Abstract
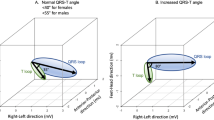
Ventricular repolarisation abnormalities are important in arrhythmia provocation. The dispersion of repolarisation duration is not the only aspect of repolarisation heterogeneity. Spatial vectorcardiographic descriptors constitute a novel approach to quantify ventricular repolarisation. To test the ability of vectorcardiographic descriptors to discriminate between hypertensives with high or low blood pressure (BP), 110 treated hypertensives (mean age 63.6 ± 12.1 years) were classified in the high (systolic BP ⩾160 mm Hg or diastolic BP ⩾95 mm Hg) (n = 67), or the low (systolic BP < 160 mm hg and diastolic bp <95 mm hg) (n = 43) BP group. The maximum QT, JT, and T peak–T end intervals and the QT, JT, and T peak–T end dispersion were calculated from a digitally recorded 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). X, Y, and Z leads were reconstructed from the 12-lead ECG. The amplitude of the maximum spatial T vector (spatial T amplitude), the angle between the maximum spatial QRS and T vectors (spatial QRS-T angle) and the frontal plane QRS-T angle were calculated. The spatial QRS-T angle was higher in patients with high compared to those with low BP (P = 0.025). All conventional ECG markers of the dispersion of ventricular repolarisation duration failed to demonstrate significant differences between hypertensives with high or low BP. In conclusion, the spatial QRS-T angle was significantly increased in those treated hypertensive patients who showed repeatedly high BP values. Hence, we may suggest that the angle between the directions of ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation is a sensitive marker of the repolarisation alterations in systemic hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dilaveris, P., Gialafos, E., Pantazis, A. et al. The spatial QRS-T angle as a marker of ventricular repolarisation in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 15, 63–70 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001129
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001129
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Improved evaluation of left ventricular hypertrophy using the spatial QRS-T angle by electrocardiography
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Electrocardiographic differences in patients with true and pseudo-resistant hypertension
Journal of Human Hypertension (2022)
-
Electrocardiographic Detection of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy; Adding Body Mass Index and Spatial QRS-T Angle: A Cross-Sectional Study
Cardiology and Therapy (2019)
-
Clinical Application of the QRS-T Angle for the Prediction of Ventricular Arrhythmias in Patients with the Fontan Palliation
Pediatric Cardiology (2017)
-
Factors associated with abnormal T-wave axis and increased QRS-T angle in type 2 diabetes
Acta Diabetologica (2013)