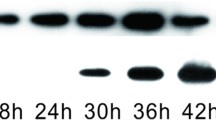
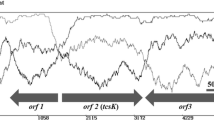
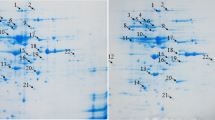
Abstract
Two-component systems (TCSs) are highly conserved in prokaryotes, endowing cells with multiple physiological functions to respond to changes in the ambient environment. The signaling pathway of a typical TCS consists of a sensory histidine kinase and a response regulator. The TCSs of Kocuria rhizophila, which is usually used as a target strain for various antibiotics and other adverse factors, have captured our interest due to their potential roles in bacterial adaptation for survival. Herein, the distribution and putative biological functions of the TCSs of K. rhizophila DC2201 were analyzed by using bioinformatics, and a preliminary TCS regulatory network was constructed. A representative and important TCS (i.e., HK8700–RR8701 system), which is homologous to the LiaS–LiaR system previously discovered in Bacillus subtilis, was identified and characterized through yeast two-hybrid screening and phosphorylation assays. Detailed information of TCSs is expected to offer novel insights into the adaptation mechanism of K. rhizophila and thus boost its application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nixon BT, Ronson CW, Ausubel FM (1986) Two-component regulatory systems responsive to environmental stimuli share strongly conserved domains with the nitrogen assimilation regulatory genes ntrB and ntrC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83(20):7850–7854
Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN (2000) Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 69(1):183–215
Galperin MY (2006) Structural classification of bacterial response regulators: diversity of output domains and domain combinations. J Bacteriol 188(12):4169–4182
Wolanin PM, Thomason PA, Stock JB (2002) Histidine protein kinases: key signal transducers outside the animal kingdom. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-10-reviews3013
Ulrich LE, Zhulin IB (2009) The MiST2 database: a comprehensive genomics resource on microbial signal transduction. Nucleic Acids Res 38(Database issue):D401–D407
Kovács G, Burghardt J, Pradella S, Schumann P, Stackebrandt E, Màrialigeti K (1999) Kocuria palustris sp. nov. and Kocuria rhizophila sp. nov., isolated from the rhizoplane of the narrow-leaved cattail (Typha angustifolia). Int J Syst Bacteriol 49(1):167–173
Takarada H, Sekine M, Kosugi H, Matsuo Y, Fujisawa T, Omata S, Kishi E, Shimizu A, Tsukatani N, Tanikawa S (2008) Complete genome sequence of the soil actinomycete Kocuria rhizophila. J Bacteriol 190(12):4139–4146
Pękala A, Paździor E, Antychowicz J, Bernad A, Głowacka H, Więcek B, Niemczuk W (2017) Kocuria rhizophila and Micrococcus luteus as emerging opportunist pathogens in brown trout (Salmo trutta Linnaeus, 1758) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792). Aquaculture 486:285–289
Moissenet D, Becker K, Mérens A, Ferroni A, Dubern B, Vuthien H (2012) Persistent bloodstream infection with Kocuria rhizophila related to a damaged central catheter. J Clin Microbiol 50(4):1495–1498
Becker K, Rutsch F, Uekötter A, Kipp F, König J, Marquardt T, Peters G, Eiff CV (2008) Kocuria rhizophila adds to the emerging spectrum of micrococcal species involved in human infections. J Clin Microbiol 46(10):3537–3539
Alby K, Glaser LJ, Edelstein PH (2015) Kocuria rhizophila misidentified as Corynebacterium jeikeium and other errors caused by the Vitek MS system call for maintained microbiological competence in the era of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol 53(1):360–361
Tang JS, Gillevet PM (2003) Reclassification of ATCC 9341 from Micrococcus luteus to Kocuria rhizophila. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(Pt 4):995–997
Tiwari S, Jamal SB, Hassan SS, Carvalho PVSD, Almedia S, Barh D, Ghosh P, Silva A, Castro T, Azevedo VAC (2017) Two-component signal transduction systems of pathogenic bacteria as targets for antimicrobial therapy: an overview. Front Microbiol 8:1878
