Abstract
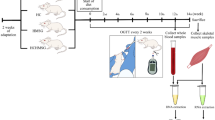
Diabetic prevalence is at speedy increase globally. Previous studies stated that other than genetics, factors such as environment, lifestyle, and paternal-maternal condition play critical roles in diabetes through DNA methylation in specific areas of the genome. The purpose of this study is to investigate the methylation pattern of the PDK4 promoter in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice until the 12th week of the observation. The methylation pattern in the blood samples was analyzed periodically, while the pattern in the muscle sample was only analyzed at the end of the experiment using the blood of the sacrificed animals. Three methylated CpG site 1, CpG site 6, and CpG site 7 were analyzed and quantified based on the band density using bisulfite treatment and methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The hyperglycemia period was developed at the 9th week of experiment. However, there was a significant increase of methylation, specifically on CpG site 6 started from week 6 to week 12. This peculiar methylation on CpG site 6 of PDK4 promoter in the blood sample before the hyperglycemic period might serve as a potential biomarker for early detection of diabetes in the patients. No significant difference was found between the methylation level of streptozotocin (STZ)–treated mice and of the control group in the muscle sample.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho, N. H., Shaw, J. E., Karuranga, S., Huang, Y., da Rocha Fernandes, J. D., Ohlrogge, A. W., & Malanda, B. (2018). IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 138, 271–281.
Das, S. K., & Elbein, S. C. (2006). The genetic basis of type 2 diabetes. Cellscience., 2(4), 100–131.
Kolb, H., & Martin, S. (2017). Environmental/lifestyle factors in the pathogenesis and prevention of type 2 diabetes. BMC Medicine, 15(1), 131.
Reichetzeder, C., Dwi Putra, S. E., Li, J., & Hocher, B. (2016). Developmental origins of disease - crisis precipitates change.Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry,39(3), 919–938.
Mamrut, S., Harony, H., Sood, R., Shahar-Gold, H., Gainer, H., Shi, Y.-J., et al. (2013). DNA methylation of specific CpG sites in the promoter region regulates the transcription of the mouse oxytocin receptor. PLoS One, 8(2), e56869.
Chen, X., Liu, L., Mims, J., Punska, E. C., Williams, K. E., Zhao, W., et al. (2015). Analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression in radiation-resistant head and neck tumors. Epigenetics., 10(6), 545–561.
Shao, W.-J., Tao, L.-Y., Gao, C., Xie, J.-Y., & Zhao, R.-Q. (2008). Alterations in methylation and expression levels of imprinted genes H19 and Igf2 in the fetuses of diabetic mice. Comparative Medicine, 58(4), 341–346.
Pang, J., Xi, C., Huang, X., Cui, J., Gong, H., & Zhang, T. (2016). Effects of excess energy intake on glucose and lipid metabolism in C57BL/6 mice. PLoS One, 11(1), e0146675.
Galgani, J. E., Moro, C., & Ravussin, E. (2008). Metabolic flexibility and insulin resistance. The American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism, 295(5), E1009–E1017.
Tareen, S. H., Kutmon, M., Adriaens, M. E., Mariman, E. C., de Kok, T. M., Arts, I. C., & Evelo, C. T. (2018). Exploring the cellular network of metabolic flexibility in the adipose tissue. Genes & Nutrition, 13(1), 17.
Zhang, S., Hulver, M. W., McMillan, R. P., Cline, M. A., & Gilbert, E. R. (2014). The pivotal role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases in metabolic flexibility. Nutrition and Metabolism, 11, 10.
Jeoung, N. H., & Harris, R. A. (2010). Role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 in regulation of blood glucose levels. Korean Diabetes Journal, 34(5), 274–283.
de la Rocha, C., Pérez-Mojica, J. E., León, S. Z.-D., Cervantes-Paz, B., Tristán-Flores, F. E., Rodríguez-Ríos, D., et al. (2016). Associations between whole peripheral blood fatty acids and DNA methylation in humans. Scientific Reports, 6:25867.
Kirchner, H., Nylen, C., Laber, S., Barrès, R., Yan, J., Krook, A., et al. (2014). Altered promoter methylation of PDK4, IL1 B, IL6, and TNF after Roux-en Y gastric bypass. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, (4), 671–678.
Kulkarni, S. S., Salehzadeh, F., Fritz, T., Zierath, J. R., Krook, A., & Osler, M. E. (2012). Mitochondrial regulators of fatty acid metabolism reflect metabolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism., 61(2), 175–185.
