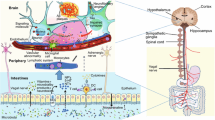
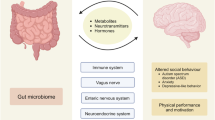
Abstract
Emerging evidences indicate a critical role of the gut microbiota in etiopathogenesis of dementia, a debilitating multifactorial disorder characterized by progressive deterioration of cognition and behavior that interferes with the social and professional functions of the sufferer. Available data suggest that gut microbiota disorder that triggers development of dementia is characterized by substantial reduction in specific species belonging to the Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes phyla and presence of pathogenic species, predominantly, pro-inflammatory bacteria of the Proteobacteria phylum. These changes in gut microbiota microecology promote the production of toxic metabolites and pro-inflammatory cytokines, and reduction in beneficial substances such as short chain fatty acids and other anti-inflammatory factors, thereby, enhancing destruction of the gut epithelial barrier with concomitant activation of local and distant immune cells as well as dysregulation of enteric neurons and glia. This subsequently leads to blood–brain barrier dysfunctions that trigger neuroinflammatory reactions and predisposes to apoptotic neuronal and glial cell death, particularly in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex, which underlie the development of dementia. However, the molecular switches that control these processes in the histo-hematic barriers of the gut and brain are not exactly known. This review integrates very recent data on the molecular mechanisms that link gut microbiota disorder to gut epithelial and blood–brain barrier dysfunctions, underlying the development of dementia. The signaling pathways that link gut microbiota disorder with impairment in cognition and behavior are also discussed. The review also highlights potential therapeutic options for dementia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari, E., Asemi, Z., Daneshvar Kakhaki, R., Bahmani, F., Kouchaki, E., Tamtaji, O. R., et al. (2016). Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 8, 256.
Akkasheh, G., Kashani-Poor, Z., Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M., Jafari, P., Akbari, H., Taghizadeh, M., et al. (2016). Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition, 32(3), 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2015.09.003.
Alhasson, F., Das, S., Seth, R., Dattaroy, D., Chandrashekaran, V., Ryan, C. N., et al. (2017). Altered gut microbiome in a mouse model of Gulf War Illness causes neuroinflammation and intestinal injury via leaky gut and TLR4 activation. PLoS ONE, 12(3), e0172914.
Alkasir, R., Li, J., Li, X., Jin, M., & Zhu, B. (2017). Human gut microbiota: The links with dementia development. Protein Cell, 8(2), 90–102.
Almeida, O. P., & Lautenschlager, N. T. (2005). Dementia associated with infectious diseases. International Psychogeriatrics, 17(Suppl 1), S65–S77.
Amasheh, S., Fromm, M., & Günzel, D. (2011). Claudins of intestine and nephron: A correlation of molecular tight junction structure and barrier function. Acta Psychologica, 201(1), 133–140.
Araos, R., Andreatos, N., Ugalde, J., Mitchell, S., Mylonakis, E., & D’Agata, E. M. C. (2018). Fecal microbiome among nursing home residents with advanced dementia and Clostridium difficile. Digestive Diseases and Sciences., 63, 1525–1531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5030-7.
Asgari, E., Farrar, C. A., Lynch, N., Ali, Y. M., Roscher, S., Stover, C., et al. (2014). Mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2 is critical for the development of renal ischemia reperfusion injury and mediates tissue injury in the absence of complement C4. The THE FASEB JOURNALournal, 28(9), 3996–4003.
Awad, W. A., Hess, C., & Hess, M. (2017). Enteric pathogens and their toxin-induced disruption of the intestinal barrier through alteration of tight junctions in chickens. Toxins (Basel), 9(2), 60.
Bambury, A., Sandhu, K., Cryan, J. F., & Dinan, T. G. (2018). Finding the needle in the haystack: Systematic identification of psychobiotics. British Journal of Pharmacology., 175, 4430–4438. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14127.
Bäuerl, C., Collado, M. C., Diaz Cuevas, A., Viña, J., & Pérez Martínez, G. (2018). Shifts in gut microbiota composition in an APP/PSS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease during lifespan. Letters in Applied Microbiology., 66, 464–471. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12882.
Bayliss, J. A., Lemus, M., Santos, V. V., Deo, M., Elsworth, J. D., & Andrews, Z. B. (2016). Acylated but not des-acyl ghrelin is neuroprotective in an MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 137, 460–471.
Bhat, M. I., & Kapila, R. (2017). Dietary metabolites derived from gut microbiota: Critical modulators of epigenetic changes in mammals. Nutrition Reviews, 75(5), 374–389.
Bjarnadottir, H., Arnardottir, M., & Ludviksson, B. R. (2016). Frequency and distribution of FCN2 and FCN3 functional variants among MBL2 genotypes. Immunogenetics, 68, 315–325.
Bonder, M. J., Kurilshikov, A., Tigchelaar, E. F., Mujagic, Z., Imhann, F., Vila, A. V., et al. (2016). The effect of host genetics on the gut microbiome. Nature Genetics, 48(11), 1407–1412.
Bonfili, L., Cecarini, V., Berardi, S., Scarpona, S., Suchodolski, J. S., Nasuti, C., et al. (2017). Microbiota modulation counteracts Alzheimer’s disease progression influencing neuronal proteolysis and gut hormones plasma levels. Scientific Report, 7, 2426.
Bonfili, L., Cecarini, V., Cuccioloni, M., Angeletti, M., Berardi, S., Scarpona, S., et al. (2018). SLAB51 probiotic formulation activates SIRT1 pathway promoting antioxidant and neuroprotective effects in an AD mouse model. Molecular Neurobiology, 55(10), 7987–8000.
Brady, A. M., Geno, K. A., Dalecki, A. G., Cheng, X., & Nahm, M. H. (2014). Commercially available complement component-depleted sera are unexpectedly codepleted of ficolin-2. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 21(9), 1323–1329.
Braniste, V., Al-Asmakh, M., Kowal, C., Anuar, F., Abbaspour, A., Tóth, M., et al. (2014). The gut microbiota influences blood–brain barrier permeability in mice. Science Translational Medicine, 6(263), 263ra158.
Britton, E., & McLaughlin, J. T. (2013). Ageing and the gut. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 72(1), 173–177.
Browne, T. C., McQuillan, K., McManus, R. M., O’Reilly, J. A., Mills, K. H., & Lynch, M. A. (2013). IFN-γ Production by amyloid β-specific Th1 cells promotes microglial activation and increases plaque burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Immunology, 190(5), 2241–2251.
Buford, T. W. (2017). (Dis)Trust your gut: The gut microbiome in age-related inflammation, health, and disease. Microbiome, 5, 80.
Burokas, A., Arboleya, S., Moloney, R. D., Peterson, V. L., Murphy, K., Clarke, G., et al. (2017). Targeting the microbiota–gut–brain axis: Prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice. Biological Psychiatry, 82(7), 472–487.
Butterfield, D. A., & Boyd-Kimball, D. (2018). Oxidative stress, amyloid-β peptide, and altered key molecular pathways in the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 62(3), 1345–1367.
