Abstract
Background
This study evaluated the clinical significance of pathological factors associated with T3a upstaging according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer/Union for International Cancer Control 8th edition TNM-staging system in patients with clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma undergoing definitive surgery.
Methods
We retrospectively investigated 418 patients with renal cell carcinoma who underwent partial or radical nephrectomy at our institution between 2006 and 2016. Surgical specimens were grossly and microscopically re-reviewed with respect to extrarenal extension patterns by two urological pathologists. Kaplan–Meier analysis and Cox regression were used to determine the impact of the factors associated with pathological stage T3a on recurrence-free survival. Harrell’s c-index was used to compare the prognostic accuracy of the current and previous staging systems.
Results
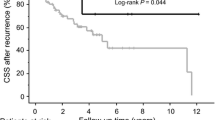
Overall, the 5-year recurrence-free survival was 94.5% (median follow-up duration, 60.8 months). Of 418 patients, 46 (11.0%) were upstaged to pathological stage T3a, including 12/267 (4.5%) and 34/151 (22.5%) in the partial and radical nephrectomy groups, respectively. Among these upstaged patients, partial nephrectomy was significantly associated with a higher recurrence rate than radical nephrectomy (5-year recurrence-free survival: 48.9 vs. 83.9%, P = 0.0172). Although perinephric fat invasion had the highest c-index in all patients (0.580–0.679), microscopic segmental renal vein invasion was a significant predictor of recurrence in patients undergoing partial nephrectomy (c-index, 0.60).
Conclusion
Assessing microscopic segmental renal vein invasion, which has been included in the current staging system recently, is essential to accurately predict the oncological outcome in the era of partial nephrectomy for clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AJCC:
-
American Joint Committee on Cancer
- ASA:
-
American Society of Anesthesiologists
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- cT1:
-
Clinical T1
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- ISUP:
-
International Society of Urological Pathology
- LVI:
-
Lymphovascular invasion
- M-RVI:
-
Main renal vein invasion
- PFI:
-
Perinephric fat invasion
- PN:
-
Partial nephrectomy
- pT3a:
-
Pathological T3a
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
- RN:
-
Radical nephrectomy
- S-RVI:
-
Segmental renal vein invasion
- SFI:
-
Sinus fat invasion
- UICC:
-
Union for International Cancer Control
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S et al (2015) EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur Urol 67(5):913–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.01.005
Campbell S, Uzzo RG, Allaf ME et al (2017) Renal mass and localized renal cancer: AUA guideline. J Urol 198(3):520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.04.100
Bianchi M, Becker A, Abdollah F et al (2013) Rates of open versus laparoscopic and partial versus radical nephrectomy for T1a renal cell carcinoma: a population-based evaluation. Int J Urol 20(11):1064–1071. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.12110
Kunath F, Schmidt S, Krabbe LM et al (2017) Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy for clinical localised renal masses. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:CD012045
Gorin MA, Ball MW, Pierorazio PM et al (2013) Outcomes and predictors of clinical T1 to pathological T3a tumor up-staging after robotic partial nephrectomy: a multi-institutional analysis. J Urol 190(5):1907–1911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2013.06.014
Lee H, Lee M, Lee SE et al (2018) Outcomes of pathologic stage T3a renal cell carcinoma up-staged from small renal tumor: emphasis on partial nephrectomy. BMC Cancer 18(1):427. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4338-1
Nayak JG, Patel P, Saarela O et al (2016) Pathological upstaging of clinical T1 to pathological T3a renal cell carcinoma: a multi-institutional analysis of short-term outcomes. Urology 94:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2016.03.029
Ramaswamy K, Kheterpal E, Pham H et al (2015) Significance of pathologic T3a upstaging in clinical T1 renal masses undergoing nephrectomy. Clin Genitourin Cancer 13(4):344–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2015.01.001
Russell CM, Lebastchi AH, Chipollini J et al (2018) Multi-institutional survival analysis of incidental pathologic T3a upstaging in clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma following partial nephrectomy. Urology 117:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.04.002
Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC et al (2010) American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Cancer Staging Manual, 7th edn. Springer, New York
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (2010) Union for International Cancer Control. TNM classification of malignant tumours. 7th edn. Wiley, New York
Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL et al (2017) American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Cancer Staging Manual, 8th edn. Springer, New York
Brierley JD, Gospodarowics MK, Wittekind C (2017) Union for International Cancer Control. TNM classification of malignant tumours, 8th edn. Wiley, New York
Kutikov A, Uzzo RG (2009) The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urol 182(3):844–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.05.035
Trpkov K, Grignon DJ, Bonsib SM et al (2013) Handling and staging of renal cell carcinoma: the International Society of Urological Pathology Consensus (ISUP) conference recommendations. Am J Surg Pathol 37(10):1505–1517. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e31829a85d0
Moch H, Humphrey PA, Ulbright TM et al (2016) WHO classification tumors of the urinary system and male genital organs, 4th edn. IARC, Lyon
Williamson SR, Rao P, Hes O et al (2018) Challenges in pathologic staging of renal cell carcinoma: a study of interobserver variability among urologic pathologists. Am J Surg Pathol 42(9):1253–1261. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000001087
Harrell FE, Lee KL, Mark DB (1996) Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med 15(4):361–387. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19960229)15:4%3c361:AID-SIM168%3e3.0.CO;2-4
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Trans 48(3):452–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Shah PH, Moreira DM, Patel VR et al (2017) Partial nephrectomy is associated with higher risk of relapse compared with radical nephrectomy for clinical stage T1 renal cell carcinoma pathologically up staged to T3a. J Urol 198(2):289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.03.012
Sokhi HK, Mok WY, Patel U (2015) Stage T3a renal cell carcinoma: staging accuracy of CT for sinus fat, perinephric fat or renal vein invasion. Br J Radiol 88(1045):20140504. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20140504
Kikuchi H, Abe T, Matsumoto R et al (2019) Nephrometry score correlated with tumor proliferative activity inT1 clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol 37(5):301.e319–301.e325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2019.02.005
Shah PH, Lyon TD, Lohse CM et al (2018) Prognostic evaluation of perinephric fat, renal sinus fat, and renal vein invasion for patients with pathological stage T3a clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14523
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No author has any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, T., Ohe, C., Tsuzuki, T. et al. Clinical impact of segmental renal vein invasion on recurrence in patients with clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma undergoing partial nephrectomy. Int J Clin Oncol 25, 464–471 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01543-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01543-6