Abstract
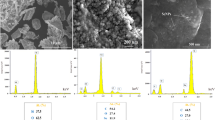
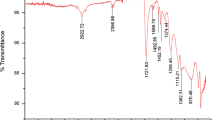
The antifouling, antimicrobial, elution behavior, skin irritant, and cytotoxicity properties of water-soluble phosphate glass on stainless steel were evaluated. Water-soluble phosphate glass samples with 35% Cu (mol/mol) were prepared by altering the network modifier (Na2O, K2O) and network former (P2O5, B2O3) compositions. The materials were melted at temperatures within the range of 850–950 °C. The melt was then quenched and ground into fine particles using a twin roll mill. The resulting water-soluble glasses were prepared as glass frit (size < 100 μm) using a sieve. The amorphous phase was determined by X-ray diffraction and differential thermal analysis. Water-soluble glasses with a reduced Cu ion elution rate of 1.2 ppm per week were formed because the chemical resistances of the formulated glasses improved as the P2O5 content decreased and the B2O3 content increased. To test its antifouling properties, the glass frit was mixed with paint and coated onto a STS316L sheet. The surface roughness was increased markedly from 1.4 to 19.2 nm, increasing the specific surface area for antimicrobial activity. It was demonstrated that the proposed method was able to form noncytotoxic, nonirritant, water-soluble glasses with 99.9% antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus. These results suggest that water-soluble phosphate glass on STS316L sheets could be useful in filtration plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae BS, Weinberg MC (1991) Oxidation–reduction equilibrium in copper phosphate glass melted in air. J Am Ceram Soc 74(12):3039–3045. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1991.tb04299.x
Cao XL, Cheng C, Ma YL, Zhao CS (2010) Preparation of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activities and the researches of their biocompatibilities. J Mater Sci Mater Med 21:2861–2868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-4133-2
Dietrich AM, Burlingame GA (2015) Critical review and rethinking of USEPA secondary standards for maintaining organoleptic quality of drinking water. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):708–720. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504403t
Dietzel A, Emil D (1957) A dynamic model of glass structure. Glastech Ber 30:282–287
Djeribi R, Bouchloukh W, Jouenne T, Menaa B (2012) Characterization of bacterial biofilms formed on urinary catheters. Am J Infect Control 40:854–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2011.10.009
Gholap H, Warule S, Sangshetti J, Kulkarni G, Banpurkar A, Satpute S, Patil R (2016) Hierarchical nanostructures of Au@ ZnO: antibacterial and antibiofilm agent. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(13):5849–5858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7391-1
Imlay JA (2013) The molecular mechanisms and physiological consequences of oxidative stress: lessons from a model bacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(7):443–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3032
Jain N, Bhargava A, Tarafdar JC, Singh SK, Panwar J (2013) A biomimetic approach towards synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(2):859–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3934-2
Jia WT, Zhang X, Zhang CQ, Liu X, Huang WH, Rahaman MN, Day DE (2010) Elution characteristics of teicoplanin-loaded biodegradable borate glass/chitosan composite. Int J Pharm 387(1–2):184–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.12.002
Josephs-Spaulding J, Beeler E, Singh OV (2016) Human microbiome versus food-borne pathogens: friend or foe. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(11):4845–4863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7523-7
Sułowska J, Wacławska I, Szumera MJ (2012) Effect of copper addition on glass transition of silicate–phosphate glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim 109(2):705–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2328-0
Kuang H, Yang L, Shah NP, Aguilar ZP, Wang L, Xu H, Wei H (2016) Synergistic in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial effect of a mixture of ZnO nanoparticles and Lactobacillus fermentation liquor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(8):3757–3766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7221-x
Kumar M, Tekcan B, Okyay AK (2014) Atomic layer deposited HfO2 based metal insulator semiconductor GaN ultraviolet photodetectors. Curr Appl Phys 14:1703–1706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2014.10.001
Kumar R, Sidhu MK, Ganguly NK, Chakraborti A (1999) Identification of copper-zinc superoxide dismutase gene from enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Microbiol Immunol 43:481–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.1999.tb02431.x
Neel EA, Ahmed I, Pratten J, Nazhat SN, Knowles JC (2005) Characterisation of antibacterial copper releasing degradable phosphate glass fibres. Biomaterials 26(15):2247–2254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.07.024
Madhumitha G, Elango G, Roopan SM (2016) Biotechnological aspects of ZnO nanoparticles: overview on synthesis and its applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(2):571–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7108-x
Mishra N, Rai VK, Yadav KS, Sinha P, Kanaujia A, Chanda D, Yadav NP (2016) Encapsulation of mentha oil in chitosan polymer matrix alleviates skin irritation. AAPS PharmSciTech 17(2):482–492. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-015-0378-x
Ren G, Hu D, Cheng EW, Vargas-Reus MA, Reip P, Allaker RP (2009) Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33:587–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2008.12.004
Rouxel T, Sellappan P, Célarié F, Houizot P, Sangleboeuf JC (2014) Toward glasses with better indentation cracking resistance. C R Mec 342:46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crme.2013.10.008
Sellappan P, Rouxel T, Célarié F, Becker E, Houizot P, Conradt R (2013) Composition dependence of indentation deformation and indentation cracking in glass. Acta Mater 61:5949–5965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.06.034
Sharmin N, Rudd CD (2017) Structure, thermal properties, dissolution behaviour and biomedical applications of phosphate glasses and fibres: a review. J Mater Sci 52(15):8733–8760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0784-4
Shih PY, Chin TS (1999) Effect of redox state of copper on the properties of P2O5–Na2O–CuO glasses. Mater Chem Phys 60(1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8099-6
Shim K, Abdellatif M, Choi E, Kim D (2017) Nanostructured ZnO films on stainless steel are highly safe and effective for antimicrobial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(7):2801–2809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8099-6
Sin MC, Sun YM, Chang Y (2014) Zwitterionic-based stainless steel with well-defined polysulfobetaine brushes for general bioadhesive control. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(2):861–873. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4041256
Szumera M, Wacławska I, Olejniczak Z (2010) Influence of B2O3 on the structure and crystallization of soil active glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim 99(3):879–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0550-1
Vasudevan S, Oturan MA (2014) Electrochemistry: as cause and cure in water pollution-an overview. Environ Chem Lett 12(1):97–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0434-2
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Shim for his critical reading of the manuscript and for assistance with the data analysis.
Funding
This study was supported by the Basic Research Laboratory Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Project No. NRF 2015-041523).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were performed with the approval of the Korea Testing and Research Institute. All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, K., Abdellatif, M., Park, J. et al. Antifouling effect of water-soluble phosphate glass frit for filtration plants. Folia Microbiol 65, 363–370 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00743-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00743-x