Cai, Z., Hussain, M. D., & Yan, L. J. (2014a). Microglia, neuroinflammation, and beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease. International Journal of Neuroscience, 124(5), 307–321.
Cai, W., Uribarri, J., Zhu, L., Chen, X., Swamy, S., Zhao, Z., et al. (2014b). Oral glycotoxins are a modifiable cause of dementia and the metabolic syndrome in mice and humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(13), 4940–4945.
Canani, R. B., Costanzo, M. D., Leone, L., Bedogni, G., Brambilla, P., Cianfarani, S., et al. (2011). Epigenetic mechanisms elicited by nutrition in early life. Nutrition Research Reviews, 24(2), 198–205.
Capaldo, C. T., Powell, D. N., & Kalman, D. (2017). Layered defense: How mucus and tight junctions seal the intestinal barrier. Journal of Molecular Medicine (Berlin), 95(9), 927–934.
Cattaneo, A., Cattane, N., Galluzzi, S., Provasi, S., Lopizzo, N., Festari, C., et al. (2017). INDIA-FBP Group. Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiology of Aging, 49, 60–68.
Ceccarelli, G., Brenchley, J. M., Cavallari, E. N., Scheri, G. C., Fratino, M., Pinacchio, C., et al. (2017). Impact of high-dose multi-strain probiotic supplementation on neurocognitive performance and central nervous system immune activation of HIV-1 infected individuals. Nutrients, 9(11), 1269.
Cenit, M. C., Sanz, Y., & Codoñer-Franch, P. (2017). Influence of gut microbiota on neuropsychiatric disorders. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 23(30), 5486–5498.
Chaudhuri, K., Samarakoon, S. M. S., Chandola, H. M., Kumar, R., & Ravishankar, B. (2011). Evaluation of diet and life style in etiopathogenesis of senile dementia: A survey study. Ayu, 32(2), 171–176.
Chen, W. W., Zhang, X., & Huang, W. J. (2016). Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports, 13(4), 3391–3396.
Cheng, D., Wang, X., Xi, Y., Cao, J., & Jiang, W. (2017). Identification of the Al-binding proteins that account for aluminum neurotoxicity and transport in vivo. Toxicol Research (Cambridge), 7(1), 127–135.
Chertkow, H., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., & Massoud, F. (2013). Definitions of dementia and predementia states in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive impairment: Consensus from the Canadian conference on diagnosis of dementia. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 5(Suppl 1), S2.
Chia, W. J., Tan, F. C., Ong, W. Y., & Dawe, G. S. (2015). Expression and localisation of brain-type organic cation transporter (BOCT/24p3R/LCN2R) in the normal rat hippocampus and after kainate-induced excitotoxicity. Neurochemistry International, 87, 43–59.
Chiappelli, F. (2018). Advances in psychobiology. New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Chin-Chan, M., Navarro-Yepes, J., & Quintanilla-Vega, B. (2015). Environmental pollutants as risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 9, 124.
Chio, C. C., Chang, C. H., Wang, C. C., Cheong, C. U., Chao, C. M., Cheng, B. C., et al. (2013). Etanercept attenuates traumatic brain injury in rats by reducing early microglial expression of tumor necrosis factor-α. BMC Neuroscience, 14, 33.
Chunchai, T., Thunapong, W., Yasom, S., Wanchai, K., Eaimworawuthikul, S., Metzler, G., et al. (2018). Decreased microglial activation through gut–brain axis by prebiotics, probiotics, or synbiotics effectively restored cognitive function in obese-insulin resistant rats. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 15, 11.
Clark, A., & Mach, N. (2016). Exercise-induced stress behavior, gut-microbiota-brain axis and diet: A systematic review for athletes. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 13, 43.
Clarke, G., Stilling, R. M., Kennedy, P. J., Stanton, C., Cryan, J. F., & Dinan, T. G. (2014). Gut microbiota: The neglected endocrine organ. Molecular Endocrinology, 28(8), 1221–1238.
Cong, X., Judge, M., Xu, W., Diallo, A., Janton, S., Brownell, E. A., et al. (2017). Influence of feeding type on gut microbiome development in hospitalized preterm infants. Nursing Research, 66(2), 123–133.
Coppo, R. (2018). The gut-kidney axis in IgA nephropathy: Role of microbiota and diet on genetic predisposition. Pediatric Nephrology (Berlin, Germany), 33(1), 53–61.
Coraci, I. S., Husemann, J., Berman, J. W., Hulette, C., Dufour, J. H., Campanella, G. K., et al. (2002). CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is expressed on microglia in Alzheimer’s disease brains and can mediate production of reactive oxygen species in response to beta-amyloid fibrils. American Journal of Pathology, 160(1), 101–112.
Corraini, P., Henderson, V. W., Ording, A. G., Pedersen, L., Horváth-Puhó, E., & Sørensen, H. T. (2017). Long-term risk of dementia among survivors of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. Stroke, 48(1), 180–186.
Crehan, H., Hardy, J., & Pocock, J. (2012). Microglia, Alzheimer’s disease, and complement. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2012, 983640.
Cristiano, C., Lama, A., Lembo, F., Mollica, M. P., Calignano, A., & Mattace Raso, G. (2018). Interplay between peripheral and central inflammation in autism spectrum disorders: Possible nutritional and therapeutic strategies. Frontiers Physiology, 9, 184.
Cupidi, C., Frangipane, F., Gallo, M., Clodomiro, A., Colao, R., Bernardi, L., et al. (2017). Role of Niemann-Pick Type C disease mutations in dementia. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 55(3), 1249–1259.
Daulatzai, M. A. (2014). Obesity and gut’s dysbiosis promote neuroinflammation, cognitive impairment, and vulnerability to Alzheimer’s disease: New directions and therapeutic implications. Journal of Molecular and Genetic Medicine, 1, 005. https://doi.org/10.4172/1747-0862.S1-005.
Davenport, E. R., Cusanovich, D. A., Michelini, K., Barreiro, L. B., Ober, C., & Gilad, Y. (2015). Genome-wide association studies of the human gut microbiota. PLoS ONE, 10(11), e0140301.
David, L. A., Maurice, C. F., Carmody, R. N., Gootenberg, D. B., Button, J. E., Wolfe, B. E., et al. (2014). Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature, 505(7484), 559–563.
de Jager, C. A., Msemburi, W., Pepper, K., & Combrinck, M. I. (2017). Dementia prevalence in a rural region of South Africa: A cross-sectional community study. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 60(3), 1087–1096.
De Preter, V., Vanhoutte, T., Huys, G., Swings, J., Rutgeerts, P., & Verbeke, K. (2006). Effect of lactulose and Saccharomyces boulardii administration on the colonic urea-nitrogen metabolism and the bifidobacteria concentration in healthy human subjects. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 23(7), 963–974.
Degn, S. E., Jensen, L., Olszowski, T., Jensenius, J. C., & Thiel, S. (2013). Co-complexes of MASP-1 and MASP-2 associated with the soluble pattern-recognition molecules drive lectin pathway activation in a manner inhibitable by MAp44. Journal of Immunology, 191(3), 1334–1345.
Di Fede, G., Giaccone, G., Salmona, M., & Tagliavini, F. (2018). Translational research in Alzheimer’s and Prion diseases. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 62(3), 1247–1259.
