Abstract
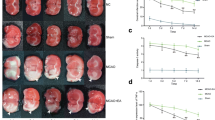
Hippocampal 5-HT1A receptors and the PKA signaling pathway have been implicated in learning and memory. This study aimed to investigate whether PKA signaling mediated by 5-HT1A receptors was involved in the electroacupuncture (EA)-mediated learning and memory in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced cognitive deficit (MICD). Compared to no treatment or non-acupoint EA treatment, EA at DU20 and DU24 acupoints improved the neurological deficit of scores, shortened escape latency and increased the frequency of crossing the platform in the Morris water maze test. T2-weighted imaging demonstrated that the MICD rat brain lesions were mainly located in the cortex and hippocampus, and injured volumes were reduced after EA. Furthermore, we found that these behavioral changes were concomitant with the deficit of the 5HT1A and PKA signaling pathways in the hippocampus, as the activation of the 5-HT1A receptor, the reduction of PKA kinase activity, and AMPA and NMDA receptor phosphorylation occurred in the injured hippocampus at Day 14 after MICD. Additionally, EA dramatically elevated the activation of PKA. Moreover, EA significantly increased intracellular calcium concentrations regulated by the activation of NMDA receptors. Therefore, PKA kinase and NMDA receptors mediated by 5-HT1A receptors in the hippocampus might contribute to improving learning and memory during the recovery process following ischemic stroke with an EA intervention.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes NM, Sharp T (1999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38:1083–1152
Buckley MJ (2005) The role of the perirhinal cortex and hippocampus in learning, memory, and perception. Q J Exp Psychol B 58:246–268
Cai J, Yang S, Tao J, Huang J, Li Y, Ye H, Chen S, Hong W, Chen L (2016) Clinical efficacy of acupuncture treatment in combination with RehaCom cognitive training for improving cognitive function in stroke: a 2× 2 factorial design randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc 17(12):1114
Chavez LM, Huang SS, MacDonald I, Lin JG, Lee YC, Chen YH (2017) Mechanisms of acupuncture therapy in ischemic stroke rehabilitation: a literature review of basic studies. Int J Mol Sci 28;18(11)
Chen J, Wang J, Huang Y, Lai X, Tang C, Yang J, Wu J, Zeng T, Qu S (2014) Modulatory effect of acupuncture at Waiguan (TE5) on the functional connectivity of the central nervous system of patients with ischemic stroke in the left basal ganglia. PLoS One 9(6):e96777
Chen L, Fang J, Ma R, Gu X, Chen L, Li J, Xu S (2016) Additional effects of acupuncture on early comprehensive rehabilitation in patients with mild to moderate acute ischemic stroke: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 16(1):226
Chin Y, Kishi M, Sekino M, Nakajo F, Abe Y, Terazono Y, Hiroyuki O, Kato F, Koizumi S, Gachet C, Hisatsune T (2013) Involvement of glial P2Y1 receptors in cognitive deficit after focal cerebral stroke in a rodent model. J Neuroinflammation 10:95
Egashira N, Yano A, Ishigami N, Mishima K, Iwasaki K, Fujioka M, Matsushita M, Nishimura R, Fujiwara M (2006) Investigation of mechanisms mediating 8-OH-DPAT-induced impairment of spatial memory: involvement of 5-HT1A receptors in the dorsal hippocampus in rats. Brain Res 1069:54–62
Fernandez SP, Muzerelle A, Scotto-Lomassese S, Barik J, Gruart A, Delgado-García JMS, Gaspar P (2017) Constitutive and acquired serotonin deficiency alters memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology. 42:512–523
Glikmann-Johnston Y, Saling MM, Reutens DC, Stout JC (2015) Hippocampal 5-HT1A receptor and spatial learning and memory. Front Pharmacol 10:289
Guo K, Yin G, Zi XH, Zhu HX, Pan Q (2016) Effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on expression of 5-HT1AR and neurotransmitters in rats with vascular dementia. Genet Mol Res 15:gmr15049031
Hachinski V, Iadecola C, Petersen RC, Breteler MM, Nyenhuis DL, Black SE, Powers WJ, DeCarli C, Merino JG, Kalaria RN, Vinters HV, Holtzman DM, Rosenberg GA, Wallin A, Dichgans M, Marler JR, Leblanc GG (2006) National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Canadian stroke network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards. Stroke. 37:2220–2241
He X, Yan T, Chen R, Ran D (2012) Acute effects of electroacupuncture (EA) on hippocampal long term potentiation(LTP) of perforant path-dentate gyrus granule cells synapse related to memory. Acupuncture and Electro-Terapeutics Research 37:89–101
