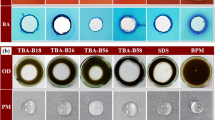
Abstract
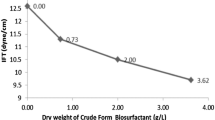
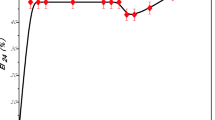
Pseudomonas strains isolated from oil contaminated soils were screened for biosurfactant production. Three out of eleven Pseudomonas isolates were selected for their high emulsifying activity (E24 value on n-hexadecane ~ 78%). These isolates (E39, E311 and E313) were identified as members of the P. putida group using phenotypical methods and a molecular approach. To identify the chemical nature of produced biosurfactants, thin layer chromatography and MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry analysis were carried out and revealed lipopeptides belonging to the syringafactin family. The activity of the produced biosurfactants was stable over a pH range of 6–12, at high salinity (10%) and after heating at 80 °C. Tests in contaminated sand micro-bioreactors showed that the three strains were able to degrade diesel. These results suggest the potential of these syringafactin producing strains for application in hydrocarbon bioremediation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Aboulwafa MM, Hassouna NAH (2009) Characterization of rhamnolipid produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate Bs20. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157:329–345
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Lépine F, Déziel E (2010) Rhamnolipids: diversity of structures, microbial origins and roles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1323–1336
Anyanwu CU, Obi SKC, Okolo BN (2011) Lipopeptide biosurfactant production by Serratia marcescens NSK-1 strain isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. J Appl Sci Res 7:79–87
Aparna A, Srinikethan G, Smitha H (2012) Production and characterization of biosurfactant produced by a novel Pseudomonas sp. 2B. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 95:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.01.043
Arima K, Kakinuma A, Tamura G (1968) Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 31:488–494
Bak F, Bonnichsen L, Jørgensen NO, Nicolaisen MH, Nybroe O (2015) The biosurfactant viscosin transiently stimulates n-hexadecane mineralization by a bacterial consortium. Appl Microbiol Biot 99:1475–1483
Bento FM, De Oliveira Camargo FA, Okeke BC, Frankenberger WT (2005) Diversity of biosurfactant producing microorganisms isolated from soils contaminated with diesel oil. Microbiol Res 160:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2004.08.005
Berti AD, Greve NJ, Christensen QH, Thomas MG (2007) Identification of a biosynthetic gene cluster and the six associated lipopeptides involved in swarming motility of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. J Bacteriol 189:6312–6323. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00725-07
Bodour AA, Miller-Maier RM (1998) Application of a modified drop-collapse technique for surfactant quantitation and screening of biosurfactant-producing microorganisms. J Microbiol Meth 32:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(98)00031-1
Bodour AA, Drees KP, Maier RM (2003) Distribution of biosurfactant-producing bacteria in undisturbed and contaminated arid southwestern soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3280–3287. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.6.3280-3287.2003
Cameotra SS, Makkar RS (2004) Recent applications of biosurfactants as biological and immunological molecules. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:262–266
Cameotra SS, Makkar RS (2010) Biosurfactant-enhanced bioremediation of hydrophobic pollutants. Pure Appl Chem 82:97–116
Campos JM, Montenegro Stamford TL, Sarubbo LA, de Luna JM, Rufino RD, Banat IM (2013) Microbial biosurfactants as additives for food industries. Biotechnol Prog 29:1097–1108. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.1796
Chakraborty T, Chakraborty I, Ghosh S (2011) The methods of determination of critical micellar concentrations of the amphiphilic systems in aqueous medium. Arab J Chem 4:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.06.045
Cooper DG, Goldenberg BG (1987) Surface-active agents from two Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:224–229.