Di Lorenzo, F., & Di Lorenzo, B. (2013). Iron and aluminum in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroendocrinology Letters, 34(6), 504–507.
Dinan, T. G., & Cryan, J. F. (2017). Gut instincts: Microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, ageing and neurodegeneration. Journal of Physiology, 595(2), 489–503.
Doens, D., & Fernández, P. L. (2014). Microglia receptors and their implications in the response to amyloid β for Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 11, 48.
Dong, S., Duan, Y., Hu, Y., & Zhao, Z. (2012). Advances in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: A re-evaluation of amyloid cascade hypothesis. Translational Neurodegeneration, 1, 18.
Dong, J., Robertson, J. D., Markesbery, W. R., & Lovell, M. A. (2008). Serum zinc in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 15(3), 443–450.
Du, X., Wang, X., & Geng, M. (2018). Alzheimer’s disease hypothesis and related therapies. Translational Neurodegeneration, 7, 2.
Dunn, N., Mullee, M., Perry, V. H., & Holmes, C. (2005). Association between dementia and infectious disease: Evidence from a case-control study. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 19(2), 91–94.
El Khoury, J., Hickman, S. E., Thomas, C. A., Loike, J. D., & Silverstein, S. C. (1998). Microglia, scavenger receptors, and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 19(1 Suppl), S81–S84.
Engel, G. L. (1954). Studies of ulcerative colitis. II. The nature of the somatic processes and the adequacy of psychosomatic hypotheses. American Journal of Medicine, 16, 416–433.
Erdő, F., Denes, L., & de Lange, E. (2017). Age-associated physiological and pathological changes at the blood–brain barrier: A review. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 37(1), 4–24.
Evans, P. H. (1993). Free radicals in brain metabolism and pathology. British Medical Bulletin, 49(3), 577–587.
Evans, P. H., Klinowski, J., & Yano, E. (1991). Cephaloconiosis: A free radical perspective on the proposed particulate-induced etiopathogenesis of Alzheimer’s dementia and related disorders. Medical Hypotheses, 34(3), 209–219.
Evans, P. H., Yano, E., Klinowski, J., & Peterhans, E. (1992). Oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s dementia, and the potential etiopathogenic role of aluminosilicates, microglia and micronutrient interactions. EXS, 62, 178–189.
Fang, X. (2016). Potential role of gut microbiota and tissue barriers in Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. International Journal of Neuroscience, 126(9), 771–776.
Farzi, A., Fröhlich, E. E., & Holzer, P. (2018). Gut microbiota and the neuroendocrine system. Neurotherapeutics, 15(1), 5–22.
Fattahi, M. J., & Mirshafiey, A. (2014). Positive and negative effects of prostaglandins in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 68(1), 50–60.
Fernandez-Prado, R., Esteras, R., Perez-Gomez, M. V., Gracia-Iguacel, C., Gonzalez-Parra, E., Sanz, A. B., et al. (2017). Nutrients turned into toxins: Microbiota modulation of nutrient properties in chronic kidney disease. Nutrients, 9(5), 489.
Fiebich, B. L., Schleicher, S., Spleiss, O., Czygan, M., & Hüll, M. (2001). Mechanisms of prostaglandin E2-induced interleukin-6 release in astrocytes: Possible involvement of EP4-like receptors, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase C. Journal of Neurochemistry, 79(5), 950–958.
Fiest, K. M., Jetté, N., Roberts, J. I., Maxwell, C. J., Smith, E. E., Black, S. E., et al. (2016). The prevalence and incidence of dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences, 43(1), S3–S50.
Figarska, S. M., Vonk, J. M., & Boezen, H. M. (2014). NFE2L2 polymorphisms, mortality, and metabolism in the general population. Physiological Genomics, 46(12), 411–417.
Förster, C. (2008). Tight junctions and the modulation of barrier function in disease. Histochemistry and Cell Biology, 130(1), 55–70.
Foster, J. A., Rinaman, L., & Cryan, J. F. (2017). Stress & the gut–brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiology of Stress, 7, 124–136.
Fransen, F., van Beek, A. A., Borghuis, T., El Aidy, S., Hugenholtz, F., van der Gaast, et al. (2017). Aged gut microbiota contributes to systemical inflammaging after transfer to germ-free mice. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 1385.
Fratiglioni, L., De Ronchi, D., & Agüero-Torres, H. (1999). Worldwide prevalence and incidence of dementia. Drugs and Aging, 15(5), 365–375.
Friedland, R. P., & Chapman, M. R. (2017). The role of microbial amyloid in neurodegeneration. PLoS Pathogens, 13(12), e1006654.
Gambuzza, M. E., Sofo, V., Salmeri, F. M., Soraci, L., Marino, S., & Bramanti, P. (2014). Toll-like receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: A therapeutic perspective. CNS & Neurological Disorders: Drug Targets, 13(9), 1542–1558.
Genuis, S. J., & Kelln, K. L. (2015). Toxicant exposure and bioaccumulation: A common and potentially reversible cause of cognitive dysfunction and dementia. Behavioural Neurology, 2015, 620143.
Geschwind, M. D. (2010). Rapidly progressive dementia: Prion diseases and other rapid dementias. Continuum (Minneap Minn)., 16(2), 31–56.
Ghaisas, S., Maher, J., & Kanthasamy, A. (2016). Gut microbiome in health and disease: Linking the microbiome–gut–brain axis and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of systemic and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 158, 52–62.
Ghosh, S., Wu, M. D., Shaftel, S. S., Kyrkanides, S., LaFerla, F. M., Olschowka, J. A., et al. (2013). Sustained interleukin-1β overexpression exacerbates tau pathology despite reduced amyloid burden in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(11), 5053–5064.
Gordon, S. (2002). Pattern recognition receptors: Doubling up for the innate immune response. Cell, 111(7), 927–930.
Griñán-Ferré, C., Corpas, R., Puigoriol-Illamola, D., Palomera-Ávalos, V., Sanfeliu, C., & Pallàs, M. (2018). Understanding epigenetics in the neurodegeneration of Alzheimer’s disease: SAMP8 mouse model. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 62(3), 943–963.
Hanamsagar, R., Hanke, M. L., & Kielian, T. (2012). Toll-like receptor (TLR) and inflammasome actions in the central nervous system. Trends in Immunology, 33(7), 333–342.
Hang, L., Basil, A. H., & Lim, K.-L. (2016). Nutraceuticals in Parkinson’s disease. Neuromolecular Medicine, 18, 306–321.
Hartz, A., Pagel, J., Humberg, A., Preuss, M., Schreiter, L., Rupp, J., et al. (2017). The association of mannose-binding lectin 2 polymorphisms with outcome in very low birth weight infants. PLoS ONE, 12(5), e0178032.
Hasan, M. K., Liu, C., Wang, F., Ahammed, G. J., Zhou, J., Xu, M. X., et al. (2016). Glutathione-mediated regulation of nitric oxide, S-nitrosothiol and redox homeostasis confers cadmium tolerance by inducing transcription factors and stress response genes in tomato. Chemosphere, 161, 536–545.
