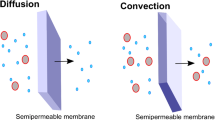
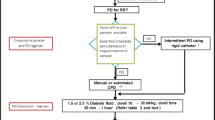
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is an increasingly frequent complication among hospitalized children. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality, especially in neonates and children requiring dialysis. The different renal replacement therapy (RRT) options for AKI have expanded from peritoneal dialysis (PD) and intermittent hemodialysis (HD) to continuous RRT (CRRT) and hybrid modalities. Recent advances in the provision of RRT in children allow a higher standard of care for increasingly ill and young patients. In the absence of evidence indicating better survival with any dialysis method, the most appropriate dialysis choice for children with AKI is based on the patient’s characteristics, on dialytic modality performance, and on the institutional resources and local practice. In this review, the available dialysis modalities for pediatric AKI will be discussed, focusing on indications, advantages, and limitations of each of them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J, Abulfaraj M, Alqahtani F, Koulouridis I, Jaber BL (2013) World incidence of AKI: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1482–1493
Rewa O, Bagshaw SM (2014) Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat Rev Nephrol 10:193–207
Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, Goldstein SL, AWARE Investigators (2017) Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N Engl J Med 376:11–20
Hsu RK, McCulloch CE, Dudley RA, Lo LJ, Hsu CY (2013) Temporal changes in incidence of dialysis-requiring AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:37–42
Sutherland SM, Ji J, Sheikhi FH, Widen E, Tian L, Alexander SR, Ling XB (2013) AKI in hospitalized children: epidemiology and clinical associations in a national cohort. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1661–1669
Symons JM, Chua AN, Somers MJ, Baum MA, Bunchman TE, Benfield MR, Brophy PD, Blowey D, Fortenberry JD, Chand D, Flores FX, Hackbarth R, Alexander SR, Mahan J, McBryde KD, Goldstein SL (2007) Demographic characteristics of pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy: a report of the prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy registry. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:732–738
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, Tchervenkov CI, Gottesman R, Dancea A, Hyder A, Alkandari O (2009) A small postoperative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 76:885–892
Askenazi DJ, Feig DI, Graham NM, Hui-Stickle S, Goldstein SL (2006) 3-5 year longitudinal follow-up of pediatric patients after acute renal failure. Kidney Int 69:184–189
Mammen C, Al Abbas A, Skippen P, Nadel H, Levine D, Collet JP, Matsell DG (2012) Long-term risk of CKD in children surviving episodes of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis 59:523–530
Bunchman TE, McBryde KD, Mottes TE, Gardner JJ, Maxvold NJ, Brophy PD (2001) Pediatric acute renal failure: outcome by modality and disease. Pediatr Nephrol 16:1067–1071
Bagshaw SM, Darmon M, Ostermann M, Finkelstein FO, Wald R, Tolwani AJ, Goldstein SL, Gattas DJ, Uchino S, Hoste EA, Gaudry S (2017) Current state of the art for renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med 43:841–854
Neri M, Villa G, Garzotto F, Bagshaw S, Bellomo R, Cerda J, Ferrari F, Guggia S, Joannidis M, Kellum J, Kim JC, Mehta RL, Ricci Z, Trevisani A, Marafon S, Clark WR, Vincent JL, Ronco C, Nomenclature Standardization Initiative (NSI) alliance (2016) Nomenclature for renal replacement therapy in acute kidney injury: basic principles. Crit Care 20:318
Walters S, Porter C, Brophy PD (2009) Dialysis and pediatric acute kidney injury: choice of renal support modality. Pediatr Nephrol 24:37–48
Ponce D, Gobo-Oliveira M, Balbi AL (2017) Peritoneal dialysis treatment modality option in acute kidney injury. Blood Purif 43:173–178
Chionh CY, Soni SS, Finkelstein FO, Ronco C, Cruz DN (2013) Use of peritoneal dialysis in AKI: a systematic review. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1649–1660
Cullis B, Abdelraheem M, Abraham G, Balbi A, Cruz DN, Frishberg Y, Koch V, McCulloch M, Numanoglu A, Nourse P, Pecoits-Filho R, Ponce D, Warady B, Yeates K, Finkelstein FO (2014) Peritoneal dialysis for acute kidney injury. Perit Dial Int 34:494–517
Stojanović VD, Bukarica SS, Antić JB, Doronjski AD (2017) Peritoneal dialysis in very low birth weight neonates. Perit Dial Int 37:389–396
