Abstract
Objective: To determine the influence of weight loss on multiple cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors.
Design: Overweight women (n=12; mean 44.2% fat) and men (n=10; mean 30.7% fat) participated in an 8 week weight-loss program that included dietary, exercise, multi-vitamin/mineral supplementation, and behavior modification components. Measurement of total and regional body composition assessed using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), circumferences and blood sampling for total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triacylglycerols, homocysteine, insulin and leptin were performed before and after the weight loss intervention.
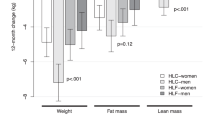
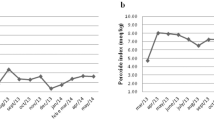
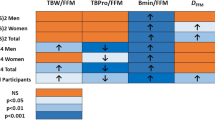
Results: Subjects increased their physical activity and decreased their energy intake, resulting in a mean decrease in body mass of −4.3±3.4 kg in women and −4.7±3.1 kg in men. Fat accounted for 88 and 58% of the decrease in body mass in men and women, respectively. Proportionally, men lost significantly more fat mass from the trunk region compared to women. Serum total and LDL cholesterol were significantly decreased in men (−11 and −14%, respectively) but not women (−3 and −3%, respectively) and there were no changes in HDL cholesterol and triacylglycerols. Serum leptin was significantly decreased (−36%) and highly correlated to fat mass (r=0.839). There were no changes in serum insulin and plasma homocysteine.
Conclusions: These data indicate that short-term weight loss resulting from reducing percentage energy from fat, increasing physical activity and vitamin/mineral supplements including folic acid has a favorable effect on regional body composition and total and LDL cholesterol with minimal effects on HDL cholesterol, triacylglycerols, homocysteine and insulin and the effects are greater in men compared to women. Supplementation with folic acid or emphasis on folic acid-rich foods may be an important component of a weight loss program to prevent increases in homocysteine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American College of Sports Medicine. 1995 ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription 5th edn, eds, LW Kenny, RH Humphrey & CX Bryant, eds pp 153–176 Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins
Anderson RA . 1998 Chromium, glucose tolerence and diabetes J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 17: 548–555
Anderson RE, Wadden TA, Barlett SJ, Vogt RA, Weinstock RS . 1995 Relation of weight loss to changes in serum lipids and lipoproteins in obese women Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 62: 350–357
Austin MA, Hokanson JE, Edwards KL . 1998 Hypertriglyceridemia as a cardiovascular risk factor Am. J. Cardiol. 81: 7B–12B
Ballor DL, Katch VH, Becque MD, Marks CR . 1988 Resistance weight training during caloric restriction enhances lean body weight maintenance Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 47: 19–25
Bjorntorp P . 1991 Metabolic implications of body fat distribution Diabetes Care 14: 1132–1143
Borson-Chazot F, Harthe C, Tebou F, Labrousse F, Gaume C, Guadagnino L, Claustrat B, Berthezene F, Moulin P . 1999 Occurrence of hyperhomocysteinemia 1 year after gastroplasty for severe obesity J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84: 541–545
Caso Marasco A, Vargas Ruiz R, Salas Villagomez A, Begona Infante C . 1996 Double-blind study of a multivitamin complex supplemented with ginseng extract Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 22: 323–329
Dattilo AM, Kris-Etherton PM . 1992 Effects of weight reduction on blood lipids and lipoproteins: a meta-analysis Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 56: 320–328
De Cree C, Malinow MR, van Kranenburg GP, Geurten PG, Longford NT, Keizer HA . 1999 Influence of exercise and menstrual cycle phase on plasma homocyst(e)ine levels in young women–a prospective study Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 9: 272–278
Dixon JB, Dixon ME, Brien PE . 2001 Elevated homocysteine levels with weight loss after Lap-Band® surgery: higher folate and vitamin B12 levels required to maintain homocysteine level Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 25: 219–227
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS . 1972 Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge Clin. Chem. 18: 499–502
Garrow JS, Summerball CD . 1995 Meta-analysis: effects of exercise, with or without dieting, on body composition of overweight subjects Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 49: 1–10
Gordon T, Kannel WB, Castelli WP, Dawber TR . 1981 Lipoproteins, cardiovascular disease, and death: the Framingham study Arch. Intern. Med. 141: 1128–1131
Gordon DJ, Probstfeld JL, Garrison RJ, Neaton JD, Castelli WP, Knoke JD, Jacobs DR Jr, Bangdiwala S, Tyroler HA . 1989 High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease: four prospective American studies Circulation 79: 8–15
Halle M, Berg A, Garwers U, Grathwohl D, Knisel W, Keul J . 1999 Concurrent reductions of serum leptin and lipids during weight loss in obese men with type II diabetes Am. J. Physiol. 277: E277–E282
Henning BF, Tepel M, Riezler R, Gillessen A, Doberauer C . 1998 Vitamin supplementation during weight reduction-favourable effect on homocysteine metabolism Res. Exp. Med. 198: 37–42
Jensen MD, Caruso M, Heiling VJ, Miles JM . 1989 Insulin regulation of lipolysis in nondiabetic and IDDM subjects Diabetes 38: 1595–1601
Kaats GR, Keith SC, Pullin D, Squires WG, Wise JA, Hesslink R Jr, Morin RJ . 1998 Safety and efficacy evaluation of a fitness club weight-loss program Adv. Natural Ther. 15: 1–17
Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, Clark KL, Gordon SE, Incledon T, Puhl SM, Triplett-McBride NT, McBride JM, Putukian M, Sebastianelli WJ . 1997 Physiological adaptations to a weight-loss dietary regimen and exercise programs in women J. Appl. Physiol. 83: 270–279
Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, Clark KL, Gordon SE, Puhl SM, Koziris LP, McBride JM, Triplett-McBride NT, Putukian M, Newton RU, Hakkinen K, Bush JA, Sebastianelli WJ . 1999 Influence of exercise training on physiological and performance changes with weight loss in men Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 31: 1320–1329
Kuczmarski R, Flegal KM, Campbell SM, Johnson CL . 1994 Increasing prevalence of overweight among US adults–The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1960 to 1991 JAMA 272: 205–211
Kumpulainen JT . 1992 Chromium content of foods and diets Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 32: 9–18
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R . 1988 Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Books
Manson JE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willet WC, Rosner B, Monson RR, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH . 1990 A prospective study of obesity and risk of coronary heart disease in women New Engl. J. Med. 322: 882–889
Marks BL, Ward A, Morris DH, Castellani J, Rippe JM . 1995 Fat-free mass is maintained in women following a moderate diet and exercise program Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 27: 1243–1251
Niskanen LK, Haffner S, Karhunen LJ, Turpeinen AK, Miettinen H, Uusitupa MI . 1997 Serum leptin in obesity is related to gender and body fat topography but does not predict successful weight loss Eur. J. Endocrinol. 137: 61–67
Noakes M, Clifton PM . 2000 Weight loss and plasma lipids Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 11: 65–70
Perry IJ, Refsum H, Morris RW, Ebrahim SB, Ueland PM, Shaper AG . 1995 Prospective study of serum total homocysteine concentration and risk of stroke in middle-aged British men Lancet 346: 1395–1398
Riddell LJ, Chisholm A, Williams S, Mann JI . 2000 Dietary strategies for lowering homocysteine concentrations Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71: 1448–1454
Ross R, Pedwell H, Rissanen J . 1995 Response of total and regional lean tissue and skeletal muscle to a program of energy restriction and resistance exercise Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 19: 781–787
Stampfer MJ, Malinow MR, Willett WC, Newcomer LM, Upson B, Ullman D, Tisher PV, Hennekens CH . 1992 A prospective study of plasma homocyst(e)ine and risk of myocardial infarction in US physicians J.A.M.A. 268: 877–881
Tallova J, Tomandl J, Bicikova M, Hill M . 1999 Changes of total homocysteine levels during the menstrual cycle Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 29: 1041–1044
Teirmaa T, Luukkaa V, Rouru J, Koulu M, Huupponen R . 1998 Correlation between circulating leptin and lutenizing hormone during the menstrual cycle in normal-weight women Eur. J. Endocrinol. 139: 190–194
Ubbink JB, Vermaak WJH, Bissbort S . 1991 Rapid high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for total homocysteine levels in human serum J. Chromatogr. 565: 441–446
Ubbink JB, Vermaak WJ, van der Merwe A, Becker PJ, Delport R, Potgieter HC . 1994 Vitamin requirements for the treatment of hyperhomocysteinemia in humans J. Nutr. 124: 1927–1933
Wald NJ, Watt HC, Law MR, Weir DG, McPartlin J, Scott JM . 1998 Homocysteine and ischemic heart disease: results of a prospective study with implications regarding prevention Arch. Intern. Med. 158: 862–867
Wood PD, Stefanick ML, Williams PT, Haskell WL . 1991 The effects of plasma lipoproteins of a prudent weight-reducing diet, with or without exercise, in overweight men and women New Engl. J. Med. 325: 461–466
Yamada M, Irahara M, Tezuka M, Murakami T, Shima K, Aono T . 2000 Serum leptin in the normal menstrual cycles and gonadotropin treatment cycles Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 49: 119–123
Yri-Jarvinen H, Westerbacka J . 2000 Vascular actions of insulin in obesity Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 24: (Suppl 2): S25–S28
Acknowledgements
We thank a dedicated group of subjects for making this study possible. This study was sponsored by Natural Alternatives International, San Marcos, CA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volek, J., Gómez, A., Love, D. et al. Effects of an 8-week weight-loss program on cardiovascular disease risk factors and regional body composition. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 585–592 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601362
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601362
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Points-based physical activity: a novel approach to facilitate changes in body composition in inactive women with overweight and obesity
BMC Public Health (2018)
-
Improvement in insulin resistance and favourable changes in plasma inflammatory adipokines after weight loss associated with two months’ consumption of a combination of bioactive food ingredients in overweight subjects
Endocrine (2013)
-
Body Fat Content Determination in Premenopausal, Overweight, and Obese Young Women Using DXA and FT-NIR
Obesity (2011)
-
Changes in weight loss, body composition and cardiovascular disease risk after altering macronutrient distributions during a regular exercise program in obese women
Nutrition Journal (2010)
-
Effects of multivitamin and mineral supplementation on adiposity, energy expenditure and lipid profiles in obese Chinese women
International Journal of Obesity (2010)