Héja, D., Kocsis, A., Dobó, J., Szilágyi, K., Szász, R., Závodszky, P., et al. (2012). Revised mechanism of complement lectin-pathway activation revealing the role of serine protease MASP-1 as the exclusive activator of MASP-2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(26), 10498–10503.
Hickman, S. E., Allison, E. K., & El Khoury, J. (2008). Microglial dysfunction and defective β-amyloid clearance pathways in aging Alzheimer’s disease mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(33), 8354–8360.
Ho, J. T. K., Chan, G. C. F., & Li, J. C. B. (2015). Systemic effects of gut microbiota and its relationship with disease and modulation. BMC Immunology, 16, 21.
Houghteling, P. D., & Walker, W. A. (2015). Why is initial bacterial colonization of the intestine important to the infant’s and child’s health? Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 60(3), 294–307.
Hoyles, L., Snelling, T., Umlai, U. K., Nicholson, J. K., Carding, S. R., Glen, R. C., et al. (2018). Microbiome-host systems interactions: Protective effects of propionate upon the blood–brain barrier. Microbiome, 6(1), 55.
Hu, N., Tan, M.-S., Sun, L., Jiang, T., Wang, Y.-L., Tan, L., et al. (2014). Decreased expression of CD33 in peripheral mononuclear cells of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neuroscience Letters, 563, 51–54.
Hu, X., Wang, T., & Jin, F. (2016). Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota. Science China Life Sciences, 59(10), 1006–1023.
Hulse, G. K., Lautenschlager, N. T., Tait, R. J., & Almeida, O. P. (2005). Dementia associated with alcohol and other drug use. International Psychogeriatrics, 17(1), S109–S127.
Hung, Y.-N., Kadziola, Z., Brnabic, A. J. M., Yeh, J.-F., Fuh, J.-L., Hwang, J.-P., et al. (2016). The epidemiology and burden of Alzheimer’s disease in Taiwan utilizing data from the National Health Insurance Research Database. ClinicoEconomics and Outcomes Research, 8, 387–395.
Huo, R., Zeng, B., Zeng, L., Cheng, K., Li, B., Luo, Y., et al. (2017). Microbiota modulate anxiety-like behavior and endocrine abnormalities in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 7, 489. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00489.
Hwang, S., Lim, J. W., & Kim, H. (2017). Inhibitory effect of lycopene on amyloid-β-induced apoptosis in neuronal cells. Nutrients, 9(8), 883.
Iemolo, F., Duro, G., Rizzo, C., Castiglia, L., Hachinski, V., & Caruso, C. (2009). Pathophysiology of vascular dementia. Immunity & Ageing, 6, 13.
Inglese, M., & Petracca, M. (2013). Imaging multiple sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases. Prion, 7(1), 47–54.
Jacobson, A., Lam, L., Rajendram, M., Tamburini, F., Honeycutt, J., Pham, T., et al. (2018). A gut commensal-produced metabolite mediates colonization resistance to salmonella infection. Cell Host & Microbe, 24(2), 296–307.
James, B. D., & Schneider, J. A. (2010). Increasing incidence of dementia in the oldest old: Evidence and implications. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 2, 9.
Jamilian, M., Bahmani, F., Vahedpoor, Z., Salmani, A., Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M., Jafari, P., et al. (2016). Effects of probiotic supplementation on metabolic status in pregnant women: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Archives of Iranian Medicine, 19(10), 687–692.
Jana, M., Palencia, C. A., & Pahan, K. (2008). Fibrillar amyloid-β peptides activate microglia via TLR2: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Immunology, 181(10), 7254–7262.
Jiang, C., Li, G., Huang, P., Liu, Z., & Zhao, B. (2017). The gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 58(1), 1–15.
Jo, E.-K., Kim, J. K., Shin, D.-M., & Sasakawa, C. (2016). Molecular mechanisms regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 13(2), 148–159.
Johnell, K. (2015). Inappropriate drug use in people with cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review. Current Clinical Pharmacology, 10(3), 178–184.
Juárez-Rebollar, D., Rios, C., Nava-Ruíz, C., & Méndez-Armenta, M. (2017). Metallothionein in brain disorders. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2017, 5828056.
Kalantari, P. (2018). The emerging role of pattern recognition receptors in the pathogenesis of malaria. Vaccines, 6(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010013.
Kalaria, R. N. (2016). Neuropathological diagnosis of vascular cognitive impairment and vascular dementia with implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica, 131, 659–685.
Kang, D.-W., Adams, J. B., Gregory, A. C., Borody, T., Chittick, L., Fasano, A., et al. (2017). Microbiota transfer therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: An open-label study. Microbiome, 5, 10.
Katan, M., Moon, Y. P., Paik, M. C., Sacco, R. L., Wright, C. B., & Elkind, M. S. V. (2013). Infectious burden and cognitive function: The Northern Manhattan study. Neurology, 80(13), 1209–1215.
Kaushal, V., Dye, R., Pakavathkumar, P., Foveau, B., Flores, J., Hyman, B., et al. (2015). Neuronal NLRP1 inflammasome activation of Caspase-1 coordinately regulates inflammatory interleukin-1-beta production and axonal degeneration-associated Caspase-6 activation. Cell Death and Differentiation, 22(10), 1676–1686.
Kelly, J. R., Kennedy, P. J., Cryan, J. F., Dinan, T. G., Clarke, G., & Hyland, N. P. (2015). Breaking down the barriers: The gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 9, 392.
Killin, L. O. J., Starr, J. M., Shiue, I. J., & Russ, T. C. (2016). Environmental risk factors for dementia: A systematic review. BMC Geriatrics, 16, 175.
Kilpatrick, D. C., & Chalmers, J. D. (2012). Human L-ficolin (ficolin-2) and its clinical significance. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2012, 138797.
Kim, S.-H., Turnbull, J., & Guimond, S. (2011). Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: The dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. Journal of Endocrinology, 209, 139–151.
Kjeldsen, L., Johnsen, A. H., Sengeløv, H., & Borregaard, N. (1993). Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268(14), 10425–10432.
Knopman, D. S. (2006). Dementia and cerebrovascular disease. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 81(2), 223–230.
Kobylecki, C., Jones, M., Thompson, J. C., Richardson, A. M., Neary, D., Mann, D. M. A., et al. (2015). Cognitive-behavioural features of progressive supranuclear palsy syndrome overlap with frontotemporal dementia. Journal of Neurology, 262(4), 916–922.
Koedrith, P., & Seo, Y. R. (2011). Advances in carcinogenic metal toxicity and potential molecular markers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(12), 9576–9595.
Kumar, H., Lund, R., Laiho, A., Lundelin, K., Ley, R. E., Isolauri, E., et al. (2014). Gut microbiota as an epigenetic regulator: Pilot study based on whole-genome methylation analysis. MBio, 5(6), e02113–e02114. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.02113-14.
Lach, G., Schellekens, H., Dinan, T. G., & Cryan, J. F. (2018). Anxiety, depression, and the microbiome: A role for gut peptides. Neurotherapeutics, 15(1), 36–59.
Land, W. G. (2015). The role of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in human diseases Part II: DAMPs as diagnostics, prognostics and therapeutics in clinical medicine. Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal, 15(2), e157–e170.