Hommel M, Carey L, Jaillard A (2015) Depression: cognition relations after stroke. Int J Stroke 10(6):893–896
Ifergane G, Boyko M, Frank D, Shiyntum HN, Grinshpun J, Kuts R, Geva AB, Kaplan Z, Zeldetz V, Cohen H (2018) Biological and behavioral patterns of post-stroke depression in rats. Can J Neurol Sci 45(4):451–461
Jafari-Sabet M (2011) Involvement of dorsal hippocampal muscarinic cholinergic receptors on muscimol state-dependent memory of passive avoidance in mice[J]. Life Sciences88:1136–1141
Jiang Y, Yang S, Tao J, Lin Z, Ye X, You Y, Peng J, Hong Z, Chen L (2016) Opposing needling promotes behavior recovery and exerts neuroprotection via the cAMP/PKA/CREB signal transduction pathway in transient MCAO rats. Mol Med Rep 13:2060–2070
Kawanishi K, Koshino H, Toyoshita Y, Tanaka M, Hirai T (2010) Effect of mastication on functional recoveries after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 19(5):398–403
Kim MH, Leem YH (2014) Chronic exercise improves repeated restraint stress-induced anxiety and depression through 5HT1A receptor and cAMP signaling in hippocampus. J Exerc Nutr Biochem 18:97–104
King MV, Marsden CA, Fone KC (2008) A role for the 5-HT(1A), 5-HT4 and 5-HT6 receptors in learning and memory. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:482–492
Koizumi JI, Yoshida Y, Nakazawa T, Ooneda G (1986) Experimental studies of ischemic brain edema:1. A new experimental model of cerebral embolism in rats in which recirculation can be introduced in the ischemic area. Jpn.j.stroke 8:1–8
Kutlu MG, Gould TJ (2016) Nicotinic modulation of hippocampal cell signaling and associated effects on learning and memory. Physiol Behav 155:162–171
Lau CG, Takeuchi K, Rodenas-Ruano A, Takayasu Y, Murphy J, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2009) Regulation of NMDA receptor Ca2+ signalling and synaptic plasticity. Biochem Soc Trans 37:1369–1374
Lee CH, Ahn JH, Won MH (2015) New expression of 5-HT1A receptor in astrocytes in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region following transient global cerebral ischemia. Neurol Sci 36:383–389
Lees R, Fearon P, Harrison JK, Broomfield NM, Quinn TJ (2012) Cognitive and mood assessment in stroke research: focused review of contemporary studies. Stroke 43:1678–1680
Li W, Huang R, Shetty RA, Thangthaeng N, Liu R, Chen Z, Sumien N, Rutledge M, Dillon GH, Yuan F, Forster MJ, Simpkins JW, Yang SH (2013) Transient focal cerebral ischemia induces long-term cognitive function deficit in an experimental ischemic stroke model. Neurobiol. 59:18–25
Li HQ, Li JH, Liu AJ, Ye MY, Zheng GQ (2014) GV20-based acupuncture for animal models of acute intracerebral haemorrhage: a preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupuncture in Medicine Journal of the British Medical Acupuncture Society 32(6):495–502
Li QQ, Shi GX, Yang JW, Li ZX, Zhang ZH, He T, Wang J, Liu LY, Liu CZ (2015) Hippocampal cAMP/PKA/CREB is required for neuroprotective effect of acupuncture. Physiol Behav 139:482–490
Lin YW, Hsieh CL (2010) Electroacupuncture at Baihui acupoint (GV20) reverses behavior deficit and long-term potentiation through N-methyl-d-aspartate and transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 receptors in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. J Integr Neurosci 9:269–282
Lin R, Wu Y, Tao J, Chen B, Chen J, Zhao C, Yu K, Li X, Chen LD (2016) Electroacupuncture improves cognitive function through rho GTPases and enhances dendritic spine plasticity in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Mol Med Rep 13:2655–2660
Liu F, Li ZM, Jiang YJ, Chen LD (2014) A meta-analysis of acupuncture use in the treatment of cognitive impairment after stroke. J Altern Complement Med 20:535–544
Liu AJ, Li JH, Li HQ, Fu DL, Lu L, Bian ZX, Zheng GQ (2015) Electroacupuncture for acute ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Chin Med 43:1541–1566
Liu W, Wu J, Huang J, Zhuo P, Lin Y, Wang L, Lin R, Chen L, Tao J (2017) Electroacupuncture regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity via miR-134-mediated LIMK1 function in rats with ischemic stroke. Neural Plast: 9545646
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Lüttgen M, Elvander E, Madjid N, Ogren SO (2005) Analysis of the role of 5-HT1A receptors in spatial and aversive learning in the rat. Neuropharmacology 48:830–852
Malenka RC (2003) Synaptic plasticity and AMPA receptor trafficking. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:1–11
