Abstract
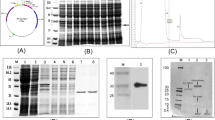
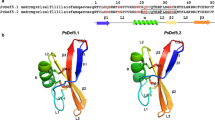
We isolated a stamen-specific cDNA, BSD1 (Brassica stamen specific plant defensin 1) that encodes a novel plant defensin peptide in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis). Plant defensins are antimicrobial peptides containing eight highly conserved cysteine residues linked by disulfide bridges. In BSD1, the eight cysteine residues and a glutamate residue at position 29 are conserved whereas other amino acid residues of the plant defensins consensus sequence are substituted. BSD1 transcripts accumulate specifically in the stamen of developing flowers and its level drops as the flowers mature. The recombinant BSD1 produced in Escherichia coli showed antifungal activity against several phytopathogenic fungi. Furthermore, constitutive over-expression of the BSD1 gene under the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter conferred enhanced tolerance against the Phytophthora parasitica in the transgenic tobacco plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, G., Ebert, P.R., Mitra, A. and Ha, S.B. 1988. Binary vectors. In: S.B. Gelvin, R.A. Schilperoort and D.P.S. Verma (Eds) Plant Molecular Biology Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. A3/1–A3/19.
Bloch, C. and Richardson, M. 1991. A new family of small (5 kDa) protein inhibitors of insect ?-amylases from seeds of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) have sequence homologies with wheat ?-purothionins. FEBS Lett. 279: 101–104.
Bohlmann, H. 1994. The role of thionins in plant protection. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 13: 1–6.
Bohlmann, H. and Apel, K. 1991. Thionins. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 42: 227–240.
Broekaert, W.F., Terras, F.R.G., Cammue, B.P.A. and Osborn, R.W. 1995. Plant defensins: novel antimicrobial peptides as components of the host defense system. Plant Physiol. 108: 1353–1358.
Broekaert, W.F., Cammue, B.P.A., De Bolle, M.F.C., Thevissen, K., De Samblanx, G.W. and Osborn, R.W. 1997. Antimicrobial peptides from plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 16: 297–323.
Cammue, B.P.A., De Bolle, M.F., Terras, F.R.G., Proost, P., Van Damme, J., Rees, S.B., Vanderleyden, J. and Broekaert, W.F. 1992. Isolation and characterization of a novel class of plant antimicrobial peptides form Mirabilis jalapa L. seeds. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 2228–2233.
Chiang, C.C. and Hadwiger, L.A. 1991. The Fusarium solaniinduced expression of a pea gene family encoding high cysteine content proteins. Mol. Plant-Microbe. Interact. 4: 324–331.
Colilla, F.J., Rocher, A. and Mendez, E. 1990. ?-purothionins: amino acid sequence of two polypeptides of a new family of thionins from wheat endosperm. FEBS Lett. 270: 191–194.
De Samblanx, G.W., Fernandez, A., Sijtsma, L., Plasman, H.H., Schaaper, W.M.M., Posthuma, G.A., Fant, F., Meloen, R.H., Broekaert, W.F. and van Amerongen, A. 1996. Antifungal activity of synthetic 15-mer peptides based on the Rs-AFP2 (Raphanus sativus antifungal protein 2) sequence. Peptide Res. 9: 262–268.
De Samblanx, G.W., Goderis, I.J., Thevissen, K., Raemaekers, R., Fant, F., Borremans, F., Acland, D., Osborn, R.W., Patel, S. and Broekaert, W.F. 1997. Mutational analysis of a plant defensin from radish (Raphanus sativus L.) reveals two adjacent sites important for antifungal activity. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 1171–1179.
Dellaporta, S., Wood, J. and Hicks, J. 1983. A plant DNA miniprep. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1: 19–21.
Dixon, R.A. 1986. The phytoalexin response: elicitation, signaling and control of host gene expression. Biol. Rev. 61: 239–291.
Duvick, J.P., Rood, T., Rao, A.G. and Marshak, D.R. 1992. Purifi-cation and characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from maize (Zea mays L.) kernels. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 18814–18820.
Epple, P., Apel, K. and Bohlmann, H. 1997. ESTs reveal a multigene family for plant defensins in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 400: 168–172.
Gao, A.-G., Hakimi, S. M., Mittanck, C. A., Wu, Y., Woerner, B. M., Stark, D. M., Shah, D. M., Liang, J. and Rommens, C. M. T. 2000. Fungal pathogen protection in potato by expression of a plant defensin peptide. Nature Biotechnol. 18: 1307–1310.