Lee, S., Kim, J. H., Kim, J. H., Seo, J. W., Han, H. S., Lee, W. H., et al. (2011). Lipocalin-2 Is a chemokine inducer in the central nervous system: Role of chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) in lipocalin-2-induced cell migration. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(51), 43855–43870.
Lee, S., Lee, W. H., Lee, M. S., Mori, K., & Suk, K. (2012). Regulation by lipocalin-2 of neuronal cell death, migration, and morphology. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 90(3), 540–550.
Lee, E. S., Song, E. J., & Nam, Y. D. (2017). Dysbiosis of gut microbiome and its impact on epigenetic regulation. Journal of Clinical Epigenetics, 3, S1.
Leverenz, J. B., Quinn, J. F., Zabetian, C., Zhang, J., Montine, K. S., & Montine, T. J. (2009). Cognitive impairment and dementia in patients with Parkinson disease. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 9(10), 903–912.
Lewis, K. N., Mele, J., Hayes, J. D., & Buffenstein, R. (2010). Nrf2, a guardian of healthspan and gatekeeper of species longevity. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 50(5), 829–843.
Li, M.-F., Li, Jun, & Sun, Li. (2016). CsMAP34, a teleost MAP with dual role: A promoter of MASP-assisted complement activation and a regulator of immune cell activity. Scientific Report, 6, 39287.
Li, X., Melief, E., Postupna, N., Montine, K. S., Keene, C. D., & Montine, T. J. (2015). Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype 2 regulation of scavenger receptor CD36 modulates microglial Aβ42 phagocytosis. American Journal of Pathology, 185(1), 230–239.
Li, D.-D., Zhang, W., Wang, Z.-Y., & Zhao, P. (2017). Serum copper, zinc, and iron levels in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 300.
Lian, H., Litvinchuk, A., Chiang, A. C., Aithmitti, N., Jankowsky, J. L., & Zheng, H. (2016). Astrocyte-microglia cross talk through complement activation modulates amyloid pathology in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 36(2), 577–589.
Liang, X., Wang, Q., Hand, T., Wu, L., Breyer, R. M., Montine, T. J., et al. (2005). Deletion of the prostaglandin E2 EP2 receptor reduces oxidative damage and amyloid burden in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(44), 10180–10187.
Licastro, F., & Porcellini, E. (2016). Persistent infections, immune-senescence and Alzheimer’s disease. Oncoscience, 3(5–6), 135–142.
Lin, H. V., Frassetto, A., Kowalik, E. J., Jr., Nawrocki, A. R., Lu, M. M., Kosinski, J. R., et al. (2012). Butyrate and propionate protect against diet-induced obesity and regulate gut hormones via free fatty acid receptor 3-independent mechanisms. PLoS ONE, 7(4), e35240.
Liu, S., Liu, Y., Hao, W., Wolf, L., Kiliaan, A. J., Penke, B., et al. (2012). TLR2 is a primary receptor for Alzheimer’s amyloid β peptide to trigger neuroinflammatory activation. Journal of Immunology, 188(3), 1098–1107.
Luettig, J., Rosenthal, R., Barmeyer, C., & Schulzke, J. D. (2015). Claudin-2 as a mediator of leaky gut barrier during intestinal inflammation. Tissue Barriers, 3(1–2), e977176.
Magni, G., Bernasconi, G., Mauro, P., D’Odorico, A., Sturniolo, G. C., Canton, G., et al. (1991). Psychiatric diagnoses in ulcerative colitis. A controlled study. British Journal of Psychiatry, 158, 413–415.
Maguen, S., Madden, E., Cohen, B., Bertenthal, D., & Seal, K. (2014). Association of mental health problems with gastrointestinal disorders in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans. Depression and Anxiety, 31(2), 160–165.
Mahla, R. S., Reddy, M. C., Prasad, D. V. R., & Kumar, H. (2013). Sweeten PAMPs: Role of sugar complexed PAMPs in innate immunity and vaccine biology. Frontiers in Immunology, 4, 248.
Maloney, B., & Lahiri, D. K. (2016). Epigenetics of dementia: Understanding the disease as a transformation rather than a state. The Lancet Neurology, 15(7), 760–774.
Mariadason, J. M., Barkla, D. H., & Gibson, P. R. (1997). Effect of short-chain fatty acids on paracellular permeability in Caco-2 intestinal epithelium model. American Journal of Physiology, 272, G705–G712.
Mariadason, J. M., Catto-Smith, A., & Gibson, P. R. (1999). Modulation of distal colonic epithelial barrier function by dietary fibre in normal rats. Gut, 44, 394–399.
Martin, C. M. (2006). The “reversible” dementia of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. The Consultant pharmacist, 21(11), 888–893.
Mattson, M. P., Barger, S. W., Cheng, B., Lieberburg, I., Smith-Swintosky, V. L., & Rydel, R. E. (1993). Beta-Amyloid precursor protein metabolites and loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends in Neurosciences, 16(10), 409–414.
Mattsson, E., Heying, R., Van De Gevel, J. S., Hartung, T., & Beekhuizen, H. (2008). Staphylococcal peptidoglycan initiates an inflammatory response and procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells: A comparison with highly purified lipoteichoic acid and TSST-1. FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology, 52(1), 110–117.
Mawanda, F., & Wallace, R. (2013). Can infections cause Alzheimer’s disease? Epidemiologic Reviews, 35(1), 161–180.
McCarthy, C. G., Goulopoulou, S., Wenceslau, C. F., Spitler, K., Matsumoto, T., & Webb, R. C. (2014). Toll-like receptors and damage-associated molecular patterns: Novel links between inflammation and hypertension. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 306(2), H184–H196.
McKegney, F. P., Gordon, R. O., & Levine, S. M. (1970). A psychosomatic comparison of patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Psychosomatic Medicine, 32, 153–166.
Megyeri, M., Harmat, V., Major, B., Végh, Á., Balczer, J., Héja, D., et al. (2013). Quantitative characterization of the activation steps of mannan-binding lectin (MBL)-associated serine proteases (MASPs) points to the central role of MASP-1 in the initiation of the complement lectin pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(13), 8922–8934.
Messaoudi, M., Lalonde, R., Violle, N., Javelot, H., Desor, D., Nejdi, A., et al. (2011). Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. British Journal of Nutrition, 105(5), 755–764.
Millington, C., Sonego, S., Karunaweera, N., Rangel, A., Aldrich-Wright, J. R., Campbell, I. L., et al. (2014). Chronic neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: New perspectives on animal models and promising candidate drugs. BioMed Research International, 2014, 309129.
Mishra, S., & Palanivelu, K. (2008). The effect of curcumin (turmeric) on Alzheimer’s disease: An overview. Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology, 11(1), 13–19.
Mittermaier, C., Dejaco, C., Waldhoer, T., Oefferlbauer-Ernst, A., Miehsler, W., Beier, M., et al. (2004). Impact of depressive mood on relapse in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A prospective 18-month follow-up study. Psychosomatic Medicine, 66(1), 79–84.
