Abstract
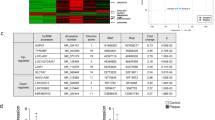
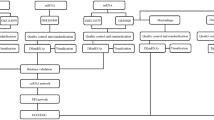
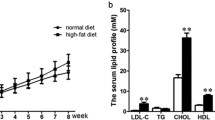
Atherosclerosis, a multifactorial and chronic immune inflammatory disorder, is the main cause of multiple cardiovascular diseases. Researchers recently reported that lncRNAs may exert important functions in the progression of atherosclerosis (AS). Some studies found that lncRNAs can act as ceRNAs to communicate with each other by the competition of common miRNA response elements. However, lncRNA-associated ceRNA network in terms of atherosclerosis is limited. In present study, we pioneered to construct and systematically analyze the lncRNA-mRNA network and reveal its potential roles in carotid atherosclerotic rabbit models. Atherosclerosis was induced in rabbits (n = 3) carotid arteries via a high-fat diet and balloon injury, while age-matched rabbits (n = 3) were treated with normal chow as controls. RNA-seq analysis was conducted on rabbits carotid arteries (n = 6) with or without plaque formation. Based on the ceRNA mechanism, a ternary interaction network including lncRNA, mRNA, and miRNA was generated and an AS-related lncRNA-mRNA network (ASLMN) was extracted. Furthermore, we analyzed the properties of ASLMN and discovered that six lncRNAs (MSTRG.10603.16, 5258.4, 12799.3, 5352.1, 12022.1, and 12250.4) were highly related to AS through topological analysis. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis indicated that lncRNA MSTRG.5258.4 may downregulate inducible co-stimulator to perform a downregulated role in AS through T cell receptor signaling pathway and downregulate THBS1 to conduct a upregulated function in AS through ECM-receptor interaction pathway. Finally, our results elucidated the important function of lncRNAs in the origination and progression of AS. We provided an ASLMN of atherosclerosis development in carotid arteries of rabbits and probable targets which may lay the foundation for future research of clinical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein E, Allis CD (2005) RNA meets chromatin. Genes Dev 19:1635–1655. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1324305
Bis JC et al (2011) Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies from the CHARGE consortium identifies common variants associated with carotid intima media thickness and plaque. Nat Genet 43:940–947. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.920
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Burillo E et al (2009) Proteomic study of macrophages exposed to oxLDL identifies a CAPG polymorphism associated with carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 207:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.03.054
Chen L et al (2016) Global transcriptomic study of atherosclerosis development in rats. Gene 592:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.07.023
da Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Figueroa-Vega N, Moreno-Frias C, Malacara JM (2015) Alterations in adhesion molecules, pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell-derived microparticles contribute to intima-media thickness and symptoms in postmenopausal women. PLoS One 10:e0120990. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120990
Friedlander MR, Mackowiak SD, Li N, Chen W, Rajewsky N (2012) miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res 40:37–52. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr688
Gerdes N, Zirlik A (2011) Co-stimulatory molecules in and beyond co-stimulation - tipping the balance in atherosclerosis? Thromb Haemost 106:804–813. https://doi.org/10.1160/th11-09-0605
Guttman M et al (2009) Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 458:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07672
Hu W, Wei R, Wang L, Lu J, Liu H, Zhang W (2018) Correlations of MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-12 with the degree of atherosclerosis, plaque stability and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Exp Ther Med 15:1994–1998. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5623
Huang X et al (2016) Detection of CD28/CD86 co-stimulatory molecules and surface properties of T and dendritic cells: an AFM study. Scanning 38:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.21279
Husain K, Hernandez W, Ansari RA, Ferder L (2015) Inflammation, oxidative stress and renin angiotensin system in atherosclerosis. World J Biol Chem 6:209–217. https://doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.209
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS (2004) Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2:e363. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020363
Jung YY et al (2018) Atherosclerosis is exacerbated by chitinase-3-like-1 in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Theranostics 8:749–766. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.20183
Khosravi M, Najafi M, Amirfarhangi A, Karimi M, Fattahi F, Shabani M (2019) The increase of pFAK and THBS1 protein and gene expression levels in vascular smooth muscle cells by histamine-treated M1 macrophages. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 18:72–79
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2015) HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12:357–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3317
Koenen RR, Weber C (2010) Therapeutic targeting of chemokine interactions in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3048
Li A, Zhang J, Zhou Z (2014) PLEK: a tool for predicting long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs based on an improved k-mer scheme. BMC Bioinformatics 15:311. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-15-311
Li H, Zhu H, Ge J (2016) Long noncoding RNA: recent updates in atherosclerosis. Int J Biol Sci 12:898–910. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.14430
Li M, Yang J, Wu FX, Pan Y, Wang J (2018) DyNetViewer: a Cytoscape app for dynamic network construction, analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 34:1597–1599. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx821
Ling S, Nheu L, Komesaroff PA (2012) Cell adhesion molecules as pharmaceutical target in atherosclerosis. Mini-Rev Med Chem 12:175–183
