Abstract
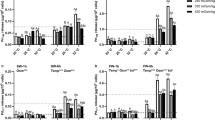
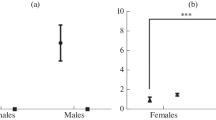
Euryhaline Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) are native to estuaries where they encounter tidal fluctuations in environmental salinity. These fluctuations can be dramatic, subjecting individuals to salinities characteristic of fresh water (FW < 0.5‰) and seawater (SW 35‰) within a single tidal cycle. In the current study, we reared tilapia under a tidal regimen that simulated the dynamic conditions of their native habitat. Tilapia were sampled every 3 h over a 24 h period to temporally resolve how prolactin (PRL) signaling is modulated in parallel with genes encoding branchial effectors of osmoregulation. The following parameters were measured: plasma osmolality, plasma PRL177 and PRL188 concentrations, pituitary prl177 and prl188 gene expression, and branchial prl receptor (prlr1 and prlr2), Na+/Cl−-cotransporter (ncc2), Na+/K+/2Cl−-cotransporter (nkcc1a), Na+/K+-ATPase (nkaα1a and nkaα1b), cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (cftr), and aquaporin 3 (aqp3) gene expression. Throughout the 24 h sampling period, plasma osmolality reflected whether tilapia were sampled during the FW or SW phases of the tidal cycle, whereas pituitary prl gene expression and plasma PRL levels remained stable. Branchial patterns of ncc2, nkcc1a, nkaα1a, nkaα1b, cftr, and aqp3 gene expression indicated that fish exposed to tidally changing salinities regulate the expression of these gene transcripts in a similar fashion as fish held under static SW conditions. By contrast, branchial prlr1 and prlr2 levels were highly labile throughout the tidal cycle. We conclude that local (branchial) regulation of endocrine signaling underlies the capacity of euryhaline fishes, such as Mozambique tilapia, to thrive under dynamic salinity conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayson FG, Tagawa M, Kaneko T, Hasegawa S, Grau EG, Nishioka RS, Bern HA, Hirano T (1993) Homologous radioimmunoassays for tilapia prolactins and growth hormone. Gen Comp Endocrinol 89:138–148
Ayson FG, Kaneko T, Hasegawa S, Hirano T (1994) Differential expression of two prolactin and growth hormone genes during early development of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) in fresh water and seawater: implications for possible involvement in osmoregulation during early life stages. Gen Comp Endocrinol 95(1):143–152. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1994.1111
Ball JN, Ingleton PM (1973) Adaptive variations in prolactin secretion in relation to external salinity in the teleost Poecilia latipinna. Gen Comp Endocrinol 20(2):312–325
Batten TF, Ball JN (1976) Circadian changes in prolactin cell activity in the pituitary of the teleost Poecilia latipinna in freshwater. Cell Tissue Res 165(2):267–280
Borski RJ, Hansen MU, Nishioka RS, Grau EG (1992) Differential processing of the two prolactins of the tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus), in relation to environmental salinity. J Exp Zool 264(1):46–54
Breves JP, Watanabe S, Kaneko T, Hirano T, Grau EG (2010) Prolactin restores branchial mitochondrion-rich cells expressing Na +/Cl− cotransporter in hypophysectomized mozambique tilapia. Am J Physiol 299(2):R702–R710. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00213.2010 (ajpregu.00213.2010 [pii])
Breves JP, Seale AP, Helms RE, Tipsmark CK, Hirano T, Grau EG (2011) Dynamic gene expression of GH/PRL-family hormone receptors in gill and kidney during freshwater-acclimation of Mozambique tilapia. Comp Biochem Physiol 158(2):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.10.030 (S1095-6433(10)00518-0 [pii])
Breves JP, Inokuchi M, Yamaguchi Y, Seale AP, Hunt BL, Watanabe S, Lerner DT, Kaneko T, Grau EG (2016) Hormonal regulation of aquaporin 3: opposing actions of prolactin and cortisol in tilapia gill. J Endocrinol 230(3):325–337. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-16-0162
Chang YJ, Min BH, Choi CY (2007) Black porgy (Acanthopagrus schlegeli) prolactin cDNA sequence: mRNA expression and blood physiological responses during freshwater acclimation. Comp Biochem Physiol 147(1):122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2007.01.006
Cutler CP, Cramb G (2002) Branchial expression of an aquaporin 3 (AQP-3) homologue is downregulated in the European eel Anguilla anguilla following seawater acclimation. J Exp Biol 205(Pt 17):2643–2651