Møller-Kristensen, M., Thiel, S., Sjöholm, A., Matsushita, M., & Jensenius, J. C. (2007). Cooperation between MASP-1 and MASP-2 in the generation of C3 convertase through the MBL pathway. International Immunology, 19(2), 141–149.
Myhre, O., Utkilen, H., Duale, N., Brunborg, G., & Hofer, T. (2013). Metal dyshomeostasis and inflammation in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: Possible impact of environmental exposures. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2013, 726954.
Naudé, P. J. W., Nyakas, C., Eiden, L. E., Ait-Ali, D., van der Heide, R., Engelborghs, S., et al. (2012). Lipocalin 2: Novel component of proinflammatory signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. The FASEB Journal, 26(7), 2811–2823.
Neufeld, K. M., Kang, N., Bienenstock, J., & Foster, J. A. (2011). Reduced anxiety-like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ-free mice. Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 23(3), 255–264.
Neugroschl, J., & Wang, S. (2011). Alzheimer’s disease: Diagnosis and treatment across the spectrum of disease severity. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine, 78(4), 596–612.
Nielsen, B. S., Borregaard, N., Bundgaard, J. R., Timshel, S., Sehested, M., & Kjeldsen, L. (1996). Induction of NGAL synthesis in epithelial cells of human colorectal neoplasia and inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut, 38, 414–420.
Nitti, M., Piras, S., Brondolo, L., Marinari, U. M., Pronzato, M. A., & Furfaro, A. L. (2018). Heme oxygenase 1 in the nervous system: Does it favor neuronal cell survival or induce neurodegeneration? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19, 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082260.
Nzengue, Y., Candéias, S. M., Sauvaigo, S., Douki, T., Favier, A., Rachidi, W., et al. (2011). The toxicity redox mechanisms of cadmium alone or together with copper and zinc homeostasis alteration: Its redox biomarkers. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 25(3), 171–180.
O’Toole, P. W., & Jeffery, I. B. (2015). Gut microbiota and aging. Science, 350(6265), 1214–1215.
O’Mahony, S. M., Clarke, G., Borre, Y. E., Dinan, T. G., & Cryan, J. F. (2015). Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain–gut–microbiome axis. Behavioural Brain Research, 277, 32–48.
Park, J.-H., Lee, D.-W., Park, K. S., & Joung, H. J. (2013). Serum trace metal levels in Alzheimer’s disease and normal control groups. American Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease & Other Dementias, 29(1), 76–83.
Peng, L., He, Z., Chen, W., Holzman, I. R., & Lin, J. (2007). Effects of butyrate on intestinal barrier function in a Caco-2 cell monolayer model of intestinal barrier. Pediatric Research, 61, 37–41.
Peng, L., Yu, Y., Liu, J., Li, S., He, H., Cheng, N., et al. (2015). The chemerin receptor CMKLR1 is a functional receptor for amyloid-β peptide. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 43(1), 227–242. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-141227.
Percy, M. E., Kruck, T. P. A., Pogue, A. I., & Lukiw, W. J. (2011). Towards the prevention of potential aluminum toxic effects and an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 105(11), 1505–1512.
Pinto-Sanchez, M. I., Hall, G. B., Ghajar, K., Nardelli, A., Bolino, C., Lau, J. T., et al. (2017). Probiotic Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 reduces depression scores and alters brain activity: A pilot study in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology, 153(2), 448–459.
Psichas, A., Sleeth, M. L., Murphy, K. G., Brooks, L., Bewick, G. A., Hanyaloglu, A. C., et al. (2015). The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. International Journal of Obesity, 39(3), 424–429.
Rangaraju, S., Raza, S. A., Li, N. X., Betarbet, R., Dammer, E. B., Duong, D., et al. (2018). Differential phagocytic properties of CD45low microglia and CD45high brain mononuclear phagocytes-activation and age-related effects. Frontiers in Immunology, 9, 405.
Ransohoff, R. M. (2016). How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration. Science, 353(6301), 777–783.
Ray, R., Juranek, J. K., & Rai, V. (2016). RAGE axis in neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration and its emerging role in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 62, 48–55.
Rayaprolu, S., Mullen, B., Baker, M., Lynch, T., Finger, E., Seeley, W. W., et al. (2013). TREM2 in neurodegeneration: Evidence for association of the p.R47H variant with frontotemporal dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 8, 19.
Rayner, C. K., & Horowitz, M. (2013). Physiology of the ageing gut. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care, 16(1), 33–38.
Remely, M., Aumueller, E., Jahn, D., Hippe, B., Brath, H., & Haslberger, A. G. (2014a). Microbiota and epigenetic regulation of inflammatory mediators in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Beneficial Microbes, 5(1), 33–43.
Remely, M., Aumueller, E., Merold, C., Dworzak, S., Hippe, B., Zanner, J., et al. (2014b). Effects of short chain fatty acid producing bacteria on epigenetic regulation of FFAR3 in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Gene, 537(1), 85–92.
Ribet, D., & Cossart, P. (2015). How bacterial pathogens colonize their hosts and invade deeper tissues. Microbes and Infection, 17(3), 173–183.
Richardson, K., Fox, C., Maidment, I., Steel, N., Loke, Y. K., Arthur, A., et al. (2018). Anticholinergic drugs and risk of dementia: Case–control study. The BMJ, 361, k1315. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k1315.
Ridley, N. J., Draper, B., & Withall, A. (2013). Alcohol-related dementia: An update of the evidence. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt157.
Rizzi, L., Rosset, I., & Roriz-Cruz, M. (2014). Global epidemiology of dementia: Alzheimer’s and vascular types. BioMed Research International, 2014, 908915.
Robinson, L., Tang, E., & Taylor, J.-P. (2015). Dementia: Timely diagnosis and early intervention. The BMJ, 350, h3029.
Romijn, A. R., Rucklidge, J. J., Kuijer, R. G., & Frampton, C. (2017). A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum for the symptoms of depression. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 51(8), 810–821.
Roos, R. A. (2010). Huntington’s disease: A clinical review. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 5, 40. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-5-40.
Rossi, M., Johnson, D. W., & Campbell, K. L. (2015). The kidney–gut axis: Implications for nutrition care. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 25(5), 399–403.
Russo, R., Cristiano, C., Avagliano, C., De Caro, C., La Rana, G., Raso, G. M., et al. (2017). Gut–brain axis: Role of lipids in the regulation of inflammation, pain and CNS diseases. Current Medicinal Chemistry., 25, 3930–3952. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170216113756.
Sambamurti, K., Greig, N. H., & Lahiri, D. K. (2002). Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroMolecular Medicine, 1(1), 1–31.
Sánchez-Villegas, A., Delgado-Rodríguez, M., Alonso, A., Schlatter, J., Lahortiga, F., Serra Majem, L., et al. (2009). Association of the Mediterranean dietary pattern with the incidence of depression: The Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra/University of Navarra follow-up (SUN) cohort. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66(10), 1090–1098.
Sandahl, T. D., Kelsen, J., Dige, A., Dahlerup, J. F., Agnholt, J., Hvas, C. L., et al. (2014). The lectin pathway of the complement system is downregulated in Crohn’s disease patients who respond to anti-TNF-α therapy. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis, 8(6), 521–528.