Mark DB, Christof F, Roy M, Tjakko A, Siezen RJ (2006) Comparative analysis of two-component signal transduction systems of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus anthracis. Microbiology 152(10):3035–3048
Hutchings MI, Hoskisson P, Chandra G, Buttner MJ (2004) Sensing and responding to diverse extracellular signals? Analysis of the sensor kinases and response regulators of Streptomyces coelicolor a3(2). Microbiology 150(9):2795–2806
Wible BA, Yang Q, Kuryshev YA, Accili EA, Brown AM (1998) Cloning and expression of a novel K+ channel regulatory protein, KChAP. J Biol Chem 273(19):11745–11751
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH, Willems AR, Woods RA (1995) Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast 11(4):355–360
Wang W, Shu D, Chen L, Jiang W, Lu Y (2009) Cross-talk between an orphan response regulator and a noncognate histidine kinase in Streptomyces coelicolor. FEMS Microbiol Lett 294(2):150–156
Schmelling NM, Lehmann R, Chaudhury P, Beck C, Albers SV, Axmann IM, Wiegard A (2017) Minimal tool set for a prokaryotic circadian clock. BMC Evol Biol 17(1):169
Cutting JA, Roth TF (1973) Staining of phosphoprotein on acrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 54(2):386–394
Hyyryläinen HL, Sarvas M, Kontinen VP (2005) Transcriptome analysis of the secretion stress response of Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67(3):389–396
Mascher T, Zimmer SL, Smith TA, Helmann JD (2004) Antibiotic-inducible promoter regulated by the cell envelope stress-sensing two-component system LiaRS of Bacillus subtilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(8):2888–2896
Hutchings MI, Hong HJ, Leibovitz E, Sutcliffe IC, Buttner MJ (2006) The σE cell envelope stress response of Streptomyces coelicolor is influenced by a novel lipoprotein, CseA. J Bacteriol 188(20):7222–7229
Song L, Sudhakar P, Wang W, Conrads G, Brock A, Sun J, Wagner-Döbler I, Zeng AP (2012) A genome-wide study of two-component signal transduction systems in eight newly sequenced mutans streptococci strains. BMC Genom 13(1):128
Fields S, Song O (1989) A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature 340(6230):245–246
Niu X, Guiltinan MJ (1994) DNA binding specificity of the wheat bZIP protein EmBP-1. Nucleic Acids Res 22(23):4969–4978
Crowe J, Masone BS, Ribbe J (1995) One-step purification of recombinant proteins with the 6xHis tag and Ni-NTA resin. Mol Biotechnol 4(3):247–258
Kim SY, Chung HJ, Thomas TL (1997) Isolation of a novel class of bZIP transcription factors that interact with ABA-responsive and embryo-specification elements in the Dc3 promoter using a modified yeast one-hybrid system. Plant J 11(6):1237–1251
Tang WH, Zhang JL, Wang ZY, Hong MM (2000) The cause of deviation made in determining the molecular weight of His-tag fusion proteins by SDS-PAGE. J Plant Physiol 26(1):64–68
Wuichet K, Cantwell BJ, Zhulin IB (2010) Evolution and phyletic distribution of two-component signal transduction systems. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(2):219–225
Urano H, Umezawa Y, Yamamoto K, Ishihama A, Ogasawara H (2015) Cooperative regulation of the common target genes between hydrogen peroxide-response YedVW and copper-response CusSR in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 161:729–738
Selvamani V, Maruthamuthu MK, Arulsamy K, Eom GT, Hong SH (2017) Construction of methanol sensing Escherichia coli by the introduction of novel chimeric MxcQZ/OmpR two-component system from Methylobacterium organophilum XX. Korean J Chem Eng 34(6):1–6
Watanabe T, Hashimoto Y, Yamamoto K, Hirao K, Ishihama A, Hino M, Utsumi R (2003) Isolation and characterization of inhibitors of the essential histidine kinase, YycG in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. J Antibiot 56(12):1045–1052
