Abstract
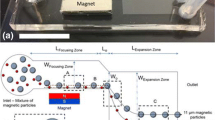
A new sorting scheme based on ferrofluid hydrodynamics (ferrohydrodynamics) was used to separate mixtures of particles and live cells simultaneously. Two species of cells, including Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, as well as fluorescent polystyrene microparticles were studied for their sorting throughput and efficiency. Ferrofluids are stable magnetic nanoparticles suspensions. Under external magnetic field gradients, magnetic buoyancy forces exerted on particles and cells lead to size-dependent deflections from their laminar flow paths and result in spatial separation. We report the design, modeling, fabrication and characterization of the sorting device. This scheme is simple, low-cost and label-free compared to other existing techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams AA, Okagbare PI, Feng J, Hupert ML, Patterson D, Gottert J, McCarley RL, Nikitopoulos D, Murphy MC, Soper SA (2008) Highly efficient circulating tumor cell isolation from whole blood and label-free enumeration using polymer-based microfluidics with an integrated conductivity sensor. J Am Chem Soc 130(27):8633–8641. doi:10.1021/Ja8015022
Beyor N, Seo TS, Liu P, Mathies RA (2008) Immunomagnetic bead-based cell concentration microdevice for dilute pathogen detection. Biomed Microdevices 10(6):909–917. doi:10.1007/S10544-008-9206-3
Bonner WA, Sweet RG, Hulett HR, Herzenbe La (1972) Fluorescence activated cell sorting. Rev Sci Instrum 43(3):404–409
Brody JP, Yager P, Goldstein RE, Austin RH (1996) Biotechnology at low Reynolds numbers. Biophys J 71(6):3430–3441
Davis JA, Inglis DW, Morton KJ, Lawrence DA, Huang LR, Chou SY, Sturm JC, Austin RH (2006) Deterministic hydrodynamics: taking blood apart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(40):14779–14784. doi:10.1073/Pnas.0605967103
Dharmasiri U, Witek MA, Adams AA, Osiri JK, Hupert ML, Bianchi TS, Roelke DL, Soper SA (2010) Enrichment and detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from water samples using an antibody modified microfluidic chip. Anal Chem 82(7):2844–2849. doi:10.1021/Ac100323k
Di Carlo D (2009) Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 9(21):3038–3046. doi:10.1039/B912547g
Frable WJ (2007) Error reduction and risk management in cytopathology. Semin Diagn Pathol 24(2):77–88
Furlani EP, Sahoo Y (2006) Analytical model for the magnetic field and force in a magnetophoretic microsystem. J Phys D Appl Phys 39(9):1724–1732. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/39/9/003
Gijs MAM, Lacharme F, Lehmann U (2010) Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem Rev 110(3):1518–1563
Gossett DR, Weaver WM, Mach AJ, Hur SC, Tse HTK, Lee W, Amini H, Di Carlo D (2010) Label-free cell separation and sorting in microfluidic systems. Anal Bioanal Chem 397(8):3249–3267
Hafeli U, Schutt W, Teller J, Zborowski M (1997) Scientific and clinical applications of magnetic carriers. Springer, New York
Hatch A, Kamholz AE, Holman G, Yager P, Bohringer KF (2001) A ferrofluidic magnetic micropump. J Microelectromechanical Syst 10(2):215–221
Hoshino K, Huang YY, Lane N, Huebschman M, Uhr JW, Frenkel EP, Zhang XJ (2011) Microchip-based immunomagnetic detection of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 11(20):3449–3457. doi:10.1039/C1lc20270g
Huang LR, Cox EC, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2004) Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304(5673):987–990. doi:10.1126/science.1094567
Jorgensen P, Nishikawa JL, Breitkreutz BJ, Tyers M (2002) Systematic identification of pathways that couple cell growth and division in yeast. Science 297(5580):395–400. doi:10.1126/Science.1070850
Kaya T, Koser H (2009) Characterization of hydrodynamic surface Interactions of Escherichia coli cell bodies in shear flow. Phys Rev Lett 103(13):138103. doi:10.1103/Physrevlett.103.138103
Kose AR, Koser H (2012) Ferrofluid mediated nanocytometry. Lab Chip 12(1):190–196. doi:10.1039/C1lc20864k
Kose AR, Fischer B, Mao L, Koser H (2009) Label-free cellular manipulation and sorting via biocompatible ferrofluids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(51):21478–21483. doi:10.1073/Pnas.0912138106
Krebs Melissa D, Erb Randall M, Yellen Benjamin B, Samanta B, Bajaj A, Rotello Vincent M, Alsberg E (2009) Formation of ordered cellular structures in suspension via label-free negative magnetophoresis. Nano Lett 9(5):1812–1817
Laurell T, Petersson F, Nilsson A (2007) Chip integrated strategies for acoustic separation and manipulation of cells and particles. Chem Soc Rev 36(3):492–506. doi:10.1039/B601326k