Sanguinetti, E., Collado, M. C., Marrachelli, V. G., Monleon, D., Selma-Royo, M., Pardo-Tendero, M. M., et al. (2018). Microbiome-metabolome signatures in mice genetically prone to develop dementia, fed a normal or fatty diet. Scientific Report, 8(1), 4907.
Santocchi, E., Guiducci, L., Fulceri, F., Billeci, L., Buzzigoli, E., Apicella, F., et al. (2016). Gut to brain interaction in autism spectrum disorders: A randomized controlled trial on the role of probiotics on clinical, biochemical and neurophysiological parameters. BMC Psychiatry, 16, 183. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-0887-5.
Saraswati, S., & Sitaraman, R. (2014). Aging and the human gut microbiota-from correlation to causality. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 764.
Saresella, M., La Rosa, F., Piancone, F., Zoppis, M., Marventano, I., Calabrese, E., et al. (2016). The NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are activated in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 11, 23.
Savignac, H. M., Corona, G., Mills, H., Chen, L., Spencer, J. P., Tzortzis, G., et al. (2013). Prebiotic feeding elevates central brain derived neurotrophic factor, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits and d-serine. Neurochemistry International, 63(8), 756–764.
Sawada, N., Murata, M., Kikuchi, K., Osanai, M., Tobioka, H., Kojima, T., et al. (2003). Tight junctions and human diseases. Medical Electron Microscopy, 36(3), 147–156.
Schaefer, A. K., Melnyk, J. E., He, Z., Del Rosario, F., & Grimes, C. L. (2018). Pathogen- and microbial- associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs) and the innate immune response in Crohn’s disease. In S. Chatterjee, W. Jungraithmayr, & D. Bagchi (Eds.), Immunity and inflammation in health and disease: Emerging roles of nutraceuticals and functional foods in immune support (pp. 175–187). Amsterdam: Academic Press.
Scheltens, P., Blennow, K., Breteler, M. M., de Strooper, B., Frisoni, G. B., Salloway, S., et al. (2016). Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet, 388(10043), 505–517.
Schneider, J. A. (2007). Brain microbleeds and cognitive function. Stroke, 38, 1730–1731.
Serrano-Pozo, A., Frosch, M. P., Masliah, E., & Hyman, B. T. (2011). Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 1(1), a006189.
Shen, X.-L., Song, N., Du, X.-X., Li, Y., Xie, J.-X., & Jiang, H. (2017). Nesfatin-1 protects dopaminergic neurons against MPP +/MPTP-induced neurotoxicity through the C-Raf–ERK1/2-dependent anti-apoptotic pathway. Scientific Report, 7, 40961.
Shi, S., Wang, G., Zhang, K., Zhang, Z., Liang, K., Li, K., et al. (2017). Expression of S100β protein in patients with vascular dementia after basal ganglia hemorrhage and its clinical significance. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 13(5), 1917–1921.
Shprecher, D., Schwalb, J., & Kurlan, R. (2008). Normal pressure hydrocephalus: Diagnosis and treatment. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports, 8(5), 371–376.
Skandalis, S. S., Dobra, K., Götte, M., Karousou, E., & Misra, S. (2015). Impact of extracellular matrix on cellular behavior: A source of molecular targets in disease. BioMed Research International, 2015, 482879.
Sochocka, M., Zwolińska, K., & Leszek, J. (2017). The infectious etiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Current Neuropharmacology, 15(7), 996–1009.
Soenen, S., Rayner, C. K., Jones, K. L., & Horowitz, M. (2016). The ageing gastrointestinal tract. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care, 19(1), 12–18.
Song, J., & Kim, O. Y. (2018). Perspectives in lipocalin-2: Emerging biomarker for medical diagnosis and prognosis for Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical Nutrition Research, 7(1), 1–10.
Srikanth, V., Maczurek, A., Phan, T., Steele, M., Westcott, B., Juskiw, D., et al. (2011). Advanced glycation endproducts and their receptor RAGE in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 32(5), 763–777.
Stanga, S., Lanni, C., Govoni, S., Uberti, D., D’Orazi, G., & Racchi, M. (2010). Unfolded p53 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Is HIPK2 the link? Aging (Albany, NY), 2(9), 545–554.
Starr, J. M., & Whalley, L. J. (1994). Drug-induced dementia: Incidence, management and prevention. Drug Safety, 11(5), 310–317.
Streit, W. J., Mrak, R. E., & Griffin, W. S. T. (2004). Microglia and neuroinflammation: A pathological perspective. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 1, 14.
Stuart, M. J., Corrigan, F., & Baune, B. T. (2014). Knockout of CXCR227 increases the population of immature neural cells and decreases proliferation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 11, 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-31.
Sudo, N., Chida, Y., Aiba, Y., Sonoda, J., Oyama, N., Yu, X. N., et al. (2004). Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system for stress response in mice. Journal of Physiology, 558(Pt 1), 263–275.
Tahara, Y., Yamazaki, M., Sukigara, H., Motohashi, H., Sasaki, H., Miyakawa, H., et al. (2018). Gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids induce circadian clock entrainment in mouse peripheral tissue. Scientific Report, 8(1), 1395.
Takeuchi, O., & Akira, S. (2010). Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell, 140(6), 805–820.
Takeuchi, M., & Yamagishi, S. (2008). Possible involvement of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 14(10), 973–978.
Tan, J., McKenzie, C., Potamitis, M., Thorburn, A. N., Mackay, C. R., & Macia, L. (2014). The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Advances in Immunology, 121, 91–119.
Tanaka, S., & Nagashima, H. (2018). Establishment of an Alzheimer’s disease model with latent herpesvirus infection using PS2 and Tg2576 double transgenic mice. Experimental Animals, 67(2), 185–192.
Tang, S.-C., Yang, K.-C., Hu, C.-J., Chiou, H.-Y., Wu, C. C., & Jeng, J.-S. (2017). Elevated plasma level of soluble form of RAGE in ischemic stroke patients with dementia. NeuroMolecular Medicine, 19(4), 579–583.
Taskesen, E., Mishra, A., van der Sluis, S., International FTD-Genomics Consortium, Ferrari, R., Veldink, J. H., et al. (2017). Susceptible genes and disease mechanisms identified in frontotemporal dementia and frontotemporal dementia with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by DNA-methylation and GWAS. Scientific Report, 7, 8899.
Thakur, A. K., Shakya, A., Husain, G. M., Emerald, M., & Kumar, V. (2014). Gut-microbiota and mental health: Current and future perspectives. Journal of Pharmacology & Clinical Toxicology, 2(1), 1016.
Thelen, T., Hao, Y., Medeiros, A. I., Curtis, J. L., Serezani, C. H., Kobzik, L., et al. (2010). The class A scavenger receptor, macrophage receptor with collagenous structure, is the major phagocytic receptor for Clostridium sordellii expressed by human decidual macrophages. Journal of Immunology, 185(7), 4328–4335.
Theocharis, A. D., Skandalis, S. S., Gialeli, C., & Karamanos, N. K. (2016). Extracellular matrix structure. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 97, 4–27.
