Abstract
The efficacy and safety of intracavernosal alprostadil was evaluated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with type I or type II diabetes mellitus. This was an open-label, flexible dose-escalating study involving 336 men (77% of whom were Asian/Oriental) enrolled by 15 centres in Australia, Canada and seven countries in Asia. The effective alprostadil dose, ie the dose producing penile rigidity adequate for intercourse and lasting up to 60 min, was established by titration at the clinic prior to entry into the 6 month self-treatment home phase. All men were fully trained in the self-injection technique before entry into the home phase. Efficacy and safety were assessed using patient and partner diaries and by interview at clinic visits during the titration phase and after 1, 3 and 6 months of treatment.
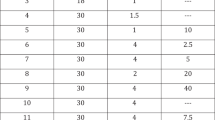
An effective home dose was established by titration for 94% of the 336 men (median dose 20 μg, range 2.5–60 μg). Of 278 (83%) men who entered the home phase, 277 men (247 with type II diabetes and 30 with type I diabetes) had evaluable data for alprostadil dosage and clinical response. During the home phase, a satisfactory erectile response was achieved after 99% of injections, and the median alprostadil dose remained unchanged. The initial home dose and clinical response were similar in type I and type II diabetic men. Treatment was generally well tolerated with a low incidence of penile pain (24%) In conclusion, intracavernosal alprostadil was effective and well tolerated in type I and type II diabetic men with erectile dysfunction of mixed aetiology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCulloch DK et al.. The prevalence of diabetic impotence. Diabetologia 1980 18, 279–283.
Dunsmuir WD, Holmes SAV. . The aetiology and management of erectile, ejaculatory and fertility problems in men with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Medicine 1996 13, 700–708.
Linet OI, Ogrinc FG. . Efficacy and safety of intracavernosal alprostadil in men with erectile dysfunction. New Engl J Med 1996 334, 873–877.
The European Alprostadil Study Group. . The long-term safety of alprostadil (prostaglandin-E1) in patients with erectile dysfunction. Br J Urol 1998 82, 538–543.
Ravnik-Oblak M et al. Intracavernous injection of prostaglandin E1 in impotent diabetic men. Int J Impot Res 1990 2, 143–150.
Losada F et al. Prostaglandin E1 en el tratamiento de la impotencia erectil del diabetico. Endocrinologia 1993 40, 186–188.
Bancroft J, Gutierrez P. . Erectile dysfunction in men with and without diabetes mellitus: a comparative study. Diabetic Medicine 1996 13, 84–89.
Choi HK et al.. A dose–response study of alprostadil sterile powder (S. Po.) (Caverject) for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in Korean and Indonesian men. Int J Impot Res 1997 9, 47–51.
Metro MJ, Broderick GA. . Diabetes and vascular impotence: does insulin dependence increase the relative severity? Int J Impot Res 1999 11, 87–89.
Wang CJ et al. Penile blood flow in diabetic impotence. Urol Int 1993 50, 209–212.
Linet OI, Alprostadil Study Group. . Long-term safety of Caverject™ (alprostadil S. Po., PGE1) in erectile dysfunction (ED). In: Meuleman E, Lycklama a Nijeholt G, Vanderschureren D, eds. Proceedings of the 3rd world meeting on impotence research, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–28 August 1998. Monduzzi Editore: Bologna 1998 251–254.
Lehmann K, Casella R, Blochlinger A, Gasser TC. . Reasons for discontinuing intracavernous injection therapy with prostaglandin E1 (alprostadil). Urology 1999 53, 397–400.
Gupta R, Kirschen J, Barrow RC II, Eid JF. . Predictors of success and risk factors for attrition in the use of intracavernous injections. J Urol 1997 157, 1681–1686.
Mulhall JP et al. The causes of patient dropout from penile self-injection therapy for impotence. J Urol 1999 162, 1291–1294.
Alprostadil Data Sheet, Pharmacia & Upjohn.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from Pharmacia & Upjohn AB, Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heaton, J., Lording, D., Liu, SN. et al. Intracavernosal alprostadil is effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic men. Int J Impot Res 13, 317–321 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900760
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900760
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Erectile dysfunction
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2016)
-
Konservative Therapie der erektilen Dysfunktion
Der Urologe (2015)
-
A comprehensive review of urologic complications in patients with diabetes
SpringerPlus (2014)
-
How to Treat Erectile Dysfunction in Men with Diabetes: from Pathophysiology to Treatment
Current Diabetes Reports (2014)
-
Twenty years of IJIR
International Journal of Impotence Research (2008)