Dharmamba M, Handin RI, Nandi J, Bern HA (1967) Effect of prolactin on freshwater survival and on plasma osmotic pressure of hypophysectomized Tilapia mossambica. Gen Comp Endocrinol 9(2):295–302
Evans DH (2008) Teleost fish osmoregulation: what have we learned since August Krogh, Homer Smith, and Ancel Keys. Am J Physiol 295(2):R704–R713. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.90337.2008
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85(1):97–177. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00050.2003
Fiol DF, Kultz D (2007) Osmotic stress sensing and signaling in fishes. FEBS J 274(22):5790–5798. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06099.x
Fiol DF, Sanmarti E, Sacchi R, Kultz D (2009) A novel tilapia prolactin receptor is functionally distinct from its paralog. J Exp Biol 212(Pt 13):2007–2015. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.025601
Furukawa F, Watanabe S, Seale AP, Breves JP, Lerner DT, Grau EG, Kaneko T (2015) In vivo and in vitro effects of high-K(+) stress on branchial expression of ROMKa in seawater-acclimated Mozambique tilapia. Comp Biochem Physiol 187:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.05.017
Gibson RN (1984) Hydrostatic pressure and the rhythmic behaviour of intertidal marine fishes. Trans Am Fish Soc 113(4):479–483
Grau EG, Nishioka RS, Bern HA (1981) Effects of osmotic pressure and calcium ion on prolactin release in vitro from the rostral pars distalis of the tilapia Sarotherodon mossambicus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 45(3):406–408
Helms LM, Grau EG, Borski RJ (1991) Effects of osmotic pressure and somatostatin on the cAMP messenger system of the osmosensitive prolactin cell of a teleost fish, the tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 83(1):111–117
Hiroi J, McCormick SD, Ohtani-Kaneko R, Kaneko T (2005) Functional classification of mitochondrion-rich cells in euryhaline Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) embryos, by means of triple immunofluorescence staining for Na+/K+ -ATPase, Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter and CFTR anion channel. J Exp Biol 208(Pt 11):2023–2036. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01611
Hiroi J, Yasumasu S, McCormick SD, Hwang PP, Kaneko T (2008) Evidence for an apical Na–Cl cotransporter involved in ion uptake in a teleost fish. J Exp Biol 211(Pt 16):2584–2599. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.018663
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Watanabe S, Lee KM, Kaneko T (2008) Gene expression and morphological localization of NHE3, NCC and NKCC1a in branchial mitochondria-rich cells of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) acclimated to a wide range of salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol 151(2):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.06.012
Inokuchi M, Breves JP, Moriyama S, Watanabe S, Kaneko T, Lerner DT, Grau EG, Seale AP (2015) Prolactin 177, prolactin 188, and extracellular osmolality independently regulate the gene expression of ion transport effectors in gill of Mozambique tilapia. Am J Physiol 309(10):R1251–R1263. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00168.2015
Jung D, Sato JD, Shaw JR, Stanton BA (2012) Expression of aquaporin 3 in gills of the Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus): effects of seawater acclimation. Comp Biochem Physiol 161(3):320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.11.014
Kaneko T, Watanabe S, Lee KM (2008) Functional morphology of mitochondrion-rich cells in euryhaline and stenohaline teleosts. Aqua-BioSci Monogr 1:1–68
Laiz-Carrion R, Fuentes J, Redruello B, Guzman JM, Martin del Rio MP, Power D, Mancera JM (2009) Expression of pituitary prolactin, growth hormone and somatolactin is modified in response to different stressors (salinity, crowding and food-deprivation) in gilthead sea bream Sparus auratus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 162(3):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.03.026
Lignot JH, Cutler CP, Hazon N, Cramb G (2002) Immunolocalisation of aquaporin 3 in the gill and the gastrointestinal tract of the European eel Anguilla anguilla (L.). J Exp Biol 205(Pt 17):2653–2663
Madsen SS, Jensen LN, Tipsmark CK, Kiilerich P, Borski RJ (2007) Differential regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and Na+, K+-ATPase in gills of striped bass, Morone saxatilis: effect of salinity and hormones. J Endocrinol 192(1):249–260. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-06-0016
