. Baker. risk of recurrent Helicobacter pylori infection 1 year after initial eradication therapy in 7 Latin American communities. JAMA 309(6):578–586, 2013.
O’Connor, A., C. A. O’Morain, and A. C. Ford. Population screening and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14(4):230–240, 2017.
Park, K., N. K. Sung, and A. E. Cho. Importance of accurate charges in binding affinity calculations: a case of neuraminidase series. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 34(2):545–548, 2013.
Pasala, C., C. S. R. Chilamakuri, S. K. Katari, R. M. Nalamolu, A. R. Bitla, and A. Umamaheswari. An in silico study: Novel targets for potential drug and vaccine design against drug resistant H. pylori. Microb Pathog. 122:156–161, 2018.
Pradhan, D., V. Priyadarshini, M. Munikumar, S. Swargam, A. Umamaheswari, and A. Bitla. Para-(benzoyl)-phenylalanine as a potential inhibitor against LpxC of Leptospira spp: homology modeling docking and molecular dynamics study. J Biomol Struct Dyn 32(2):171–185, 2014.
Ramsay, R. R., and K. F. Tipton. Assessment of enzyme inhibition: a review with examples from the development of monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase inhibitory drugs. Molecules. 22(7):E1192, 2017.
Rezai, T., B. Yu, G. L. Millhauser, M. P. Jacobson, and R. S. Lokey. Testing the conformational hypothesis of passive membrane permeability using synthetic cyclic peptide diastereomers. J Am Chem Soc. 128(8):2510–2511, 2006.
Sherman, W., T. Day, M. P. Jacobson, R. A. Friesner, and R. Farid. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J Med Chem. 49(2):534–553, 2006.
Silver, L. L. Appropriate targets for antibacterial drugs cold spring. Harb Perspect Med 6(12):a030239, 2016.
Truchon, J. F., and C. I. Bayly. Evaluating virtual screening methods: good and bad metrics for the “early recognition” problem. J Chem Inf Model. 47(2):488–508, 2007.
Umamaheswari, A., D. Pradhan, and M. Hemanthkumar. Virtual screening for potential inhibitors of homology modeled Leptospira interrogans MurD ligase. J Chem Biol. 3:175–187, 2010.
Umamaheswari, A., D. Pradhan, and M. Hemanthkumar. Identification of potential Leptospiraphosphoheptose isomerase inhibitors through virtual high throughput screening. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 8:246–255, 2010.
Wallner, B., and A. Elofsson. Can correct protein models be identified? Protein Sci. 12(5):1073–1086, 2003.
Webb, B., and A. Sali. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 47:561–563, 2014.
Westbrook, J. D., C. Shao, Z. Feng, M. Zhuravleva, S. Velankar, and J. Young. The chemical component dictionary: complete descriptions of constituent molecules in experimentally determined 3D macromolecules in the Protein Data Bank. Bioinformatics. 31(8):1274–1278, 2015.
Wiederstein, M., and M. J. Sippl. ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:W407–W410, 2007.
Wueppenhorst, N., H. P. Stueger, M. Kist, and E. Glocker. Identification and molecular characterization of triple- and quadruple-resistant Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates in Germany. J Antimicrob Chemother. 63(4):648–653, 2009.
Zeng, D., J. Zhao, H. S. Chung, Z. Guan, C. R. Raetz, and P. Zhou. Mutants resistant to LpxC inhibitors by rebalancing cellular homeostasis. J Biol Chem 288(8):5475–5486, 2013.
Zullo, A., C. Hassan, L. Ridola, A. Repici, R. Manta, and A. Andriani. Gastric MALT lymphoma: old and new insights. Ann Gastroenterol 27(1):27–33, 2014.
Acknowledgments
PC acknowledges to ICMR, New Delhi, for supporting him with the Senior Research Fellowship (3/1/3/JRF-2014/HRD-8). Authors are highly thankful to DBT, Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India for providing Bioinformatics infrastructure facility to SVIMS Bioinformatics Centre (BT/BI/25/037/2012 (BIF-SVIMST)).
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
Neither human studies, nor animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Yiannis Kaznessis oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasala, C., Katari, S.K., Nalamolu, R.M. et al. Hierarchical-Clustering, Scaffold-Mining Exercises and Dynamics Simulations for Effectual Inhibitors Against Lipid-A Biosynthesis of Helicobacter pylori. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 12, 255–274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-019-00572-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-019-00572-5