Lee H, Purdon AM, Chu V, Westervelt RM (2004) Controlled assembly of magnetic nanoparticles from magnetotactic bacteria using microelectromagnets arrays. Nano Lett 4(5):995–998. doi:10.1021/Nl049562x
Lenshof A, Laurell T (2010) Continuous separation of cells and particles in microfluidic systems. Chem Soc Rev 39(3):1203–1217. doi:10.1039/B915999c
Liang LT, Zhu JJ, Xuan XC (2011) Three-dimensional diamagnetic particle deflection in ferrofluid microchannel flows. Biomicrofluidics 5(3):034110. doi:0.1063/1.3618737
Liu RH, Yang JN, Lenigk R, Bonanno J, Grodzinski P (2004) Self-contained, fully integrated biochip for sample preparation, polymerase chain reaction amplification, and DNA microarray detection. Anal Chem 76(7):1824–1831. doi:10.1021/Ac0353029
Liu CX, Stakenborg T, Peeters S, Lagae L (2009) Cell manipulation with magnetic particles toward microfluidic cytometry. J Appl Phys 105(10):102014. doi:10.1063/1.3116091
Love LJ, Jansen JF, McKnight TE, Roh Y, Phelps TJ (2004) A magnetocaloric pump for microfluidic applications. IEEE T Nanobiosci 3(2):101–110. doi:10.1109/Tnb.2004.828265
Mao LD, Koser H (2006) Towards ferrofluidics for mu-TAS and lab on-a-chip applications. Nanotechnology 17(4):S34–S47. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/17/4/007
Mao L, Koser H (2007) Overcoming the diffusion barrier: ultra-fast micro-scale mixing via ferrofluids. In: 14th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Lyon, France, pp 1829–1832
Mao LD, Elborai S, He XW, Zahn M, Koser H (2011) Direct observation of closed-loop ferrohydrodynamic pumping under traveling magnetic fields. Phys Rev B 84(10):104431. doi:10.1103/Physrevb.84.104431
Mihajlovic G, Aledealat K, Xiong P, Von Molnar S, Field M, Sullivan GJ (2007) Magnetic characterization of a single superparamagnetic bead by phase-sensitive micro-Hall magnetometry. Appl Phys Lett 91(17):172518. doi:10.1063/1.2802732
Miller MM, Sheehan PE, Edelstein RL, Tamanaha CR, Zhong L, Bounnak S, Whitman LJ, Colton RJ (2001) A DNA array sensor utilizing magnetic microbeads and magnetoelectronic detection. J Magn Magn Mater 225(1–2):138–144
Miltenyi S, Muller W, Weichel W, Radbruch A (1990) High-gradient magnetic cell-separation with MACS. Cytometry 11(2):231–238
Mirica KA, Shevkoplyas SS, Phillips ST, Gupta M, Whitesides GM (2009) Measuring densities of solids and liquids using magnetic levitation: fundamentals. J Am Chem Soc 131(29):10049–10058. doi:10.1021/Ja900920s
Moriarty AT, Clayton AC, Zaleski S, Henry MR, Schwartz MR, Eversole GM, Tench WD, Fatheree LA, Souers RJ, Wilbur DC (2009) Unsatisfactory reporting rates: 2006 practices of participants in the college of American pathologists interlaboratory comparison program in gynecologic cytology. Arch Pathol Lab Med 133(12):1912–1916. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-133.12.1912
Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith MR, Kwak EL, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky A, Ryan P, Balis UJ, Tompkins RG, Haber DA, Toner M (2007) Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 450(7173):1235–1239. doi:10.1038/nature06385
Nguyen NT (2012) Micro-magnetofluidics: interactions between magnetism and fluid flow on the microscale. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):1–16. doi:10.1007/S10404-011-0903-5
Nguyen NT, Ng KM, Huang XY (2006) Manipulation of ferrofluid droplets using planar coils. Appl Phys Lett 89(5):052509. doi:10.1063/1.2335403
Odenbach S (ed) (2002) Ferrofluids: magnetically controllable fluids and their applications. Springer, London
Pamme N (2006) Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 6(1):24–38. doi:10.1039/B513005k
Pamme N (2007) Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7(12):1644–1659. doi:10.1039/B712784g
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 13:R167–R181
Peyman SA, Iwan EY, Margarson O, Iles A, Pamme N (2009) Diamagnetic repulsion—a versatile tool for label-free particle handling in microfluidic devices. J Chromatogr A 1216(52):9055–9062. doi:10.1016/J.Chroma.2009.06.039
Rife JC, Miller MM, Sheehan PE, Tamanaha CR, Tondra M, Whitman LJ (2003) Design and performance of GMR sensors for the detection of magnetic microbeads in biosensors. Sens Actuators A Phys 107(3):209–218. doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(03)00380-7
Rodriguez-Villarreal AI, Tarn MD, Madden LA, Lutz JB, Greenman J, Samitier J, Pamme N (2011) Flow focussing of particles and cells based on their intrinsic properties using a simple diamagnetic repulsion setup. Lab Chip 11(7):1240–1248. doi:10.1039/C0lc00464b