Madsen SS, Bujak J, Tipsmark CK (2014) Aquaporin expression in the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) in freshwater and seawater: challenging the paradigm of intestinal water transport? J Exp Biol 217(Pt 17):3108–3121. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.105098
Magdeldin S, Uchida K, Hirano T, Grau EG, Abdelfattah A, Nozaki M (2007) Effects of environmental salinity on somatic growth and growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-I axis in juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Sci 73:1023–1032
Manzon LA (2002) The role of prolactin in fish osmoregulation: a review. Gen Comp Endocrinol 125:291–310
Marshall WS, Grosell M (2006) Ion transport, osmoregulation, and acid-base balance. In: Evans DH, Clairborne JB (eds) The physiology of fishes, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 177–230
Marshall WS, Singer TD (2002) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in teleost fish. Biochim Biophys Acta 1566(1–2):16–27
McCormick SD (2011) The Hormonal Control of Osmoregulation in Teleost Fish. In: Farrell AP (ed) Encyclopedia of fish physiology: from genome to environment, vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 1466–1473
Moorman BP, Inokuchi M, Yamaguchi Y, Lerner DT, Grau EG, Seale AP (2014) The osmoregulatory effects of rearing Mozambique tilapia in a tidally changing salinity. Gen Comp Endocrinol 207:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.03.013
Moorman BP, Lerner DT, Grau EG, Seale AP (2015) The effects of acute salinity challenges on osmoregulation in Mozambique tilapia reared in a tidally changing salinity. J Exp Biol 218(Pt 5):731–739. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.112664
Ogasawara T, Hirano T, Akiyama T, Arai S, Tagawa M (1989) Changes in plasma prolactin and growth hormone concentrations during freshwater adaptation of juvenile chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) reared in seawater for a prolonged period. Fish Physiol Biochem 7(1–6):309–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004722
Pavlosky KK, Yamaguchi Y, Lerner DT, Seale AP (2019) The effects of transfer from steady-state to tidally-changing salinities on plasma and branchial osmoregulatory variables in adult Mozambique tilapia. Comp Biochem Physiol A 227:134–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.10.005
Pickford GE, Phillips JG (1959) Prolactin, a factor in promoting survival of hypophysectomized killifish in fresh water. Science 130(3373):454–455
Pierce AL, Fox BK, Davis LK, Visitacion N, Kitahashi T, Hirano T, Grau EG (2007) Prolactin receptor, growth hormone receptor, and putative somatolactin receptor in Mozambique tilapia: tissue specific expression and differential regulation by salinity and fasting. Gen Comp Endocrinol 154(1–3):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.06.023
Rentier-Delrue F, Swennen D, Prunet P, Lion M, Martial JA (1989) Tilapia prolactin: molecular cloning of two cDNAs and expression in Escherichia coli. DNA 3:261–270
Seale AP, Riley LG, Leedom TA, Kajimura S, Dores RM, Hirano T, Grau EG (2002) Effects of environmental osmolality on release of prolactin, growth hormone and ACTH from the tilapia pituitary. Gen Comp Endocrinol 128:91–101
Seale AP, Fiess JC, Hirano T, Cooke IM, Grau EG (2006) Disparate release of prolactin and growth hormone from the tilapia pituitary in response to osmotic stimulation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 145(3):222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.09.006
Seale AP, Moorman BP, Stagg JJ, Breves JP, Lerner D, Grau G (2012) Prolactin 177, prolactin 188 and prolactin receptor 2 in the pituitary of the euryhaline tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, are differentially osmosensitive. J Endocrinol 213:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-11-0384
Seale AP, Stagg JJ, Yamaguchi Y, Breves JP, Soma S, Watanabe S, Kaneko T, Cnaani A, Harpaz S, Lerner DT, Grau EG (2014) Effects of salinity and prolactin on gene transcript levels of ion transporters, ion pumps and prolactin receptors in Mozambique tilapia intestine. Gen Comp Endocrinol 206:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.07.020
Singer TD, Tucker SJ, Marshall WS, Higgins CF (1998) A divergent CFTR homologue: highly regulated salt transport in the euryhaline teleost F. heteroclitus. Am J Physiol 274(3 Pt 1):C715–C723