Garcia-Olmedo, F., Molina, A., Segura, A. and Moreno, M. 1995. The defensive role of nonspecific lipid-transfer proteins in plants. Trends Microbiol. 3: 72–74.
Garcia-Olmedo, F., Molina, A., Alamillo, J. M. and Rodriguez-Palenzuela, P. 1998. Plant defense peptides. Biopolymers 47: 479–491.
Gu, Q., Kawarta, E.F., Morse, M-J., Wu, H-M. and Cheung, A.Y. 1992. A flower-specific cDNA encoding a novel thionin in tobacco. Mol. Gen. Genet. 234: 89–96.
Harrison, S.J., Marcus, J.P., Goulter, K.C., Green, J.L., Maclean, D.J. and Manners, J.M. 1997. An antimicrobial peptide from the Australian native Hardenbergia violacea provides the first functionally characterized member of a subfamily of plant defensins. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 24: 571–578.
Heo, W.D., Lee, S.H., Kim, M.C., Kim, J.C., Chung, W.S., Chun, H.J., Lee, K.J., Park, C.Y., Park, H.C., Choi, J.Y. and Cho, M.J. 1999. Involvement of specific calmodulin isoforms in salicylic acid-independent activation of plant disease resistance responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 766–771.
Hoffmann, J.A. and Hetru, C. 1992. Insect defensins: inducible antibacterial peptides. Immunol. Today 13: 411–415.
Hood, M.E. and Shew, H.D. 1996. Applications of KOH-aniline blue fluorescence in the study of plant-fungal interactions. Phytophathology 86: 704–708.
Horsch, R.B., Fry, J.E., Hoffmann, N.L., Eichhoitz, D., Rogers, S.G. and Fraley, R.T. 1985. A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227: 1229–1231.
Hu, X. and Reddy, A.S.N. 1997. Cloning and expression of a PR5-like protein from Arabidopsis: inhibition of fungal growth by bacterially expressed protein. Plant Mol. Biol. 34: 949–959.
Karunanandaa, B., Singh, A. and Kao, T-h. 1994. Characterization of a predominantly pistil-expressed gene encoding a ?-thioninlike protein of Petunia inflata. Plant Mol. Biol. 26: 459–464.
Koo, J.C., Lee, S.Y., Chun, H.J., Cheong, Y.H., Choi, J.S., Kawabata, S.I., Miyagi, M., Tsunasawa, S., Ha, K.S., Bae, D.W., Han, C-D., Lee, B.L. and Cho, M.J. 1998. Two hevein homologs isolated from the seed of Pharbitis nil L. exhibit potent antifungal activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1382: 80–90.
Kragh, K.M., Nielsen, J.E., Nielsen, K.K., Dreboldt, S. and Mikkelsen, J.D. 1995. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 8: 424–434.
Lee, S.H., Kim, J.C., Lee, M.S., Heo, W.D., Seo, H.Y., Yoon, H.W., Hong, J.C., Lee, S.Y., Bahk, J.D., Hwang, I. and Cho, M.J. 1995. Identification of a novel divergent calmodulin isoform from soybean which has a different ability to activate calmodulindependent enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 21806–21812.
Lehrer, R.I., Lichtenstein, A.K. and Ganz, T. 1993. Defensins: antimicrobial and cytotoxic peptides of mammalian cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 11: 105–128.
Lim, C.O., Kim, H.Y., Kim, M.G., Lee, S.I., Chung, W.S., Park, S.H., Hwang, I. and Cho, M.J. 1996. Expressed sequence tags of Chinese cabbage flower bud cDNA. Plant Physiol. 111: 577–588.
Linthorst, H.J.M. 1991. Pathogenesis-related proteins of plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 10: 123–150.
Mendez, E., Moreno, A., Collila, F., Pelaez, F., Limas, G.G., Mendez, R., Soriano, F., Salinas, M. and DeHaro, C. 1990. Primary structure and inhibition of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cell-free system of a novel thionin, ?-hordothionin, from barley endosperm. Eur. J. Biochem. 194: 533–539.
Meyer, B., Houlné, G., Pozueta-Romero, J., Schantz, M.-L. and Schantz, R. 1996. Fruit-specific expression of a defensin-type gene family in bell pepper. Plant Physiol. 112: 615–622.