Ma Y, Yabluchanskiy A, Lindsey ML (2013) Thrombospondin-1: the good, the bad, and the complicated. Circ Res 113:1272–1274. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.113.302749
Mann M, Wright PR, Backofen R (2017) IntaRNA 2.0: enhanced and customizable prediction of RNA-RNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W435–w439. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx279
Meng L, Lv B, Zhang S, Yv B (2008) In vivo optical coherence tomography of experimental thrombosis in a rabbit carotid model. Heart 94:777–780. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2007.117382
Miteva K, Madonna R, De Caterina R, Van Linthout S (2018) Innate and adaptive immunity in atherosclerosis. Vasc Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2018.04.006
Mo XB et al (2019) Detection of lncRNA-mRNA interaction modules by integrating eQTL with weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Funct Integr Genomics 19:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0638-4
Narizhneva NV et al (2005) Thrombospondin-1 up-regulates expression of cell adhesion molecules and promotes monocyte binding to endothelium. FASEB J 19:1158–1160. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-3310fje
Pandey RR et al (2008) Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol Cell 32:232–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.022
Parsons C, Agasthi P, Mookadam F, Arsanjani R (2018) Reversal of coronary atherosclerosis: role of life style and medical management. Trends Cardiovasc Med 28:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2018.05.002
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL (2016) Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc 11:1650–1667. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.095
Pilyugin M, Irminger-Finger I (2014) Long non-coding RNA and microRNAs might act in regulating the expression of BARD1 mRNAs. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 54:356–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2014.06.018
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136:629–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Schmidt EP, Kuebler WM, Lee WL, Downey GP (2016) Adhesion molecules: master controllers of the circulatory system. Compr Physiol 6:945–973. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c150020
Schramm G, Surmann EM, Wiesberg S, Oswald M, Reinelt G, Eils R, Konig R (2010) Analyzing the regulation of metabolic pathways in human breast cancer. BMC Med Genet 3:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8794-3-39
Singh AK, Gaur P, Das SN (2014) Natural killer T cell anergy, co-stimulatory molecules and immunotherapeutic interventions. Hum Immunol 75:250–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2013.12.004
Song C et al (2016) Construction and analysis of cardiac hypertrophy-associated lncRNA-mRNA network based on competitive endogenous RNA reveal functional lncRNAs in cardiac hypertrophy. Oncotarget 7:10827–10840. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7312
Sun L, Luo H, Bu D, Zhao G, Yu K, Zhang C, Liu Y, Chen R, Zhao Y (2013) Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e166. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt646
Tian Y et al (2019) Comprehensive analysis of microarray expression profiles of circRNAs and lncRNAs with associated co-expression networks in human colorectal cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 19:311–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0641-9
Vieceli Dalla Sega F, Fortini F, Aquila G, Campo G, Vaccarezza M, Rizzo P (2019) Notch signaling regulates immune responses in atherosclerosis. Front Immunol 10:1130. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01130
Weber C, Noels H (2011) Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med 17:1410–1422. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2538
Wheelock CE et al (2009) Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease. Mol BioSyst 5:588–602. https://doi.org/10.1039/b902356a
Wu N, Li RQ, Li L (2018) SOAT1 deficiency attenuates atherosclerosis by regulating inflammation and cholesterol transportation via HO-1 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 501:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.137
Zhao R, Li FQ, Tian LL, Shang DS, Guo Y, Zhang JR, Liu M (2019) Comprehensive analysis of the whole coding and non-coding RNA transcriptome expression profiles and construction of the circRNA-lncRNA co-regulated ceRNA network in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Funct Integr Genomics 19:109–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0631-y
Funding
Present research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81671689) and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (H2017021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All performed procedures involved in this study were endorsed by the Medical Ethics Committee on Animal Research of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (Ethics No.KY2016-090) and were in compliance with the principles and regulations of laboratory animal care.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
(PNG 2050 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
(PNG 1789 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
(PNG 2066 kb)
Supplementary Figure 4
(PNG 1717 kb)
Supplementary Figure 5
(PNG 1565 kb)
Supplementary Table S1.
Differentially expressed lncRNA identified by ‘edge R’ R package. (XLSX 34 kb)
Supplementary Table S2.
Differentially expressed mRNA identified by ‘edge R’ R package. (XLSX 36 kb)
Supplementary Table S3.
AS associated lncRNA-mRNA pairs based on hypergeometric test. (XLSX 708 kb)
Supplementary Table S4.
GO enrichment analysis for the first near mRNA neighbors of lncRNA MSTRG.5258.4 in ASLMN. (XLS 25 kb)
Supplementary Table S5.
KEGG enrichment analysis for the first near mRNA neighbors of lncRNA MSTRG.5258.4 in ASLMN. (XLS 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Zhang, F., Li, X. et al. Systematic analysis of lncRNA expression profiles and atherosclerosis-associated lncRNA-mRNA network revealing functional lncRNAs in carotid atherosclerotic rabbit models. Funct Integr Genomics 20, 103–115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00705-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00705-z