Cooper DG, Zajic JE (1980) Surface-active compounds from microorganisms. Adv Appl Microbiol 26:229–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2164(08)70335-6
D’aes J, De Maeyer K, Pauwelyn E, Höfte M (2010) Biosurfactants in plant–Pseudomonas interactions and their importance to biocontrol. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:359–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-2229.2009.00104.x
Das K, Mukherjee AK (2007) Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a petroleum-oil contaminated soil from North-East India. Bioresour Technol 98:1339–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.05.032
de Sousa T, Bhosle S (2012) Isolation and characterization of a lipopeptide bioemulsifier produced by Pseudomonas nitroreducens TSB.MJ10 isolated from a mangrove ecosystem. Bioresour Technol 123:256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.07.056
Desai JD, Banat IM (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6701(97)84559-6
El Arbi A, Rochex A, Chataigné G, Béchet M, Lecouturier D, Arnauld S, Gharsallah N, Jacques P (2016) The Tunisian oasis ecosystem is a source of antagonistic Bacillus spp. producing diverse antifungal lipopeptides. Res Microbiol 167:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2015.09.003
Fechtner J, Koza A, Sterpaio PD, Hapca SM, Spiers AJ (2011) Surfactants expressed by soil pseudomonads alter local soil–water distribution, suggesting a hydrological role for these compounds. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01141.x
Gao J, Xie G, Peng F, Xie Z (2015) Pseudomonas donghuensis sp. nov., exhibiting high-yields of siderophore. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0306-1
Gomila M, Pena A, Mulet M, Lalucat J, García-Valdés E (2015) Phylogenomics and systematics in Pseudomonas. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00214
Janek T, Łukaszewicz M, Rezanka T, Krasowska A (2010) Isolation and characterization of two new lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens BD5 isolated from water from the Arctic Archipelago of Svalbard. Bioresour Technol 101:6118–6123
Janek T, Lukaszewicz M, Krasowska A (2013) Identification and characterization of biosurfactants produced by the Arctic bacterium Pseudomonas putida BD2. Colloid Surf B 110:379–386
Karanth NGK, Deo PG, Veenanadig NK (1999) Microbial production of biosurfactants and their importance. Curr Sci 77:116–126
Khopade A, Biao R, Liu X, Mahadik K, Zhang L, Kokare C (2012) Production and stability studies of the biosurfactant isolated from marine Nocardiopsis sp. B4. Desalination 285:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.10.002
Kruijt M, Tran H, Raaijmakers JM (2009) Functional, genetic and chemical characterization of biosurfactants produced by plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas putida 267. J Appl Microbiol 107:546–556
Kuiper I, Lagendijk EL, Pickford R, Derrick JP, Lamers GE, Thomas-Oates JE, Lugtenberg BJJ, Bloemberg GV (2004) Characterization of two Pseudomonas putida lipopeptide biosurfactants, putisolvin I and II, which inhibit biofilm formation and break down existing biofilms. Mol Microbiol 51:97–113
Lang S (2002) Biological amphiphiles (microbial biosurfactants). Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 7:12–20
Lang S, Wullbrandt D (1999) Rhamnose lipids-biosynthesis, microbial production and application potential. Appl Microbiol Biot 51:22–32
Marchant R, Banat IM (2012) Microbial biosurfactants: challenges and opportunities for future exploitation. Trends Biotechnol 30:558–565
Martinez-Toledo A, Rios-Leal E, Vázquez-Duhalt R, González-Chávez MDC, Esparza-Garcia JF, Rodriguez-Vazquez R (2006) Role of phenanthrene in rhamnolipid production by P. putida in different media. Environ Technol 27:137–142
Merino E, Barrientos A, Rodríguez J, Naharro G, Luengo JM, Olivera ER (2013) Isolation of cholesterol-and deoxycholate-degrading bacteria from soil samples: evidence of a common pathway. Appl Microbiol Biot 97:891–904
Mnif I, Sahnoun R, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2017) Application of bacterial biosurfactants for enhanced removal and biodegradation of diesel oil in soil using a newly isolated consortium. Process Saf Environ Prot 109:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.02.002
Mohammed IU, Deeni Y, Hapca SM, McLaughlin K, Spiers AJ (2015) Predicting the minimum liquid surface tension activity of pseudomonads expressing biosurfactants. Lett Appl Microbiol 60:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12331
Morikawa M, Daido H, Takao T, Murata S, Shimonishi Y, Imanaka T (1993) A new lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Arthrobacter sp. strain MIS38. J Bacteriol 175:6459–6466
Morikawa M, Hirata Y, Imanaka T (2000) A study on the structure–function relationship of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1488:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-1981(00)00124-4
Mukherjee AK (2007) Potential application of cyclic lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by Bacillus subtilis strains in laundry detergent formulations. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:330–335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02197.x
Mulet M, Sánchez D, Lalucat J, Lee K, Garcia-Valdes E (2015) Pseudomonas alkylphenolica sp. nov., a bacterial species able to form special aerial structures when grown on p-cresol. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:4013–4018. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000529
Müller MM, Kügler JH, Henkel M, Gerlitzki M, Hörmann B, Pöhnlein M, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2012) Rhamnolipids—next generation surfactants? J Biotechnol 162:366–380
Mulligan CN (2005) Environmental applications for biosurfactants. Environ Pollut 133:183–198