Wang, K., Tang, Z., Zheng, Z., Cao, P., Shui, W., Li, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Protective effects of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide against hyperglycemia and liver injury in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic BALB/c mice. Food & Function, 7(12), 4889–4897.
Andrikopoulos, S., Blair, A. R., Deluca, N., Fam, B. C., & Proietto, J. (2008). Evaluating the glucose tolerance test in mice. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism, 295(6), E1323–E1332.
Yang, A. S., Estécio, M. R., Doshi, K., Kondo, Y., Tajara, E. H., & Issa, J. P. J. (2004). A simple method for estimating global DNA methylation using bisulfite PCR of repetitive DNA elements. Nucleic Acids Research, 32(3), e38–e38.
Chaudhry, Z. Z., Morris, D. L., Moss, D. R., Sims, E. K., Chiong, Y., Kono, T., & Evans-Molina, C. (2013). Streptozotocin is equally diabetogenic whether administered to fed or fasted mice. Laboratory Animals, 47(4), 257–265.
Furman, B. L. (2015). Streptozotocin-induced diabetic models in mice and rats. Current Protocols in Pharmacology, 70(1), 5–47.
Vatandoust, N., Rami, F., Salehi, A. R., Khosravi, S., Dashti, G., Eslami, G., Momenzadeh, S., & Salehi, R. (2018). Novel high-fat diet formulation and streptozotocin treatment for induction of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in rats. Advanced Biomedical Research, 7, 107.
Barrière, D. A., Noll, C., Roussy, G., Lizotte, F., Kessai, A., Kirby, K., Belleville, K., Beaudet, N., Longpré, J. M., Carpentier, A. C., Geraldes, P., & Sarret, P. (2018). Combination of high-fat/high-fructose diet and low-dose streptozotocin to model long-term type-2 diabetes complications. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 424.
Dayeh, T., Tuomi, T., Almgren, P., Perfilyev, A., Jansson, P. A., de Mello, V. D., Pihlajamaki, J., Vaag, A., Groop, L., Nilsson, E., & Ling, C. (2016). DNA methylation of loci within ABCG1 and PHOSPHO1 in blood DNA is associated with future type 2 diabetes risk. Epigenetics., 11(7), 482–488.
van Otterdijk, S. D., Binder, A. M., vel Szic, K. S., Schwald, J., & Michels, K. B. (2017). DNA methylation of candidate genes in peripheral blood from patients with type 2 diabetes or the metabolic syndrome. PLoS One, 12(7), e0180955.
Willmer, T., Johnson, R., Louw, J., & Pheiffer, C. (2018). Blood-Based DNA Methylation biomarkers for type 2 diabetes: potential for clinical applications. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 9, 744..
Chokkalingam, K., Jewell, K., Norton, L., Littlewood, J., Van Loon, L. J. C., Mansell, P., MacDonald, I. A., & Tsintzas, K. (2007). High-fat/low-carbohydrate diet reduces insulin-stimulated carbohydrate oxidation but stimulates nonoxidative glucose disposal in humans: an important role for skeletal muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 92(1), 284–292.
Zhou, Z., Sun, B., Li, X., & Zhu, C. (2018). DNA methylation landscapes in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition & Metabolism (London), 15, 47.
Kurdyukov, S., & Bullock, M. (2016). DNA methylation analysis: choosing the right method. Biology., 5(1), 3.
Drąg, J., Goździalska, A., Knapik-Czajka, M., Gawędzka, A., Gawlik, K., & Jaśkiewicz, J. (2017). Effect of high carbohydrate diet on elongase and desaturase activity and accompanying gene expression in rat’s liver. Genes & Nutrition, 12(1), 2.
Rogowski, M. P., Flowers, M. T., Stamatikos, A. D., Ntambi, J. M., & Paton, C. M. (2013). SCD1 activity in muscle increases triglyceride PUFA content, exercise capacity, and PPARδ expression in mice. Journal of Lipid Research, 54(10), 2636–2646.
Funding
This research was supported by PT Nutrifood Indonesia according to research grant no. SP/LG NFI-17/171 and Indonesia Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education (021/SP-Lit/LPPM-01/DRPM/Multi/FTB/III/2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experimental procedures have passed the guidelines of institutional ethical committee, University of Surabaya, Indonesia (No. 012/KE/III/2018).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Putra, S.E.D., Singajaya, S., Thesman, F. et al. Aberrant PDK4 Promoter Methylation Preceding Hyperglycemia in a Mouse Model. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 190, 1023–1034 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03143-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03143-6