Specker JL, King DS, Nishioka RS, Shirahata K, Yamaguchi K, Bern HA (1985) Isolation and partial characterization of a pair of prolactins released in vitro by the pituitary of cichlid fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 82:7490–7494
Spieler RE, Meier AH, Noeske TA (1978) Temperature-induced phase shift of daily rhythm of serum prolactin in gulf killifish. Nature 271(5644):469–470
Tipsmark CK, Sorensen KJ, Madsen SS (2010) Aquaporin expression dynamics in osmoregulatory tissues of Atlantic salmon during smoltification and seawater acclimation. J Exp Biol 213(3):368–379. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.034785
Tipsmark CK, Breves JP, Seale AP, Lerner DT, Hirano T, Grau EG (2011) Switching of Na+, K+-ATPase isoforms by salinity and prolactin in the gill of a cichlid fish. J Endocrinol 209(2):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-10-0495
Trewavas E (1983) Tilapiine fishes of the genera Sarotherodon, Oreochromis and Danakilia. British Museum (Natural History) Publication Number 878. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Tse WK, Au DW, Wong CK (2006) Characterization of ion channel and transporter mRNA expressions in isolated gill chloride and pavement cells of seawater acclimating eels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(4):1181–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.06.028
Varsamos S, Xuereb B, Commes T, Flik G, Spanings-Pierrot C (2006) Pituitary hormone mRNA expression in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax in seawater and following acclimation to fresh water. J Endocrinol 191(2):473–480. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.1.06847
Watanabe S, Kaneko T, Aida K (2005) Aquaporin-3 expressed in the basolateral membrane of gill chloride cells in Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus adapted to freshwater and seawater. J Exp Biol 208(Pt 14):2673–2682. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01684
Wigham T, Ball JN (1977) Effect of environmental salinity changes on the secretory activity of prolactin cells in ocular pituitary transplants in Poecilia latipinna (Teleostei). Gen Comp Endocrinol 31(1):148–153
Yada T, Hirano T, Grau EG (1994) Changes in plasma levels of the two prolactins and growth hormone during adaptation to different salinities in the euryhaline tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 93:214–223
Yamaguchi K, Specker JL, King DS, Yokoo Y, Nishioka RS, Hirano T, Bern HA (1988) Complete amino acid sequences of a pair of fish (tilapia) prolactins, tPRL177 and tPRL188. J Biol Chem 263:9113–9121
Yamaguchi Y, Moriyama S, Lerner DT, Grau EG, Seale AP (2016) Autocrine positive feedback regulation of prolactin release from tilapia prolactin cells and its modulation by extracellular osmolality. Endocrinology 157(9):3505–3516. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2015-1969
Yamaguchi Y, Breves JP, Haws MC, Lerner DT, Grau EG, Seale AP (2018) Acute salinity tolerance and the control of two prolactins and their receptors in the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Mozambique tilapia (O. mossambicus): a comparative study. Gen Comp Endocrinol 257:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.06.018
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mr. Julian Leon for laboratory assistance and Dr. Lucia A. Seale and Ms. Amanda Reyes for sampling assistance.
Funding
This work was funded in part by grants from the National Science Foundation (IOS-1755016 and IOS-1755131 to APS and JPB), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NA18OAR4170347 to DTL and APS and NA14OAR4170071, which is sponsored by the University of Hawai‘i Sea Grant College Program projects R/SS-12 and R/SB-18 to APS), the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases 1R21DK111775-01 from the National Institutes of Health to APS, and the National Institute of Food and Agriculture Hatch No. HAW02051-H to APS. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the aforementioned granting agencies. University of Hawai‘i Sea Grant publication number UNIHI-SEAGRANT-JC-14-62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Additional information
Communicated by B. Pelster.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seale, A.P., Pavlosky, K.K., Celino-Brady, F.T. et al. Systemic versus tissue-level prolactin signaling in a teleost during a tidal cycle. J Comp Physiol B 189, 581–594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-019-01233-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-019-01233-9