Abstract
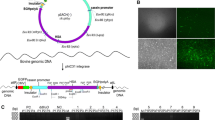
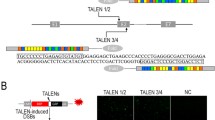
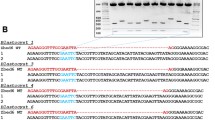
Rotavirus (RV) is the leading cause of viral gastroenteritis in neonates and VP6 protein has been discussed as a potential candidate vaccine. CRISPR/Cas9 was the latest generation of gene editing tools that can mediate the site-specific knock-in of exogenous genes, providing strong support for the expression of recombinant proteins. Here, seeking to design a rotavirus vaccine that would be suitable for both mammary-gland-based production and milk-based administration, rabbit β-casein (CSN2) locus was chosen as the target site to integrate the VP6 gene. The efficiency of inducing mutations in different target sites of rabbit CSN2 locus was analyzed and g4 site seems to be the best one to generate mutations (g4 72.76 ± 0.32% vs g1 30.14 ± 1.93%, g2 38.53 ± 0.75%, g3 52.26 ± 1.16%, P < 0.05). We further compared the knock-in efficiency through cytoplasmic injection of two group mixtures (containing 100 ng/μL Cas9 mRNA or Cas9 protein, 20 ng/μL sgRNA4, and 100 ng/μL donor vector) in rabbit zygotes, though the Cas9 mRNA group induced an HDR efficiency as high as 20.0% ± 2.6% than Cas9 protein group (10.3% ± 3.1%), 37.5% of the knock-in events were partial integration in the target site, when Cas9 protein used in the CRISPR/Cas9 system, all of the positive blastocysts showed completely integrated, results showed that the use of Cas9 protein is better than Cas9 mRNA to integrate the correct exogenous gene into the target site. Moreover, the transgenic rabbit that harbored correct integration of VP6 gene was obtained using Cas9 protein group and was used to produce an experimental milk-based rotavirus vaccine. Our research provides a novel strategy to produce rotavirus subunit vaccine and make a foundation for building broader milk-based vaccine protection against other pathogens.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya SC, Agarwal N (2012) Apropos risks associated with the use of live-attenuated vaccine poliovirus strains and the strategies for control and eradication of paralytic poliomyelitis. Expert Rev Vaccines 11:609–628. https://doi.org/10.1586/erv.12.110
Bibikova M, Golic M, Golic KG, Carroll D (2002) Targeted chromosomal cleavage and mutagenesis in Drosophila using zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics. 287:2185–2195. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5461.2185
Blazevic V, Lappalainen S, Nurminen K, Huhti L, Vesikari T (2011) Norovirus VLPs and rotavirus VP6 protein as combined vaccine for childhood gastroenteritis. Vaccine 29:8126–8133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.08.026
Bösze Z, Hiripi L (2012) Recombinant protein expression in milk of livestock species. Methods Mol Biol 824:629–641. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-433-9_34
Burnett E, Jonesteller CL, Tate JE, Yen C, Parashar UD (2017) Global impact of rotavirus vaccination on childhood hospitalizations and mortality from diarrhea. J Infect Dis 215:1666–1672. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jix186
Burns JW, Siadat-Pajouh M, Krishnaney AA, Greenberg HB (1996) Protective effect of rotavirus VP6-specific IgA monoclonal antibodies that lack neutralizing activity. Science 272(80):104–107. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5258.104
Carlson DF, Tan W, Lillico SG, Stverakova D, Proudfoot C, Christian M, Voytas DF, Long CR, Whitelaw CBA, Fahrenkrug SC (2012) Efficient TALEN-mediated gene knockout in livestock. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:17382–17387. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211446109
Cho SW, Kim S, Kim JM, Kim JS (2013) Targeted genome engineering in human cells with the Cas9 RNA-guided endonuclease. Nat Biotechnol 31:230–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2507
Choi AH, McNeal MM, Basu M et al (2002) Intranasal or oral immunization of inbred and outbred mice with murine or human rotavirus VP6 proteins protects against viral shedding after challenge with murine rotaviruses. Vaccine 20:3310–3321. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00315-8
Choi AHC, McNeal MM, Basu M, Bean JA, VanCott J, Clements JD, Ward RL (2003) Functional mapping of protective epitopes within the rotavirus VP6 protein in mice belonging to different haplotypes. Vaccine. 21:761–767
