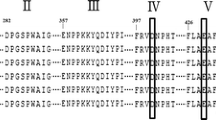
Abstract
α-Amylases are used in various biotechnological processes including the textile, paper, food, biofuels, detergents and pharmaceutical industries. In this study, a novel gene encoding α-amylase was cloned from marine bacterium Salinispora arenicola CNP193 and the protein was expressed in Escherichia coli. The α-amylase gene from S. arenicola CNP193 had a length of 1839 bp and encoded a α-amylase with an estimated molecular mass of 74 kDa. The optimum temperature and pH for the recombinant α-amylase was 50 °C and 7 respectively. Na+, K+ and Ca2+ increased the activity of the recombinant α-amylase whereas the enzyme was inhibited by Cu2+, Zn2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Fe3+ and Mn2+. Thin layer chromatography results confirmed that monosaccharide, disaccharide and maltotriose are the hydrolysis products. The results of our study suggest that this enzyme has considerable potential in industrial applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacGregor EA, Janecek S, Svensson B (2001) Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the alpha-amylase family of enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1546(1):1–20
Dou S, Chi N, Zhou X et al (2018) Molecular cloning, expression, and biochemical characterization of a novel cold-active α-amylase from Bacillus sp. dsh19-1. Extremophiles. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1034-7
Nikitkova AE, Haase EM, Scannapieco FA (2013) Taking the starch out of oral biofilm formation: molecular basis and functional significance of salivary alpha-amylase binding to oral streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(2):416–423
Xiao Z, Wu M, Grosse S et al (2014) Genome mining for new alpha-amylase and glucoamylase encoding sequences and high level expression of a glucoamylase from Talaromyces stipitatus for potential raw starch hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(1):73–86
Anamaria CS, María CR, Barbara AA et al (2019) Heterologous expression and biochemical characterization of a novel cold active α-amylase from the Antarctic bacteria Pseudoalteromonas sp. 2–3. Protein Expr Purif 155:78–85
Ahmed S, Mustafa G, Arshad M et al (2017) Fungal Biomass protein production from Trichoderma harzianum using rice polishing. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6232793
Ahmed S, Riaz S, Jamil A (2009) Molecular cloning of fungal xylanases: an overview. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84(1):19–35
Ziemert N, Lechner A, Wietz M et al (2014) Diversity and evolution of secondary metabolism in the marine actinomycete genus Salinispora. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E1130–E1139
Maldonado LA, Fenical W, Jensen PR et al (2005) Salinispora arenicola gen. nov., sp. nov. and Salinispora tropica sp. nov., obligate marine actinomycetes belonging to the family Micromonosporaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1759–1766
Mamo G, Hatti-Kaul R, Mattiasson KB (2006) A thermostable alkaline active endo-β-1-4-xylanase from Bacillus halodurans S7: purification and characterization. Enz Microb Technol 39(7):1492–1498
Xiao Z, Storms R, Tsang A (2006) Quantitative starch–iodine method for measuring alpha-amylase and glucoamylase activities. Anal Biochem 351(1):146–148
Kuriki T, Imanaka T (1999) The concept of the alpha-amylase family: structural similarity and common catalytic mechanism. J Biosci Bioeng 87(5):557–565
Zhao F, Song Q, Wang B et al (2019) Secretion of the recombination α-amylase in Escherichia coli and purification by the gram-positive enhancer matrix (GEM) particles. Int J Biol Macromol 123:91–96
Zafar M, Ahmed S, Khan MIM, Jamil A (2014) Recombinant expression and characterization of a novel endoglucanase from Bacillus subtilis in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Rep 41(5):3295–3302
Feller G, Lonhienne T, Deroanne C et al (1992) Purification, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of the thermolabile alpha-amylase from the Antarctic psychrotroph Alteromonas haloplanctis A23. J Biol Chem 267(8):5217–5221
Zhang JW, Zeng RY (2008) Purification and characterization of a cold adapted α-amylase produced by Nocardiopsis, sp. 7326 isolated from Prydz Bay, Antarctic. Mar Biotechnol 10(1):75–82
Lu M, Wang S, Fang Y et al (2010) Cloning, expression, purification, and characterization of cold-adapted α-amylase from Pseudoalteromonas arctica GS230. Protein J 29(8):591–597
Qin Y, Huang Z, Liu Z (2014) A novel cold-active and salt-tolerant α-amylase from marine bacterium Zunongwangia profunda: molecular cloning, heterologous expression and biochemical characterization. Extremophiles 18(2):271–281
Kim SM, Park H, Choi JI (2017) Cloning and characterization of cold-adapted α-amylase from Antarctic Arthrobacter agilis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 181(3):1048–1059
Li Z, Wu J, Zhang B et al (2015) AmyM, a novel maltohexaose-forming α-amylase from Corallococcus sp. strain EGB. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(6):1977–1987
Vieille C, Zeikus GJ (2001) Hyperthermophilic enzymes: sources, uses, and molecular mechanisms for thermostability. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65(1):1–43
Gupta R, Gigras P, Mohapatra H et al (2003) Microbial α-amylases: biotechnological perspective. Process Biochem 38:1599–1616
Ghorbel RE, Maktouf S, Massoud EB et al (2009) New thermostable amylase from Bacillus cohnii US147 with a broad pH applicability. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157(1):50–60
Chen J, Chen X, Dai J et al (2015) Cloning, enhanced expression and characterization of an α-amylase gene from a wild strain in B. subtilis WB800. Int J Biol Macromol 80:200–207
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31772016), Jiangsu Province Marine Science and Technology Innovation Project (HY2018-10), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, Six talent peaks project in Jiangsu Provincev (2016-SWYY-195), and Project “333” of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Ahmed, S. & Fang, Y. Cloning, Expression and Characterization of a Novel α-Amylase from Salinispora arenicola CNP193. Protein J 38, 716–722 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-019-09870-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-019-09870-3