Rosensweig RE (1985) Ferrohydrodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Shen F, Hwang H, Hahn YK, Park J-K (2012) Label-free cell separation using a tunable magnetophoretic repulsion force. Anal Chem. doi:10.1021/ac201505j
Shevkoplyas SS, Siegel AC, Westervelt RM, Prentiss MG, Whitesides GM (2007) The force acting on a superparamagnetic bead due to an applied magnetic field. Lab Chip 7(10):1294–1302. doi:10.1039/B705045c
Shi JJ, Huang H, Stratton Z, Huang YP, Huang TJ (2009) Continuous particle separation in a microfluidic channel via standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip 9(23):3354–3359. doi:10.1039/B915113c
Sun Y, Kwok YC, Nguyen NT (2007) A circular ferrofluid driven microchip for rapid polymerase chain reaction. Lab Chip 7(8):1012–1017. doi:10.1039/B700575j
Sun Y, Nguyen NT, Kwok YC (2008) High-throughput polymerase chain reaction in parallel circular loops using magnetic actuation. Anal Chem 80(15):6127–6130. doi:10.1021/Ac800787g
Toner M, Irimia D (2005) Blood-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7:77–103. doi:10.1146/Annurev.Bioeng.7.011205.135108
Tsutsui H, Ho CM (2009) Cell separation by non-inertial force fields in microfluidic systems. Mech Res Commun 36(1):92–103. doi:10.1016/J.Mechrescom.2008.08.006
Voldman J (2006) Electrical forces for microscale cell manipulation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:425–454. doi:10.1146/Annurev.Bioeng.8.061505.095739
Wang ZC, Zhe JA (2011) Recent advances in particle and droplet manipulation for lab-on-a-chip devices based on surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 11(7):1280–1285. doi:10.1039/C0lc00527d
Winkleman A, Perez-Castillejos R, Gudiksen KL, Phillips ST, Prentiss M, Whitesides GM (2007) Density-based diamagnetic separation: devices for detecting binding events and for collecting unlabeled diamagnetic particles in paramagnetic solutions. Anal Chem 79(17):6542–6550. doi:10.1021/Ac070500b
Yamada M, Nakashima M, Seki M (2004) Pinched flow fractionation: continuous size separation of particles utilizing a laminar flow profile in a pinched microchannel. Anal Chem 76(18):5465–5471. doi:10.1021/Ac049863r
Yellen BB, Hovorka O, Friedman G (2005) Arranging matter by magnetic nanoparticle assemblers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(25):8860–8864. doi:10.1073/Pnas.0500409102
Yu M, Stott S, Toner M, Maheswaran S, Haber DA (2011) Circulating tumor cells: approaches to isolation and characterization. J Cell Biol 192(3):373–382. doi:10.1083/jcb.201010021
Yung CW, Fiering J, Mueller AJ, Ingber DE (2009) Micromagnetic–microfluidic blood cleansing device. Lab Chip 9(9):1171–1177. doi:10.1039/B816986a
Zborowski M, Ostera GR, Moore LR, Milliron S, Chalmers JJ, Schechter AN (2003) Red blood cell magnetophoresis. Biophys J 84(4):2638–2645
Zhang K, Liang QL, Ai XN, Hu P, Wang YM, Luo GA (2011a) Comprehensive two-dimensional manipulations of picoliter microfluidic droplets sampled from nanoliter samples. Anal Chem 83(20):8029–8034. doi:10.1021/Ac2017458
Zhang K, Liang QL, Ai XN, Hu P, Wang YM, Luo GA (2011b) On-demand microfluidic droplet manipulation using hydrophobic ferrofluid as a continuous-phase. Lab Chip 11(7):1271–1275. doi:10.1039/C0lc00484g
Zhu TT, Marrero F, Mao LD (2010) Continuous separation of non-magnetic particles inside ferrofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(4–5):1003–1009
Zhu TT, Cheng R, Mao LD (2011a) Focusing microparticles in a microfluidic channel with ferrofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 11(6):695–701. doi:10.1007/S10404-011-0835-0
Zhu TT, Lichlyter DJ, Haidekker MA, Mao LD (2011b) Analytical model of microfluidic transport of non-magnetic particles in ferrofluids under the influence of a permanent magnet. Microfluid Nanofluid 10(6):1233–1245. doi:10.1007/S10404-010-0754-5
Zhu JJ, Liang LT, Xuan XC (2012) On-chip manipulation of nonmagnetic particles in paramagnetic solutions using embedded permanent magnets. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):65–73. doi:10.1007/S10404-011-0849-7
Acknowledgments
This work is in part supported by the National Science Foundation, American Society for Microbiology/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Postdoctoral Research Fellowship, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and University of Georgia Seed Award Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Cheng, R., Lee, S.A. et al. Continuous-flow ferrohydrodynamic sorting of particles and cells in microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 13, 645–654 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-1004-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-1004-9