Abstract
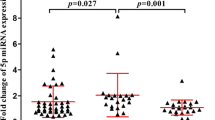
Natalizumab is effective against relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) but increases the risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), which is caused by the activation of the JCV polyomavirus. SF2/ASF (splicing factor2/alternative splicing factor) is a potent cellular inhibitor of JCV replication and large T-antigen (T-Ag) expression. We reported that SF2/ASF levels in blood cells increase during the first year of natalizumab therapy and decrease thereafter, inversely related to T-Ag expression, and suggested a correlation with JCV reactivation. Here, we report SF2/ASF levels of longitudinal blood samples of two patients undergoing natalizumab therapy, who developed PML while monitored, in comparison to natalizumab-treated controls and to one-off PML samples. After 6 months of therapy, SF2/ASF levels of the two cases were reduced, instead of increased, and their overall SF2/ASF levels were lower than those from natalizumab controls. Since SF2/ASF inhibits JCV, its early reduction might have a role in subsequent PML. We are aware of the limitations of the study, but the uniqueness of serial blood samples collected before and after PML onset in natalizumab-treated patients must be stressed. If confirmed in other patients, SF2/ASF evaluation could be a new and early biomarker of natalizumab-associated PML risk, allowing an 18–24-month interval before PML onset (presently ~ 5 months), in which clinicians could evaluate other risk factors and change therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assetta B, Atwood WJ (2017) The biology of JC polyomavirus. Biol Chem 398:839–855. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2016-0345
Berger JR, Koralnik IJ (2005) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and natalizumab--unforeseen consequences. N Engl J Med 353:414–416. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMe058122
Chalkias S, Dang X, Bord E, Stein MC, Kinkel RP, Sloane JA, Donnelly M, Ionete C, Houtchens MK, Buckle GJ, Batson S, Koralnik IJ (2014) JC virus reactivation during prolonged Natalizumab monotherapy for multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 75:925–934. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24148
Craigie M, Regan P, Otalora YL, Sariyer IK (2015) Molecular interplay between T-antigen and splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 1 (SRSF1) controls JC virus gene expression in glial cells. Virol J 12:196. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-015-0426-x
Gerevini S, Capra R, Bertoli D, Sottini A, Imberti L (2019) Immune profiling of a patient with alemtuzumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Mult Scler 25:1196-1201. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458519832259
Lee P, Plavina T, Castro A, Berman M, Jaiswal D, Rivas S, Schlain B, Subramanyam M (2013) A second-generation ELISA (STRATIFY JCV™ DxSelect™) for detection of JC virus antibodies in human serum and plasma to support progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy risk stratification. J Clin Virol 57:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2013.02.002
Lindberg RLP, Achtnichts L, Hoffman F, Kuhle J, Kappos L (2008) Natalizumab alters transcriptional expression profiles of blood cell subpopulations of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol 194:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.11.007
Mill EA, Mao-Draayer Y (2018) Understanding progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy risk in multiple sclerosis patients treated with immunomodulatory therapies: a bird’s eye view. Front Immunol 9:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00138
Scarpazza C, Signori A, Prosperini L, Sormani MP, Cosottini M, Capra R, Gerevini S, Italian PML Group (2019) Early diagnosis of progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy: longitudinal lesion evolution. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-319208
Tintore M, Vidal-Jordana A, Sastre-Garriga J (2019) Treatment of multiple sclerosis - success from bench to bedside. Nat Rev Neurol 15:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0082-z
Uleri E, Regan P, Dolei A, Sariyer IK (2013) SF2/ASF binding region within JC virus NCCR limits early gene transcription in glial cells. Virol J 10:147. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-10-147
Uleri E, Ibba G, Piu C, Caocci M, Leoni S, Arru G, Serra C, Sechi G, Dolei A (2017) JC polyomavirus expression and bell-shaped regulation of its SF2/ASF suppressor during the follow-up of multiple sclerosis patients treated with natalizumab. J Neurovirol 23:226–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-016-0492-x
Zhao Y, Zhu T, Zhang X, Wang Q, Zhang J, Ji W, Ma Y (2015) Splicing factor 2/alternative splicing factor contributes to extracellular signal regulated kinase activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep 12:3890–3894. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3851
Acknowledgments
GI and CP share the first authorship. The Authors thank Dr. C. Scarpazza (MS Centre, Spedali Civili, Brescia) for helping in the collection of clinical data.
Funding
This study was financially supported in part by Fondazione Italia Sclerosi Multipla (AD, FISM2016_R_12; LI, FISM2016_R_16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Brescia Ethical Committee Board (protocols 2713 of 05/24/2017 and NP0 of 07/18/2018).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Claudia Piu and Gabriele Ibba share the first authorship
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piu, C., Ibba, G., Bertoli, D. et al. Early reduction of the splicing factor2/alternative splicing factor: a cellular inhibitor of the JC polyomavirus in natalizumab-treated MS patients long before developing progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Neurovirol. 26, 133–137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-019-00793-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-019-00793-4