Abstract
This study investigates the implicit sequence learning abilities of dyslexic children using an artificial grammar learning task with an extended exposure period. Twenty children with developmental dyslexia participated in the study and were matched with two control groups—one matched for age and other for reading skills. During 3 days, all participants performed an acquisition task, where they were exposed to colored geometrical forms sequences with an underlying grammatical structure. On the last day, after the acquisition task, participants were tested in a grammaticality classification task. Implicit sequence learning was present in dyslexic children, as well as in both control groups, and no differences between groups were observed. These results suggest that implicit learning deficits per se cannot explain the characteristic reading difficulties of the dyslexics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blomert, L., & Vaessen, A. (2009). Differentiaal Diagnostiek van Dyslexie: cognitieve analyse van lezen en spellen [Dyslexia Differential Diagnosis: cognitive analysis of reading and spelling]. Amsterdam: Boom.
Boets, B., Beeck, H. O., Vandermosten, M., Scott, S. K., Gillebert, C. R., Mantini, D., et al. (2013). Intact but less accessible phonetic representations in adults with dyslexia. Science, 342(6163), 1251–1254. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1244333.
Cleeremans, A., Destrebecqz, A., & Boyer, M. (1998). Implicit learning: news from the front. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2(10), 406–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-6613(98)01232-7.
Conway, C. M., Bauernschmidt, A., Huang, S. S., & Pisoni, D. B. (2010). Implicit statistical learning in language processing: word predictability is the key. Cognition, 114(3), 356–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2009.10.009.
Conway, C. M., & Pisoni, D. B. (2008). Neurocognitive basis of implicit learning of sequential structure and its relation to language processing. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1145, 113–131. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1416.009.
Ehri, L. C. (2005). Learning to read words: theory, findings, and issues. Scientific Studies of Reading, 9(2), 167–188. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532799xssr0902_4.
Folia, V., Uddén, J., Forkstam, C., Ingvar, M., Hagoort, P., & Petersson, K. M. (2008). Implicit learning and dyslexia. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1145, 132–150. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1416.012.
Franceschini, S., Gori, S., Ruffino, M., Pedrolli, K., & Facoetti, A. (2012). A causal link between visual spatial attention and reading acquisition. Current Biology, 22(9), 814–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.013.
Gathercole, S. E., Pickering, S. J., Ambridge, B., & Wearing, H. (2004). The structure of working memory from 4 to 15 years of age. Developmental Psychology, 40(2), 177–190. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.40.2.177.
Hedenius, M., Persson, J., Alm, P. A., Ullman, M. T., Howard, J. H., Howard, D. V, & Jennische, M. (2013). Impaired implicit sequence learning in children with developmental dyslexia. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(11), 3924–3935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.08.014
Howard, J. H., Howard, D. V., Japikse, K. C., & Eden, G. F. (2006). Dyslexics are impaired on implicit higher-order sequence learning, but not on implicit spatial context learning. Neuropsychologia, 44(7), 1131–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.10.015.
Jiménez-Fernández, G., Vaquero, J. M. M., Jiménez, L., & Defior, S. (2010). Dyslexic children show deficits in implicit sequence learning, but not in explicit sequence learning or contextual cueing. Annals of Dyslexia, 61(1), 85–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-010-0048-3.
Kahta, S., & Schiff, R. (2016). Implicit learning deficits among adults with developmental dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 66(2), 235–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-016-0121-7.
Kaufman, S. B., Deyoung, C. G., Gray, J. R., Jiménez, L., Brown, J., & Mackintosh, N. (2010). Implicit learning as an ability. Cognition, 116(3), 321–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2010.05.011.
Kelly, S. W., Griffiths, S., & Frith, U. (2002). Evidence for implicit sequence learning in dyslexia. Dyslexia, 8(1), 43–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.208.
Knowlton, B. J., & Squire, L. R. (1996). Artificial grammar learning depends on implicit acquisition of both abstract and exemplar-specific information. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 22(1), 169–181. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.22.1.169.
Laasonen, M., Vare, J., Oksanen-Hennah, H., Leppamaki, S., Tani, P., Harno, H., et al. (2014). Project DyAdd: implicit learning in adult dyslexia and ADHD. Annals of Dyslexia, 64(1), 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-013-0083-y.
Lum, J. A. G., Ullman, M. T., & Conti-Ramsden, G. (2013). Procedural learning is impaired in dyslexia: evidence from a meta-analysis of serial reaction time studies. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(10), 3460–3476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.07.017.
Lyon, G. R., Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2003). Defining dyslexia, comorbidity, teachers’ knowledge of language and reading: a definition of dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 53, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-003-0001-9.
Menghini, D., Hagberg, G. E., Caltagirone, C., Petrosini, L., & Vicari, S. (2006). Implicit learning deficits in dyslexic adults: an fMRI study. NeuroImage, 33(4), 1218–1226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.024.
Meulemans, T., & Van Der Linden, M. (1997). Associative chunk strength in artificial grammar learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 23(4), 1007–1028. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.23.4.1007.
Nicolson, R. I., & Fawcett, A. J. (1999). Developmental dyslexia: the role of the cerebellum. Dyslexia, 5(3), 155–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0909.
Nicolson, R. I., Fawcett, A. J., & Dean, P. (2001). Developmental dyslexia: the cerebellar deficit hypothesis. Trends in Neurosciences, 24(9), 508–511 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2236(00)01896-8.
Nieuwenhuis, I. L. C., Folia, V., Forkstam, C., Jensen, O., & Petersson, K. M. (2013). Sleep promotes the extraction of grammatical rules. PLoS One, 8(6), e65046. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065046.
Nigro, L., Jiménez-Fernández, G., Simpson, I. C., & Defior, S. (2016). Implicit learning of non-linguistic and linguistic regularities in children with dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 66(2), 202–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-015-0116-9.
