Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate efficacy and complication rates of TACE with degradable starch microspheres (DSM-TACE) in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) with or without prior major liver resection (MLR).
Methods
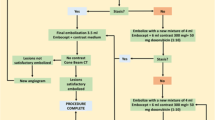
This is a retrospective single-center study on 21 patients (age 63 ± 15 years) with either unresectable ICC progressive under systemic chemotherapy or unresectable intrahepatic tumor recurrence after prior MLR. Patients were treated by multi-agent (cisplatin/doxorubicin/mitomycin C) DSM-TACE between August 2012 and July 2016, repeated 3 times at 4-week intervals. Imaging response was evaluated using RECIST 1.1. Overall survival (OS) and complication rates, stratified by history of MLR, were investigated.
Results
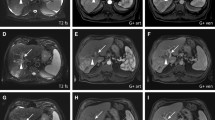
Patients underwent a total 64 DSM-TACE sessions. Two patients (without MLR) were lost to follow-up after one uneventful DSM-TACE session. One patient underwent living-donor-liver transplantation after one DSM-TACE-session yielding partial remission. Of the remaining 18 patients, imaging response according to RECIST 1.1 was: complete remission in 2/18 (11.1%); PR in 9/18 (50%), and stable disease in 7/18 (38.9%), yielding an objective response rate of 61.1% and a disease control rate of 100%. Median OS of patients with objective response was significantly longer (18.0 months) than that of survival of patients with stable disease (4.8 months) (p = 0.001). Median OS of patients with MLR (12.5 months) was similar to that of patients without MLR (13.2 months). Of 21 patients, 2 (9.5%) developed post-interventional hepatobiliary abscesses, and one of these patients died due to subsequent sepsis.
Conclusion
DSM-TACE is an effective treatment for unresectable and otherwise therapy-refractory intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, even in those patients with intrahepatic disease recurrence after prior MLR.
Level of Evidence
Level II, therapeutic study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaib Y, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24:115–25.
Anderson CD, Pinson CW, Berlin J, Chari RS. Diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Oncologist. 2004;9:43–57.
Park SY, Kim JH, Yoon HJ, Lee IS, Yoon HK, Kim KP. Transarterial chemoembolization versus supportive therapy in the palliative treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Radiol. 2011;66:322–8.
de Jong MC, Nathan H, Sotiropoulos GC, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: an international multi-institutional analysis of prognostic factors and lymph node assessment. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3140–5.
Bridgewater J, Galle PR, Khan SA, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2014;60:1268–89.
Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg. 2008;248:84–96.
Choi SB, Kim KS, Choi JY, et al. The prognosis and survival outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma following surgical resection: association of lymph node metastasis and lymph node dissection with survival. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:3048–56.
Yoh T, Hatano E, Seo S, et al. Long-term survival of recurrent intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the impact and selection of repeat surgery. World J Sur. 2018;42:1848–56.
Han K, Ko HK, Kim KW, Won HJ, Shin YM, Kim PN. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol JVIR. 2015;26:943–8.
Schnapauff D, Denecke T, Grieser C, et al. Computed tomography-guided interstitial HDR brachytherapy (CT-HDRBT) of the liver in patients with irresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2012;35:581–7.
Kiefer MV, Albert M, McNally M, et al. Chemoembolization of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with cisplatinum, doxorubicin, mitomycin C, ethiodol, and polyvinyl alcohol: a 2-center study. Cancer. 2011;117:1498–505.
Rafi S, Piduru SM, El-Rayes B, et al. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable standard-chemorefractory intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: survival, efficacy, and safety study. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2003;36:440–8.
Schernthaner RE, Lin M, Duran R, Chapiro J, Wang Z, Geschwind JF. Delayed-phase cone-beam CT improves detectability of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma during conventional transarterial chemoembolization. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 38:929–936.
Gusani NJ, Balaa FK, Steel JL, et al. Treatment of unresectable cholangiocarcinoma with gemcitabine-based transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE): a single-institution experience. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract. 2008;12:129–37.
Herber S, Otto G, Schneider J, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for inoperable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2007;30:1156–65.
Vogl TJ, Naguib NN, Nour-Eldin NE, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of patients with unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: results and prognostic factors governing treatment success. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:733–40.
Edeline J, Du FL, Rayar M, et al. Glass microspheres 90Y selective internal radiation therapy and chemotherapy as first-line treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2015;40:851–5.
Mosconi C, Gramenzi A, Ascanio S, et al. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable/recurrent intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a survival, efficacy and safety study. Br J Cancer. 2016;115:297–302.
Mouli S, Memon K, Baker T, et al. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: safety, response, and survival analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol JVIR. 2003;24:1227–344.
Saxena A, Bester L, Chua TC, Chu FC, Morris DL. Yttrium-90 radiotherapy for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a preliminary assessment of this novel treatment option. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:484–91.
Sato T, Tanaka T, Nishiofuku H, et al. Pharmacokinetics and histopathological findings of chemoembolization using cisplatin powder mixed with degradable starch microspheres in a rabbit liver tumor model. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2017;40:438–44.
Gruber-Rouh T, Naguib NN, Eichler K, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization of unresectable systemic chemotherapy-refractory liver metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results over a 10-year period. Int J Cancer. 2014;134:1225–311.
Nabil M, Gruber T, Yakoub D, Ackermann H, Zangos S, Vogl TJ. Repetitive transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) of liver metastases from renal cell carcinoma: local control and survival results. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:1456–63.
Schicho A, Pereira PL, Putzler M, et al. Degradable Starch Microspheres Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (DSM-TACE) in Intrahepatic Cholangiocellular Carcinoma (ICC): results from a National Multi-Center Study on Safety and Efficacy. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2017;23:796–800.
Vogl TJ, Naguib NN, Nour-Eldin NE, Eichler K, Zangos S, Gruber-Rouh T. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) with mitomycin C and gemcitabine for liver metastases in breast cancer. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:173–80.
Kirchhoff T, Zender L, Merkesdal S, et al. Initial experience from a combination of systemic and regional chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with nonresectable cholangiocellular carcinoma in the liver. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:1091–5.
Shitara K, Ikami I, Munakata M, Muto O, Sakata Y. Hepatic arterial infusion of mitomycin C with degradable starch microspheres for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Oncol. 2008;20:241–6.
Wu Y, Saiura A, Yamamoto J, et al. Locally advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma successfully resected after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with degradable starch microspheres: report of a case. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54:1345–7.
Halappa VG, Bonekamp S, Corona-Villalobos CP, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma treated with local-regional therapy: quantitative volumetric apparent diffusion coefficient maps for assessment of tumor response. Radiology. 2012;264:285–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goerg, F., Zimmermann, M., Bruners, P. et al. Chemoembolization with Degradable Starch Microspheres for Treatment of Patients with Primary or Recurrent Unresectable, Locally Advanced Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Pilot Study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 42, 1709–1717 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02344-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02344-0