Concordet J, Haeussler M (2018) CRISPOR: intuitive guide selection for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing experiments and screens. Nucleic Acids Res 46:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky354
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N, Hsu PD, Wu X, Jiang W, Marraffini LA, Zhang F (2013) Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339(80):819–823. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1231143
Dennehy PH (2007) Rotavirus vaccines-an update. Vaccine 25:3137–3141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.01.102
Doench JG, Hartenian E, Graham DB, Tothova Z, Hegde M, Smith I, Sullender M, Ebert BL, Xavier RJ, Root DE (2014) Rational design of highly active sgRNAs for CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene inactivation. Nat Biotechnol 32:1262–1267. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3026
Dong JL, Liang BG, Jin YS, Zhang WJ, Wang T (2005) Oral immunization with pBsVP6-transgenic alfalfa protects mice against rotavirus infection. Virology 339:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2005.06.004
Estes MK, Cohen J (1989) Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol Rev 63:2555–2562. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.13826
Goveia MG, Rodriguez ZM, Dallas MJ, Itzler RF, Boslego JW, Heaton PM, DiNubile MJ (2007) Safety and efficacy of the pentavalent human-bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine in healthy premature infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 26:1099–1104. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0b013e31814521cb
Hai T, Teng F, Guo R, Li W, Zhou Q (2014) One-step generation of knockout pigs by zygote injection of CRISPR/Cas system. Cell Res 24:372–375. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.11
Houdebine LM (2009) Production of pharmaceutical proteins by transgenic animals. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 32:107–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2007.11.005
Hsu PD, Scott DA, Weinstein JA, Ran FA, Konermann S, Agarwala V, Li Y, Fine EJ, Wu X, Shalem O, Cradick TJ, Marraffini LA, Bao G, Zhang F (2013) DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 31:827–832. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2647
Jalilvand S, Marashi SM, Shoja Z (2015) Rotavirus VP6 preparations as a non-replicating vaccine candidates. Vaccine 33:3281–3287
Jiang B, Gentsch JR, Glass RI (2008) Inactivated rotavirus vaccines: a priority for accelerated vaccine development. Vaccine 26:6754–6758
Jinek M, East A, Cheng A, Lin S, Ma E, Doudna J (2013) RNA-programmed genome editing in human cells. Elife. 2. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00471
Kim S, Kim D, Cho SW, Kim J, Kim JS (2014) Highly efficient RNA-guided genome editing in human cells via delivery of purified Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Genome Res 24:1012–1019. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.171322.113
Lamrani A, Tubert-Bitter P, Hill C, Escolano S (2017) A benefit–risk analysis of rotavirus vaccination, France, 2015. Eurosurveillance 22:28–37. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.50.17-00041
Lappalainen S, Pastor AR, Malm M, López-Guerrero V, Esquivel-Guadarrama F, Palomares LA, Vesikari T, Blazevic V (2015) Protection against live rotavirus challenge in mice induced by parenteral and mucosal delivery of VP6 subunit rotavirus vaccine. Arch Virol 160:2075–2078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2461-8
Li D, Qiu Z, Shao Y, Chen Y, Guan Y, Liu M, Li Y, Gao N, Wang L, Lu X, Zhao Y, Liu M (2013) Heritable gene targeting in the mouse and rat using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat Biotechnol 31:681–683. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2661
Liang X, Potter J, Kumar S, Ravinder N, Chesnut JD (2017) Enhanced CRISPR/Cas9-mediated precise genome editing by improved design and delivery of gRNA, Cas9 nuclease, and donor DNA. J Biotechnol 241:136–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.11.011
Lönnerdal B (2003) Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am J Clin Nutr 77:1537S–1543S
Lönnerdal B (2014) Infant formula and infant nutrition: bioactive proteins of human milk and implications for composition of infant formulas. Am J Clin Nutr 99:712S–717S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.113.071993