Milner B, Klein D (2016) Loss of recent memory afer bilateral hippocampal lesions: memory and memories—looking back and looking forward. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87:230
Moyano S, Del Rio J, Frechilla D (2004) Role of hippocampal CaMKII in serotonin 5-HT1A receptor-mediated learning deficit in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:2216–2224
Mukherjee M, McPeak LK, Redford JB, Sun C, Liu W (2007) The effect of electro-acupuncture on spasticity of the wrist joint in chronic stroke survivors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88(2):159–166
Ogren SO, Eriksson TM, Elvander-Tottie E, D'Addario C, Ekström JC, Svenningsson P, Meister B, Kehr J, Stiedl O (2008) The role of 5-HT1A receptors in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 195:54–77
Petrovic MM, Viana da Silva S, Clement JP, Vyklicky L, Mulle C, González-González IM, Henley JM (2017) Metabotropic action of postsynaptic kainate receptors triggers hippocampal long-term potentiation. Nat Neurosci 20:529–539
Pollock A, St George B, Fenton M, Firkins L (2012) Top ten research priorities relating to life after stroke. Lancet Neurol 11:209
Ratmansky M, Levy A, Messinger A, Birg A, Front L, Treger I (2015) The effects of acupuncture on cerebral blood flow in post-stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med 22(1):33
Sanderson JL, Gorski JA, Dell' Acqua ML (2016) NMDA receptor-dependent LTD requires transient synaptic incorporation of Ca2+-permeable AMPARs mediated by AKAP150-anchored PKA and Calcineurin. Neuron 89:1000–1015
Sarnyai Z, Sibille EL, Pavlides C, Fenster RJ, McEwen BS, Toth M (2000) Impaired hippocampal-dependent learning and functional abnormalities in the hippocampus in mice lacking serotonin(1A) receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:14731–14736
Sobczyk A, Scheuss V, Svoboda K (2005) NMDA receptor subunit-dependent [Ca2+] signaling in individual hippocampal dendritic spines. J Neurosci 25:6037–6046
Tatemichi TK, Desmond DW, Stern Y, Paik M, Sano M, Bagiella E (1994) Cognitive impairment after stroke: frequency, patterns, and relationship to functional abilities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:202–207
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858
Wang WW, Xie CL, Lu L, Zheng GQ (2014) A systematic review and meta-analysis of Baihui (GV20)-based scalp acupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke. Sci Rep 4(2):3981
Yang Y, Takeuchi K, Rodenas-Ruano A, Takayasu Y, Bennett MVL, Zukin RS (2009) Developmental switch in requirement for PKA RIIbeta in NMDA-receptor dependent synaptic plasticity at Schaffer collateral to CA1 pyramidal cell synapses. Neuropharmacology 56:56–65
Yasuda H, Barth AL, Stellwagen D, Malenka RC (2002) A developmental switch in the signaling cascades for LTP induction. Nat Neurosci 6:15–16
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NO.81403450) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (NO.2016 J01382) and the Foundation of Collaborative Innovation Center of Rehabilitation Technology (Fujian Province) (NO.2016001-collaborative).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhifu Wang and Bingbing Lin contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 31 kb)
ESM 2
Neuronal damage in the ischemic brain areas of MICD model rats. (A-O) showed the representative images and quantitative graphs for immunostaining with NeuN (brown cell) antibody on different brain areas of sham and MICD groups at 14 days. (A-G) present the NeuN immunostaining of the MICD group in ischemic (B-D) cortex and (E-G) CA1. (H-N) present the NeuN immunostaining of the sham group in ipsilateral (I-K) cortex and (L-N) CA1. (A)(H) Original magnification ×25. (B)(E)(I)(L) Original magnification ×100. (C)(F)(J)(M) Original magnification ×200. (D)(G)(K)(N) Original magnification ×400. Values are expressed as the means±SEM (n = 6 for each group). **P < 0.01. MICD: middle artery occlusion-induced cognitive deficit. (PNG 15 kb)
ESM 3
(PNG 3549 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Lin, B., Liu, W. et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates learning and memory deficits via hippocampal 5-HT1A receptors and the PKA signaling pathway in rats with ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis 35, 549–558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00489-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00489-y