Abstract
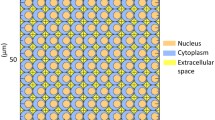
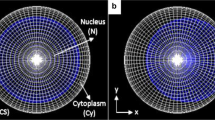
Knowledge of microdosimetric quantities of certain radionuclides is important in radio immune cancer therapies. Specific energy distribution of radionuclides, which are bound to the cell, is the microdosimetric quantity essential in the process of radionuclide selection for patient tumour treatment. The aim of this paper is to establish an applicable method to determine microdosimetric quantities for various radionuclides. The established method is based on knowledge of microdosimetric quantities of monoenergetic electrons. In this paper these quantities are determined for the single-cell model for a range of electron energies up to \(2.3\,{\text{MeV}}\), using the Monte Carlo transport code PENELOPE. The results show that using monoenergetic specific energies, reconstruction of the specific energy of beta-emitting radionuclides can be successfully done with very high accuracy. Microdosimetric quantities share information about the physical processes involved and give insight about energy depositions, which is of use in the procedure of radionuclide selection for a given type of therapy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asuero AG, Sayago A, Gonzales AG (2006) The correlation coefficient: an overview. Crit Rev Anal Chem 36:41–59
Bloch WE, Kim EH (1994) Calculations of electron single event distributions for use in internal beta microdosimetry. Radiat Prot Dosim 52:77–80
Bousis C, Emfietzoglou D, Hadjidoukas P, Nikjoo H, Pathak A (2008) Electron ionization cross-section calculations for liquid water at high impact energies. Nucl Inst Met Phys Res B 266:1185–1192
Bousis C, Emfietzoglou D, Hadjidoukas P, Nikjoo H (2010) Monte Carlo single-cell dosimetry of Auger-electron emitting radionuclides. Phys Med Biol 55:2555–2572
Bousis C, Emfietzoglou D, Nikjoo H (2012) Monte Carlo single cell dosimetry of I-131, I-125 and I-123 for targeted radioimmunotherapy of B-cell lymphoma. Int J Radiat Biol 88:908–915
Brahme A (2011) Accurate description of the cell survival and biological effectat low and high doses and LET’s. J Radiat Res 52:389–407
Cowan G (1998) Statistical data analysis. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Dash A, Knapp FF, Pillai MR (2013) Targeted radionuclide therapy—an overview. Curr Radiopharm 6(3):152–180
Dingfelder M, Hantke D, Inokuti M, Paretzke HG (1998) Electron inelastic-scattering cross sections in liquid water. Radiat Phys Chem 53:1–18
El-Ghossain MO (2017) Calculations of stopping power and range of electrons interaction with different material and human body parts. Int J Sci Tech Res 6:114–118
Fernández-Varea JM, González-Muñoz G, Galassi ME, Wiklund K, Lind BK, Ahnesjö A, Tilly N (2012) Limitations (and merits) of PENELOPE as a track-structure code. Int J Radiat Biol 88:66–70
Friesen C, Lubatschofski A, Kotzerke J, Buchmann I, Reske SN, Debatin KM (2003) Beta-irradiation used for systemic radioimmunotherapy induces apoptosis and activates apoptosis pathways in leukaemia cells. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:1251–1261
Humm JL, Roeske JC, Fisher DR, Chen GT (1993) Microdosimetric concepts in radioimmunotherapy. Med Phys 20:535–541
ICRU Report 36 (1983) Microdosimetry. Washington, DC
Itikawa Y, Mason N (2005) Cross sections for electron collisions with water. Mol J Phys Chem Ref Data 34:1–22
Kassis AI (2008) Therapeutic, radionuclides: biophysical and radiobiologic principles. Semin Nucl Med 38:358–366
Kellerer AM (1985) Fundamentals of microdosimetry. In: Kase RK, Bjarngard EB, Attix FH (eds) The dosimetry of ionizing radiation, vol 1. Academic Press, New York
Li WB, Hofmann W, Friedland W (2018) Microdosimetry and nanodosimetry for internal emitters. Radiat Meas 115:29–42
Markovic VM, Stevanovic N, Nikezic D, DzF Pucic, Urosevic V (2014) Specific energy distribution within cytoplasm and nucleoplasm of a typical mammalian cell due to various beta radionuclides. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:1723–1730
Milenic DE, Brechbiel MW (2004) Targeting of radioisotopes for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther 3:361–370
Milenic DE, Brady ED, Brechbiel MW (2004) Antibody-targeted radiation cancer therapy. Nature Rev Drug Discov 3:488–498
Rossi H, Zaider M (1996) Microdosimetry and its applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Salvat F, Fernández-Varea JM, Sempau J (2006) PENELOPE—2006 a code system for Monte Carlo simulation of electron and photon transport. OECD Nuclear Energy Agency, Issy-les-Moulineaux
Stewart RD, Wilson WE, McDonald JC, Strom DJ (2002) Microdosimetric properties of ionizing electrons in water: a test of the PENELOPE code system. Phys Med Biol 47:79–88
Syme AM, Kirkby C, Riauka TA, Fallone BG, McQuarrie SA (2004) Monte Carlo investigation of single cell beta dosimetry for intraperitoneal radionuclide therapy. Phys Med Biol 49:1959–1972
Torres-Garcia E, Garnica-Garza HM, Ferro-Flores G (2006) Monte Carlo microdosimetry 188Re- and 131I-labelled anti-CD2. Phys Med Biol 51:N349–N356
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia through the project 171021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markovic, V.M., Stevanovic, N. & Nikezic, D. Monte Carlo investigation of electron specific energy distribution in a single cell model. Radiat Environ Biophys 59, 161–171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-019-00815-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-019-00815-z