Pacheco, A., Reis, A., Araújo, S., Inácio, F., Petersson, K. M., & Faísca, L. (2014). Dyslexia heterogeneity: cognitive profiling of Portuguese children with dyslexia. Reading and Writing, 27(9), 1529–1545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-014-9504-5.
Pavlidou, E. V., Kelly, M. L., & Williams, J. M. (2010). Do children with developmental dyslexia have impairments in implicit learning? Dyslexia, 16, 143–161. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.
Pavlidou, E. V., Williams, J. M., & Kelly, L. M. (2009). Artificial grammar learning in primary school children with and without developmental dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 59(1), 55–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-009-0023-z.
Pothos, E. M., & Kirk, J. (2004). Investigating learning deficits associated with dyslexia. Dyslexia, 10(1), 61–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.266.
Ramus, F., Rosen, S., Dakin, S. C., Day, B. L., Castellote, J. M., White, S., & Frith, U. (2003). Theories of developmental dyslexia: insights from a multiple case study of dyslexic adults. Brain, 126(4), 841–865. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awg076.
Raven, J., Raven, J. C., & Court, J. H. (2009). CPM-P Matrizes Progressivas Coloridas (Forma Paralela). Lisboa: Cegoc.
Reber, A. S. (1967). Implicit learning of artificial grammars. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 6, 855–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5371(67)80149-X.
Roodenrys, S., & Dunn, N. (2008). Unimpaired implicit learning in children with developmental dyslexia. Dyslexia, 14, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.
Rüsseler, J., Gerth, I., & Münte, T. F. (2006). Implicit learning is intact in adult developmental dyslexic readers: evidence from the serial reaction time task and artificial grammar learning. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 28(5), 808–827. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803390591001007.
Santos, A. S., & Castro, S. L. (2010). Aprender a ler e avaliar a leitura. O TIL: teste de Idade de Leitura (2nd ed.). Coimbra: Almedina.
Schmalz, X., Altoè, G., & Mulatti, C. (2017). Statistical learning and dyslexia: a systematic review. Annals of Dyslexia, 67(2), 147–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-016-0136-0.
Sela, I. (2014). Visual and auditory synchronization deficits among dyslexic readers as compared to non-impaired readers: a cross-correlation algorithm analysis. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 364. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00364.
Shaywitz, S. (2003). Overcoming dyslexia. New York: Vintage Books.
Siegelman, N., Bogaerts, L., Christiansen, M. H., & Frost, R. (2017a). Towards a theory of individual differences in statistical learning. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 372(1711), 20160059. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0059.
Siegelman, N., Bogaerts, L., & Frost, R. (2017b). Measuring individual differences in statistical learning: current pitfalls and possible solutions. Behavior Research Methods, 49(2), 418–432. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-016-0719-z.
Sperling, A. J., Lu, Z.-L., & Manis, F. R. (2004). Slower implicit categorical learning in adult poor readers. Annals of Dyslexia, 54(2), 281–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-004-0014-z.
Stoodley, C. J., Harrison, E. P. D., & Stein, J. F. (2006). Implicit motor learning deficits in dyslexic adults. Neuropsychologia, 44(5), 795–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.07.009.
Stoodley, C. J., & Stein, J. F. (2011). The cerebellum and dyslexia. Cortex, 47(1), 101–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2009.10.005.
Tijms, J. (2004). Verbal memory and phonological processing in dyslexia. Journal of Research in Reading, 27(3), 300–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9817.2004.00233.x.
Trecy, M. P., Steve, M., & Martine, P. (2013). Impaired short-term memory for order in adults with dyslexia. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(7), 2211–2223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.04.005.
Tunmer, W., & Greaney, K. (2011). Defining dyslexia. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 43(3), 229–243. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219409345009.
van Witteloostuijn, M., Boersma, P., Wijnen, F., & Rispens, J. (2017). Visual artificial grammar learning in dyslexia: a meta-analysis. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 70, 126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2017.09.006
Vellutino, F. R., Fletcher, J. M., Snowling, M. J., & Scanlon, D. M. (2004). Specific reading disability (dyslexia): what have we learned in the past four decades? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45(1), 2–40. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0021-9630.2003.00305.x.
Vicari, S., Marotta, L., Menghini, D., Molinari, M., & Petrosini, L. (2003). Implicit learning deficit in children with developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia, 41(1), 108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(02)00082-9.
Waber, D. P., Marcus, D. J., Forbes, P. W., Bellinger, D. C., Weiler, M. D., Sorensen, L. G., & Curran, T. (2003). Motor sequence learning and reading ability: is poor reading associated with sequencing deficits? Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 84(4), 338–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0965(03)00030-4.
Wagner, R. K., Torgesen, J. K., & Rashotte, C. A. (1994). Development of reading-related phonological processing abilities: new evidence of bidirectional causality from a latent variable longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology, 30(1), 73–87. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.30.1.73.
Wang, S., & Gathercole, S. E. (2013). Working memory deficits in children with reading difficulties: memory span and dual task coordination. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 115(1), 188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2012.11.015.
Wechsler, D. (2006). Wechsler intelligence scale for children (3rd ed.). Lisboa: Cegoc.
Funding
This work was supported by national Portuguese funding through Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, project ref. UID/BIM/04773/2013 CBMR, PTDC/MHC-PCN/1175/2014, and SFRH/BD/85439/2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
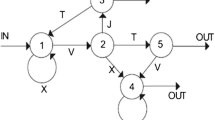
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inácio, F., Faísca, L., Forkstam, C. et al. Implicit sequence learning is preserved in dyslexic children. Ann. of Dyslexia 68, 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-018-0158-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-018-0158-x