Moreno, M., Segura, A. and Garcia-Olmedo, F. 1994. Pseudothionin, a potato peptide active against potato pathogens. Eur. J. Biochem. 223: 135–139.
Nielsen, K.K., Nielsen, J.E., Madrid, S.M. and Mikkelsen, J.D. 1997. Characterization of a new antifungal chitin-binding peptide from sugar beet leaves. Plant Physiol. 113: 83–91.
Nitti, G., Orru, S., Bloch, C. Jr, Morhy, L., Marino, G. and Pucci, P. 1995. Amino acid sequence and disulphide-bridge pattern of three gamma-thionins from Sorghum bicolor. Eur. J. Biochem. 228: 250–256.
Oh, B.J., Moon, K.K., Kostenyuk, I., Shin, B.C. and Kim, K.S. 1999. Coexpression of a defensin gene and a thionin-like gene via different signal transduction pathways in pepper and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides interactions. Plant Mol. Biol. 41: 313–319.
Osborn, R.W., De Samblanx, G.W., Thevissen, K., Goderis, I., Torrekens, S., Van Leuven, F., Attenborough, S., Rees, S.B. and Broekaert, W.F. 1995. Isolation and characterization of plant defensins from seeds of Asteraceae, Fabaceae, Hippocastanaceae and Saxifragaceae. FEBS Lett. 368: 257–262.
Patel, S.U., Osborn, R., Rees, S. and Thornton, J.M. 1998. Structural studies of Impatiens balsamina antimicrobial protein (Ib-AMP1). Biochemistry 37: 983–990.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T.A. 1989. Molecular Cloning: A laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A.R. 1977. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74: 5463–5467.
Segura, A., Moreno, M., Madueno, F., Molina, A. and Garcia-Olmedo, F. 1999. Snakin-1, a peptide from potato that is active against plant pathogens. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 12: 16–23.
Tailor, R.H., Acland, D.P., Attenborough, S., Cammue, B.P.A., Evans, I.J., Osborn, R.W., Ray, J.A., Rees, S.B. and Broekaert, W.F. 1997. A novel family of small cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides from seed of Impatiens balsamina is derived from a single precursor protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 24480–24487.
Terras, F.R.G., Eggermont, K., Kovaleva, V., Raikhel, N.V., Osborn, R.W., Kester, A., Rees, S.B., Torrekens, S., Van Leuven, F., Vanderleyden, J., Cammue, B.P.A. and Broekaert, W.F. 1995. Small cysteine-rich antifungal proteins from radish: their role in host defense. Plant Cell 7: 573–588.
Terras, F.R.G., Schoofs, H.M.E., De Bolle, M.F.C., Van Leuven, F., Rees, S.B., Vanderleyden, J., Cammue, B.P.A. and Broekaert, W.F. 1992. Analysis of two novel classes of plant antifungal proteins from radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seeds. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 15301–15309.
Terras, F.R.G., Torrekens, S., Van Leuven, F., Osborn, R.W., Vanderleyden, J., Cammue, B.P.A. and Broekaert, W.F. 1993. A new family of basic cysteine-rich plant antifungal proteins from Brassicaceae species. FEBS Lett. 316: 233–240.
van Loon, L.C. and van Kammen, A. 1970. Polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis of soluble leaf proteins from Nicotiana tabacum var. Samson NN. II. Changes in protein composition after infection with TMV. Virology 40: 199–211.
von Heijne, G. 1986. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucl. Acids Res. 14: 4683–4690.
Vorm, O., Roepstorff, P. and Mann, M. 1994. Improved resolution and very high sensitivity in MALDI TOF of matrix surfaces made by fast evaporation. Anal. Chem. 66: 3281–3287.
Yun, D.-J., D'Urzo, M.P., Abad, L., Takeda, S., Salzman, R., Chen, Z., Lee, H.S., Hasegawa, P.M. and Bressan, R.A. 1996. Novel osmotically induced antifungal chitinases and bacterial expression of an active recombinant isoform. Plant Physiol. 111: 1219–1225.
Yun, D.-J., Bressan, R.A. and Hasegawa, P.M. 1997. Plant antifungal proteins. In: J. Janick (Ed.) Plant Breeding Reviews 14, John Wiley, New York, pp. 39–88.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H.C., Hwan Kang, Y., Jin Chun, H. et al. Characterization of a stamen-specific cDNA encoding a novel plant defensin in Chinese cabbage. Plant Mol Biol 50, 57–68 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016005231852
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016005231852