Bojan M, Gioanni S, Vouhé PR, Journois D, Pouard P (2012) Early initiation of peritoneal dialysis in neonates and infants with acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery is associated with a significant decrease in mortality. Kidney Int 82:474–481
Barhight MF, Soranno D, Faubel S, Gist KM (2018) Fluid management with peritoneal dialysis after pediatric cardiac surgery. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg 9:696–704
Vasudevan A, Phadke K, Yap HK (2017) Peritoneal dialysis for the management of pediatric patients with acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1145–1156
Haubitz M, Brunkhorst R, Wrenger E, Froese P, Schulze M, Koch KM (1996) Chronic induction of C-reactive protein by hemodialysis, but not by peritoneal dialysis therapy. Perit Dial Int 16:158–162
Podel J, Hodelin-Wetzel R, Saha DC, Burns G (2000) Glucose absorption in acute peritoneal dialysis. J Ren Nutr 10:93–97
Raina R, Chauvin AM, Bunchman T, Askenazi D, Deep A, Ensley MJ, Krishnappa V, Sethi SK (2017) Treatment of AKI in developing and developed countries: an international survey of pediatric dialysis modalities. PLoS One 12:e0178233
Bonilla-Félix M (2013) Peritoneal dialysis in the pediatric intensive care unit setting: techniques, quantitations and outcomes. Blood Purif 35:77–80
Strazdins V, Watson AR, Harvey B, European Pediatric Peritoneal Dialysis Working Group (2004) Renal replacement therapy for acute renal failure in children: European guidelines. Pediatr Nephrol 19:199–207
Reznik VM, Randolph G, Collins CM, Peterson BM, Lemire JM, Mendoza SA (1993) Cost analysis of dialysis modalities for pediatric acute renal failure. Perit Dial Int 13:311–313
Picca S, Dionisi-Vici C, Abeni D, Pastore A, Rizzo C, Orzalesi M, Sabetta G, Rizzoni G, Bartuli A (2001) Extracorporeal dialysis in neonatal hyperammonemia: modalities and prognostic indicators. Pediatr Nephrol 16:862–867
Bunchman TE, Meldrum MK, Meliones JE, Sedman AB, Walters MB, Kershaw DB (1992) Pulmonary function variation in ventilator dependent critically ill infants on peritoneal dialysis. Adv Perit Dial 8:75–78
Auron A, Warady BA, Simon S, Blowey DL, Srivastava T, Musharaf G, Alon US (2007) Use of the multipurpose drainage catheter for the provision of acute peritoneal dialysis in infants and children. Am J Kidney Dis 49:650–655
White CT, Gowrishankar M, Feber J, Yiu V, Canadian Association of Pediatric Nephrologists (CAPN), Peritoneal Dialysis Working Group (2006) Clinical practice guidelines for pediatric peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 21:1059–1066
Ladd AP, Breckler FD, Novotny NM (2011) Impact of primary omentectomy on longevity of peritoneal dialysis catheters in children. Am J Surg 201:401–404
Radtke J, Schild R, Reismann M, Ridelski RR, Kempf C, Nashan B, Rothe K, Koch M (2018) Obstruction of peritoneal dialysis catheter is associated with catheter type and independent of omentectomy: a comparative data analysis from a transplant surgical and pediatric surgical department. J Pediatr Surg 53:640–643
KDIGO AKI Work Group (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl 17:1–138
Picca S, Dionisi-Vici C, Bartuli A, De Palo T, Papadia F, Montini G, Materassi M, Donati MA, Verrina E, Schiaffino MC, Pecoraro C, Iaccarino E, Vidal E, Burlina A, Emma F (2015) Short-term survival of hyperammonemic neonates treated with dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 30:839–847
Davenport A (2012) Alternatives to standard unfractionated heparin for pediatric hemodialysis treatments. Pediatr Nephrol 27:1869–1879
Raina R, Vijayaraghavan P, Kapur G, Sethi SK, Krishnappa V, Kumar D, Bunchman TE, Bolen SD, Chand D (2017) Hemodialysis in neonates and infants: a systematic review. Semin Dial 31:289–299
Pollack S, Eisenstein I, Tarabeih M, Shasha-Lavski H, Magen D, Zelikovic I (2016) Long-term hemodialysis therapy in neonates and infants with end-stage renal disease: a 16-year experience and outcome. Pediatr Nephrol 31:305–313
Fischbach M, Edefonti A, Schröder C, Watson A, European Pediatric Dialysis Working Group (2005) Hemodialysis in children: general practical guidelines. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1054–1066
Marshall MR, Golper TA (2011) Low-efficiency acute renal replacement therapy: role in acute kidney injury. Semin Dial 24:142–148
Misra M (2005) The basics of hemodialysis equipment. Hemodial Int 9:30–36
Schiffl H, Lang SM, Haider M (1998) Bioincompatibility of dialyzer membranes may have a negative impact on outcome of acute renal failure, independent of the dose of dialysis delivered: a retrospective multicenter analysis. ASAIO J 44:M418–M422