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo JE, Norville JE, Church GM (2013) RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 339(80):823–826. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1232033
Matsumura T, Itchoda N, Tsunemitsu H (2002) Production of immunogenic VP6 protein of bovine group A rotavirus in transgenic potato plants: brief report. Arch Virol 147:1263–1270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0808-4
Niu Y, Shen B, Cui Y, Chen Y, Wang J, Wang L, Kang Y, Zhao X, Si W, Li W, Xiang AP, Zhou J, Guo X, Bi Y, Si C, Hu B, Dong G, Wang H, Zhou Z, Li T, Tan T, Pu X, Wang F, Ji S, Zhou Q, Huang X, Ji W, Sha J (2014) Generation of gene-modified cynomolgus monkey via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting in one-cell embryos. Cell 156:836–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.027
Ruiz-Palacios GM, Pérez-Schael I, Velázquez FR, Abate H, Breuer T, Clemens SAC, Cheuvart B, Espinoza F, Gillard P, Innis BL, Cervantes Y, Linhares AC, López P, Macías-Parra M, Ortega-Barría E, Richardson V, Rivera-Medina DM, Rivera L, Salinas B, Pavía-Ruz N, Salmerón J, Rüttimann R, Tinoco JC, Rubio P, Nuñez E, Guerrero ML, Yarzábal JP, Damaso S, Tornieporth N, Sáez-Llorens X, Vergara RF, Vesikari T, Bouckenooghe A, Clemens R, de Vos B, O'Ryan M (2006) Safety and efficacy of an attenuated vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med 354:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa052434
Shen B, Zhang J, Wu H, Wang J, Ma K, Li Z, Zhang X, Zhang P, Huang X (2013) Generation of gene-modified mice via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting. Cell Res 23:720–723. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.46
Soler E, Le Saux A, Guinut F et al (2005) Production of two vaccinating recombinant rotavirus proteins in the milk of transgenic rabbits. Transgenic Res 14:833–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-005-1771-0
Soler E, Parez N, Passet B, Dubuquoy C, Riffault S, Pillot M, Houdebine LM, Schwartz-Cornil I (2007) Recombinant rotavirus inner core proteins produced in the milk of transgenic rabbits confer a high level of protection after intrarectal delivery. Vaccine 25:6373–6380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.06.011
Sonoda E, Hochegger H, Saberi A, Taniguchi Y, Takeda S (2006) Differential usage of non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination in double strand break repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 5:1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.05.022
Tang B, Gilbert JM, Matsui SM, Greenberg HB (1997) Comparison of the rotavirus gene 6 from different species by sequence analysis and localization of subgroup-specific epitopes using site-directed mutagenesis. Virology 237:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1997.8762
Wu X, Scott DA, Kriz AJ, Chiu AC, Hsu PD, Dadon DB, Cheng AW, Trevino AE, Konermann S, Chen S, Jaenisch R, Zhang F, Sharp PA (2014) Genome-wide binding of the CRISPR endonuclease Cas9 in mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol 32:670–676. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2889
Yu J, Langridge W (2003) Expression of rotavirus capsid protein VP6 in transgenic potato and its oral immunogenicity in mice. Transgenic Res 12:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022912130286
Zhang JH, Pandey M, Kahler JF, Loshakov A, Harris B, Dagur PK, Mo YY, Simonds WF (2014) Improving the specificity and efficacy of CRISPR/CAS9 and gRNA through target specific DNA reporter. J Biotechnol 189:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.08.033
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge our friend Laiba Shafique for helping us in revising the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 31860638) and Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. AA17204051 and AB16380042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Li, Z., Xiao, N. et al. Site-specific integration of rotavirus VP6 gene in rabbit β-casein locus by CRISPR/Cas9 system. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 55, 586–597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00382-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00382-z