Bisicchia P, Noone D, Lioliou E, Howell A, Quigley S, Jensen T, Jarmer H, Devine KM (2007) The essential YycFG two-component system controls cell wall metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 65(1):180–200
Raghavan V, Groisman EA (2010) Orphan and hybrid two-component system proteins in health and disease. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(2):226–231
Ninfa AJ (2010) Use of two-component signal transduction systems in the construction of synthetic genetic networks. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(2):240–245
Nguyen HT, Wolff KA, Cartabuke RH, Ogwang S, Nguyen L (2010) A lipoprotein modulates activity of the MtrAB two-component system to provide intrinsic multidrug resistance, cytokinetic control and cell wall homeostasis in Mycobacterium. Mol Microbiol 76(2):348–364
Möker N, Brocker M, Schaffer S, Krämer R, Morbach S, Bott M (2010) Deletion of the genes encoding the MtrA-MtrB two-component system of Corynebacterium glutamicum has a strong influence on cell morphology, antibiotics susceptibility and expression of genes involved in osmoprotection. Mol Microbiol 54(2):420–438
Parish T, Smith DA, Roberts G, Betts J, Stoker NG (2003) The SenX3-RegX3 two-component regulatory system of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is required for virulence. Microbiology 149(6):1423–1435
Glover R, Kriakov J, Garforth SJ, Betts J, Stoker NG (2007) The two-component regulatory system SenX3-RegX3 regulates phosphate-dependent gene expression in Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Bacteriol 189(15):5495–5503
Ingmer H, Miller CA, Cohen SN (1998) Destabilized inheritance of pSC101 and other Escherichia coli plasmids by DpiA, a novel two-component system regulator. Mol Microbiol 29(1):49–59
Cybulski LE, Albanesi D, Mansilla MC, Altabe S, Aguilar PS, De MD (2002) Mechanism of membrane fluidity optimization: isothermal control of the Bacillus subtilis acyl-lipid desaturase. Mol Microbiol 45(5):1379–1388
Jordan S, Junker A, Helmann JD, Mascher T (2006) Regulation of LiaRS-dependent gene expression in B acillus subtilis: identification of inhibitor proteins, regulator binding sites, and target genes of a conserved cell envelope stress-sensing two-component system. J Bacteriol 188(14):5153–5166
Ito G, Katsemonova K, Tonelli F, Lis P, Baptista MAS, Shpiro N, Duddy G, Wilson S, Ho WL, Ho SL (2016) Phos-tag analysis of Rab10 phosphorylation by LRRK2: a powerful assay for assessing kinase function and inhibitors. Biochem J 473(17):2671–2685
Danismazoglu M, Nalcacioglu R, Muratoglu H, Demirbag Z (2018) The protein-protein interactions between Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus (AMEV) protein kinases (PKs) and all viral proteins. Virus Res 248:31–38
Lee GF, Burrows GG, Lebert MR, Dutton DP, Hazelbauer GL (1994) Deducing the organization of a transmembrane domain by disulfide cross-linking. The bacterial chemoreceptor Trg. J Biol Chem 269(47):29920–29927
Borkovich KA, Simon MI (1990) The dynamics of protein phosphorylation in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell 63(6):1339–1348
Acknowledgements
We deeply appreciate Liangguo Xu for assistance with strains and plasmids. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31360018), Key R&D Program Projects of Jiangxi Province, China (Grant No. 20161BBF60076), and the Innovation Program for Graduates of Jiangxi Normal University (Grant No. YJS2018081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL designed the study. BC and TZ performed the experiments. YH and HN contributed to the results analysis and discussion. BC wrote the manuscript, and ZL and LZ revised the manuscript. All the authors approved the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Zou, T., Zou, L. et al. Identification and Characterization of the Two-Component System HK8700–RR8701 of Kocuria rhizophila DC2201. Protein J 38, 683–692 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-019-09853-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-019-09853-4