Hakim RM, Wingard RL, Parker RA (1994) Effect of the dialysis membrane in the treatment of patients with acute renal failure. N Engl J Med 331:1338–1342
Alonso A, Lau J, Jaber BL (2008) Biocompatible hemodialysis membranes for acute renal failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD005283
Ponikvar JB, Rus RR, Kenda RB, Bren AF, Ponikvar RR (2001) Low-flux versus high-flux synthetic dialysis membrane in acute renal failure: prospective randomized study. Artif Organs 25:946–950
Ricci Z, Romagnoli S, Ronco C (2017) High cut-off membranes in acute kidney injury and continuous renal replacement therapy. Int J Artif Organs 40:657–664
Haase M, Bellomo R, Baldwin I, Haase-Fielitz A, Fealy N, Davenport P, Morgera S, Goehl H, Storr M, Boyce N, Neumayer HH (2007) Hemodialysis membrane with a high-molecular-weight cutoff and cytokine levels in sepsis complicated by acute renal failure: a phase 1 randomized trial. Am J Kidney Dis 50:296–304
Davenport A (2003) Anticoagulation options for pediatric hemodialysis. Hemodial Int 7:168–176
Dutt T, Schulz M (2013) Heparin-induced thrombocytopaenia (HIT)—an overview: what does the nephrologist need to know and do? Clin Kidney J 6:563–567
Chanard J, Lavaud S, Maheut H, Kazes I, Vitry F, Rieu P (2008) The clinical evaluation of low-dose heparin in haemodialysis: a prospective study using the heparin-coated AN69 ST membrane. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:2003–2009
Kreuzer M, Bonzel KE, Büscher R, Offner G, Ehrich JH, Pape L (2010) Regional citrate anticoagulation is safe in intermittent high-flux haemodialysis treatment of children and adolescents with an increased risk of bleeding. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:3337–3342
Bunchman TE, Brophy PD, Goldstein SL (2008) Technical considerations for renal replacement therapy in children. Semin Nephrol 28:488–492
Hackbarth R, Bunchman TE, Chua AN, Somers MJ, Baum M, Symons JM, Brophy PD, Blowey D, Fortenberry JD, Chand D, Flores FX, Alexander SR, Mahan JD, McBryde KD, Benfield MR, Goldstein SL (2007) The effect of vascular access location and size on circuit survival in pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy: a report from the PPCRRT registry. Int J Artif Organs 30:1116–1121
de Galasso L, Emma F, Picca S, Di Nardo M, Rossetti E, Guzzo I (2016) Continuous renal replacement therapy in children: fluid overload does not always predict mortality. Pediatr Nephrol 31:651–659
Goldstein SL (2011) Advances in pediatric renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury. Semin Dial 24:187–191
Zhao Y, Li Z, Zhang L, Yang J, Yang Y, Tang Y, Fu P (2014) Citrate versus heparin lock for hemodialysis catheters: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Kidney Dis 63:479–490
Arechabala MC, Catoni MI, Claro JC, Rojas NP, Rubio ME, Calvo MA, Letelier LM (2018) Antimicrobial lock solutions for preventing catheter-related infections in haemodialysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD010597
Sutherland SM, Alexander SR (2012) Continuous renal replacement therapy in children. Pediatr Nephrol 27:2007–2016
Ronco C, Garzotto F, Ricci Z (2012) CA.R.PE.DI.E.M. (cardio–renal pediatric dialysis emergency machine): evolution of continuous renal replacement therapies in infants. A personal journey. Pediatr Nephrol 27:1203–1211
Coulthard MG, Crosier J, Griffiths C, Smith J, Drinnan M, Whitaker M, Beckwith R, Matthews JN, Flecknell P, Lambert HJ (2014) Haemodialysing babies weighing < 8 kg with the Newcastle infant dialysis and ultrafiltration system (Nidus): comparison with peritoneal and conventional haemodialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 29:1873–1881
Askenazi D, Ingram D, White S, Cramer M, Borasino S, Coghill C, Dill L, Tenney F, Feig D, Fathallah-Shaykh S (2016) Smaller circuits for smaller patients: improving renal support therapy with Aquadex™. Pediatr Nephrol 31:853–860
Godaly G, Carlsson O, Broman M (2016) Phoxilium® reduces hypophosphataemia and magnesium supplementation during continuous renal replacement therapy. Clin Kidney J 9:205–210
Ricci Z, Goldstein SL (2016) Pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy. Contrib Nephrol 187:121–130
VA/NIH Acute Renal Failure Trial Network, Palevsky PM, Zhang JH, O’Connor TZ, Chertow GM, Crowley ST, Choudhury D, Finkel K, Kellum JA, Paganini E, Schein RM, Smith MW, Swanson KM, Thompson BT, Vijayan A, Watnick S, Star RA, Peduzzi P (2008) Intensity of renal support in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med 359:7–20