Thome, J., Kornhuber, J., Münch, G., Schinzel, R., Taneli, Y., Zielke, B., et al. (1996). New hypothesis on etiopathogenesis of Alzheimer syndrome. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs). Nervenarzt, 67(11), 924–929.
Thorsvik, S., Bakke, I., van Beelen, Granlund A., Røyset, E. S., Jan Damås, K., Østvik, A. E., et al. (2018). Expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in the gut in Crohn’s disease. Cell and Tissue Research, 374(2), 339–348.
Tóbon-Velasco, J. C., Cuevas, E., & Torres-Ramos, M. A. (2014). Receptor for AGEs (RAGE) as mediator of NF-kB pathway activation in neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. CNS & Neurological Disorders: Drug Targets, 13(9), 1615–1626.
Tong, X. K., & Hamel, E. (1999). Regional cholinergic denervation of cortical microvessels and nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience, 92(1), 163–175.
Uribarri, J., Cai, W., Peppa, M., Goodman, S., Ferrucci, L., Striker, G., et al. (2007). Circulating glycotoxins and dietary advanced glycation endproducts: Two links to inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and aging. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 62(4), 427–433.
Valko, M., Morris, H., & Cronin, M. T. (2005). Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 12(10), 1161–1208.
Varadarajan, S., Yatin, S., Aksenova, M., & Butterfield, D. A. (2000). Review: Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide-associated free radical oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Journal of Structural Biology, 130(2–3), 184–208.
Veerappan, C. S., Sleiman, S., & Coppola, G. (2013). Epigenetics of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Neurotherapeutics, 10(4), 709–721.
Venegas, C., & Heneka, M. T. (2017). Danger-associated molecular patterns in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 101(1), 87–98.
Vogt, N. M., Kerby, R. L., Dill-McFarland, K. A., Harding, S. J., Merluzzi, A. P., Johnson, S. C., et al. (2017). Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Report, 7, 13537.
Walker, D. G., & Lue, L.-F. (2015). Immune phenotypes of microglia in human neurodegenerative disease: Challenges to detecting microglial polarization in human brains. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 7(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-015-0139-9.
Wallace, C. J. K., & Milev, R. (2017). The effects of probiotics on depressive symptoms in humans: A systematic review. Annals of General Psychiatry, 16, 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-017-0138-2.
Wang, H., Lee, I.-S., Braun, C., & Enck, P. (2016a). Effect of probiotics on central nervous system functions in animals and humans: A systematic review. Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 22(4), 589–605.
Wang, Y., Ulland, T. K., Ulrich, J. D., Song, W., Tzaferis, J. A., Hole, J. T., et al. (2016b). TREM2-mediated early microglial response limits diffusion and toxicity of amyloid plaques. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 213(5), 667–675.
Weber, C. R., Nalle, S. C., Tretiakova, M., Rubin, D. T., & Turner, J. R. (2008). Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic transformation. Laboratory Investigation, 88(10), 1110–1120.
Welcome, M. O. (2018). Gastrointestinal physiology: Development, principles and mechanism of regulation. Cham: Springer.
Wenning, G., Litvan, I., Jankovic, J., Granata, R., Mangone, C. A., McKee, A., et al. (1998). Natural history and survival of 14 patients with corticobasal degeneration confirmed at postmortem examination. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 64, 184–189.
Westfall, S., Lomis, N., Kahouli, I., Dia, S. Y., Singh, S. P., & Prakash, S. (2017). Microbiome, probiotics and neurodegenerative diseases: Deciphering the gut brain axis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 74(20), 3769–3787.
Williams, C.-A., Lin, Y., Maynard, A., & Cheng, S.-Y. (2013). Involvement of NF kappa B in potentiated effect of Mn-containing dithiocarbamates on MPP + induced cell death. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 33(6), 815–823.
Wimo, A., Jonsson, L., & Winblad, B. (2006). An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and direct costs of dementia in 2003. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 21(3), 175–181.
Wimo, A., Winblad, B., & Jönsson, L. (2010). The worldwide societal costs of dementia: Estimates for 2009. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 6(2), 98–103.
Wing, M. R., Patel, S. S., Ramezani, A., & Raj, D. S. (2016). Gut microbiome in chronic kidney disease. Experimental Physiology, 101(4), 471–477.
Woollacott, I. O. C., Nicholas, J. M., Heslegrave, A., Heller, C., Foiani, M. S., Dick, K. M., et al. (2018). Cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 levels in frontotemporal dementia differ by genetic and pathological subgroup. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 10(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-018-0405-8.
Wozniak, M. A., Mee, A. P., & Itzhaki, R. F. (2009). Herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA is located within Alzheimer’s disease amyloid plaques. Journal of Pathology, 217(1), 131–138.
Xiong, C., Liu, J., Lin, D., Zhang, J., Terrando, N., & Wu, A. (2018). Complement activation contributes to perioperative neurocognitive disorders in mice. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 15(1), 254. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1292-4.
Xu, Y., Yan, J., Zhou, P., Li, J., Gao, H., Xia, Y., et al. (2012). Neurotransmitter receptors and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Progress in Neurobiology, 97(1), 1–13.
Yin, Z., Raj, D., Saiepour, N., Van Dam, D., Brouwer, N., Holtman, I. R., et al. (2017). Immune hyperreactivity of Aβ plaque-associated microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 55, 115–122.
Yoshiike, Y., Kimura, T., Yamashita, S., Furudate, H., Mizoroki, T., Murayama, M., et al. (2008). GABA(A) receptor-mediated acceleration of aging-associated memory decline in APP/PS1 mice and its pharmacological treatment by picrotoxin. PLoS ONE, 3(8), e3029.
Yu, Y., & Ye, R. D. (2015). Microglial Aβ receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 35(1), 71–83.
Zamboni, G., Grafman, J., Krueger, F., Knutson, K. M., & Huey, E. D. (2010). Anosognosia for behavioral disturbances in frontotemporal dementia and corticobasal syndrome: A voxel-based morphometry study. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 29(1), 88–96.
Zeissig, S., Bürgel, N., Günzel, D., Richter, J., Mankertz, J., Wahnschaffe, U., et al. (2007). Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn’s disease. Gut, 56(1), 61–72.
Zhao, H., Shi, Y., Luo, X., Peng, L., Yang, Y., & Zou, L. (2017). The effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on a child with tourette syndrome. Case Reports in Medicine, 2017, 6165239. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6165239.
Zheng, P., Zeng, B., Zhou, C., Liu, M., Fang, Z., Xu, X., et al. (2016). Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Molecular Psychiatry, 21(6), 786–796.
Zhu, C. S., Grandhi, R., Patterson, T. T., & Nicholson, S. E. (2018). A review of traumatic brain injury and the gut microbiome: Insights into novel mechanisms of secondary brain injury and promising targets for neuroprotection. Brain Science, 8(6), 113.
Zihni, C., Mills, C., Matter, K., & Balda, M. S. (2016). Tight junctions: From simple barriers to multifunctional molecular gates. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 17, 564–580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welcome, M.O. Gut Microbiota Disorder, Gut Epithelial and Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunctions in Etiopathogenesis of Dementia: Molecular Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways. Neuromol Med 21, 205–226 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08547-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08547-5