Neu TR, Härtner T, Poralla K (1990) Surface active properties of viscosin: a peptidolipid antibiotic. Appl Microbiol Biot 32:518–520
Nielsen TH, Sørensen D, Tobiasen C, Andersen JB, Christophersen C, Givskov M, Sørensen J (2002) Antibiotic and biosurfactant properties of cyclic lipopeptides produced by fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. from the sugar beet rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microb 68:3416–3423
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 12:633–654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12010633
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Poliwoda A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2014) Characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading and biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas sp. P-1 strain as a potential tool for bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:9385–9395
Pauwelyn E, Huang C-J, Ongena M, Leclère V, Jacques P, Bleyaert P, Budzikiewicz H, Schaefer M, Höfte M (2013) New linear lipopeptides produced by Pseudomonas cichorii SF1-54 are involved in virulence, swarming motility, and biofilm formation. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:585–598. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-11-12-0258-R
Peypoux F, Bonmatin JM, Wallach J (1999) Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:553–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051432
Raaijmakers JM, de Bruijn I, Nybroe O, Ongena M (2010) Natural functions of lipopeptides from Bacillus and Pseudomonas: more than surfactants and antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:1037–1062. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00221.x
Rahman KSM, Thahira-Rahman J, Lakshmanaperumalsamy P, Banat IM (2002) Towards efficient crude oil degradation by a mixed bacterial consortium. Bioresour Technol 85:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00119-0
Rodrigues L, Banat IM, Teixeira J, Oliveira R (2006) Biosurfactants: potential applications in medicine. J Antimicrob Chemother 57:609–618
Rokni-Zadeh H, Li W, Sanchez-Rodriguez A, Sinnaeve D, Rozenski J, Martins JC, De Mot R (2012) Genetic and functional characterization of cyclic lipopeptide WLIP production by rice rhizosphere isolate Pseudomonas putida RW10S2. Appl Environ Microb 78:4826–4834
Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (2001) Natural roles of biosurfactants. Environ Microbiol 3:229–236
Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (2002) Biosurfactants and oil bioremediation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:249–252
Roongsawang N, Washio K, Morikawa M (2011) Diversity of nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the biosynthesis of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Int J Mol Sci 12:141–172
Sachdev DP, Cameotra SS (2013) Biosurfactants in agriculture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1005–1016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4641-8
Saikia RR, Deka S, Deka M, Banat IM (2012) Isolation of biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa RS29 from oil-contaminated soil and evaluation of different nitrogen sources in biosurfactant production. Ann Microbiol 62:753–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0315-5
Tuleva B, Christova N, Jordanov B et al (2005) Naphthalene degradation and biosurfactant activity by Bacillus cereus 28BN. Zeitschrift fur Naturforsch 60:577–582
Tvrzova L, Schumann P, Spröer C, Sedláček I, Páčová Z, Sedo O, Zdrahal Z, Steffen M, Lang E (2006) Pseudomonas moraviensis sp. nov. and Pseudomonas vranovensis sp. nov., soil bacteria isolated on nitroaromatic compounds, and emended description of Pseudomonas asplenii. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2657–2663
Van Hamme JD, Singh A, Ward OP (2006) Physiological aspects. Part 1 in a series of papers devoted to surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 24:604–620
Vater J, Kablitz B, Wilde C, Franke P, Mehta N, Cameotra SS (2002) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry of lipopeptide biosurfactants in whole cells and culture filtrates of Bacillus subtilis C-1 isolated. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6210–6219. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.12.6210
Weekers F, Jacques P, Springael D, Mergeay M, Diels L, Thonart P (1999) Improving the catabolic functions of desiccation-tolerant soil bacteria. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 77–79:251–266
Youssef NH, Duncan KE, Nagle DP, Savage KN, Knapp RM, McInerney MJ (2004) Comparison of methods to detect biosurfactant production by diverse microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 56:339–347
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research of Tunisia and a scholarship from the region Hauts-de-France. This work was supported by the European Union SMARTBIOCONTROLPORTFOLIO-Interreg FWVLBIOPROD program, the FEDER program ALIBIOTECH and the CPER project ALIBIOTECH from the region Hauts-de-France. The authors are grateful to the Advanced High Throughput Technologies Platform for Biorefineries Catalysts Design ‘REALCAT’ for allowing the implementation of MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry analysis. The authors are grateful to Kamel Maaloul, translator and English professor for having proofread the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zouari, O., Lecouturier, D., Rochex, A. et al. Bio-emulsifying and biodegradation activities of syringafactin producing Pseudomonas spp. strains isolated from oil contaminated soils. Biodegradation 30, 259–272 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-018-9861-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-018-9861-x