RENAL Replacement Study Investigators, Bellomo R, Cass A, Cole L, Finfer S, Gallagher M, Lo S, McArthur C, McGuinness S, Myburgh J, Norton R, Scheinkestel C, Su S (2009) Intensity of continuous renal-replacement therapy in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 361:1627–1638
Jun M, Heerspink HJ, Ninomiya T, Gallagher M, Bellomo R, Myburgh J, Finfer S, Palevsky PM, Kellum JA, Perkovic V, Cass A (2010) Intensities of renal replacement therapy in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:956–963
Romagnoli S, Lark WR, Ricci Z, Ronco C (2017) Renal replacement therapy for AKI: when? How much? When to stop? Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 31:371–385
Wierstra BT, Kadri S, Alomar S, Burbano X, Barrisford GW, Kao RL (2016) The impact of “early” versus “late” initiation of renal replacement therapy in critical care patients with acute kidney injury: a systematic review and evidence synthesis. Crit Care 20:122
Sutherland SM, Zappitelli M, Alexander SR, Chua AN, Brophy PD, Bunchman TE, Hackbarth R, Somers MJ, Baum M, Symons JM, Flores FX, Benfield M, Askenazi D, Chand D, Fortenberry JD, Mahan JD, McBryde K, Blowey D, Goldstein SL (2010) Fluid overload and mortality in children receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: the prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy registry. Am J Kidney Dis 55:316–325
Garzotto F, Ostermann M, Martin-Langerwerf D, Sánchez-Sánchez M, Teng J, Robert R, Marinho A, Herrera-Gutierrez ME, Mao HJ, Benavente D, Kipnis E, Lorenzin A, Marcelli D, Tetta C, Ronco C, DoReMIFA study group (2016) The dose response multicentre investigation on fluid assessment (DoReMIFA) in critically ill patients. Crit Care 20:196
Atan R, Peck L, Prowle J, Licari E, Eastwood GM, Storr M, Goehl H, Bellomo R (2018) A double-blind randomized controlled trial of high cutoff versus standard hemofiltration in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med 46:e988–e994
Bai M, Zhou M, He L, Ma F, Li Y, Yu Y, Wang P, Li L, Jing R, Zhao L, Sun S (2015) Citrate versus heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy: an updated meta-analysis of RCTs. Intensive Care Med 41:2098–2110
Bunchman TE, Maxvold NJ, Barnett J, Hutchings A, Benfield MR (2002) Pediatric hemofiltration: normocarb dialysate solution with citrate anticoagulation. Pediatr Nephrol 17:150–154
Soltysiak J, Warzywoda A, Kocinski B, Ostalska-Nowicka D, Benedyk A, Silska-Dittmar M, Zachwieja J (2014) Citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy in small children. Pediatr Nephrol 29:469–475
Rico MP, Fernández Sarmiento J, Rojas Velasquez AM, González Chaparro LS, Gastelbondo Amaya R, Mulett Hoyos H, Tibaduiza D, Quintero Gómez AM (2016) Regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy in children. Pediatr Nephrol 32:703–711
Zaoral T, Hladík M, Zapletalová J, Trávníček B, Gelnarová E (2016) Circuit lifetime with citrate versus heparin in pediatric continuous venovenous hemodialysis. Pediatr Crit Care Med 17:e399–e405
Davis TK, Neumayr T, Geile K, Doctor A, Hmeil P (2014) Citrate anticoagulation during continuous renal replacement therapy in pediatric critical care. Pediatr Crit Care Med 15:471–785
Morabito S, Pistolesi V, Tritapepe L, Fiaccadori E (2014) Regional citrate anticoagulation for RRTs in critically ill patients with AKI. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2173–2188
Slowinski T, Morgera S, Joannidis M, Henneberg T, Stocker R, Helset E, Andersson K, Wehner M, Kozik-Jaromin J, Brett S, Hasslacher J, Stover JF, Peters H, Neumayer HH, Kindgen-Milles D (2015) Safety and efficacy of regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemodialysis in the presence of liver failure: the liver citrate anticoagulation threshold (L-CAT) observational study. Crit Care 19:349
Sponholz C, Settmacher U, Bauer M, Kortgen A (2015) Regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy in the perioperative care of liver transplant recipients: a single center experience. Ther Apher Dial 19:8–15
Ronco C, Garzotto F, Brendolan A, Zanella M, Bellettato M, Vedovato S, Chiarenza F, Ricci Z, Goldstein SL (2014) Continuous renal replacement therapy in neonates and small infants: development and first-in-human use of a miniaturised machine (CARPEDIEM). Lancet 383:1807–1813
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Answers: 1. d; 2. c; 3. a; 4. d
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Galasso, L., Picca, S. & Guzzo, I. Dialysis modalities for the management of pediatric acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol 35, 753–765 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04213-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04213-x