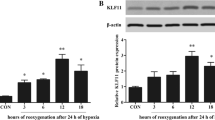
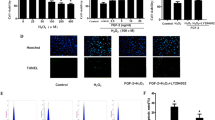
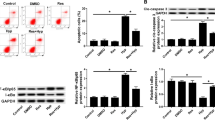
Abstract
Ischemia and hypoxia are common pathophysiological characteristics in cardiovascular diseases. c-Jun expression could be induced by extra- or intracellular stimuli and plays a pivotal role in regulating cell survival in response to the stress. However, previous studies of c-Jun in cell proliferation and apoptosis showed conflicting results. In the present study, we demonstrated that the expression of c-Jun was induced by hypoxia in H9c2 cells. Loss of function of c-Jun was investigated by CCK-8, LDH, and TUNEL assays in low oxygen (1% O2) conditions. We revealed that c-Jun could promote cell survival and inhibit cell apoptosis under hypoxia. Knockdown of c-Jun also promoted the expression of apoptosis-related proteins under hypoxia, such as cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, Bax, and Bim. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the knockdown of c-Jun inhibited the PTEN/Akt signaling pathway under hypoxia. Our findings suggested that c-Jun protected H9c2 cells from apoptosis and promoted the survival of H9c2 cells under hypoxia via PTEN/Akt signaling pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Semba H, Takeda N (2017) The roles of hypoxia signaling in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb 24:884–894. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.RV17009
Alfranca A, Gutierrez MD, Vara A, Aragones J, Vidal F, Landazuri MO (2002) c-Jun and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 functionally cooperate in hypoxia-induced gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol 22:12–22
Aune D, Schlesinger S, Norat T, Riboli E (2018) Tobacco smoking and the risk of sudden cardiac death: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Epidemiol 33:509–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0351-y
Brown E, Taylor CT (2018) Hypoxia-sensitive pathways in intestinal inflammation. J Physiol 596:2985–2989. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP274350
Chen F (2012) JNK-induced apoptosis, compensatory growth, and cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 72:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1982
Feng M, Li Z, Wang D, Wang F, Wang C, Wang C, Ding F (2018) MicroRNA-210 aggravates hypoxia-induced injury in cardiomyocyte H9c2 cells by targeting CXCR4. Biomed pharmacother 102:981–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.151
Gramley F, Lorenzen J, Pezzella F, Kettering K, Himmrich E, Plumhans C, Koellensperger E, Munzel T (2009) Hypoxia and myocardial remodeling in human cardiac allografts: a time-course study. J Heart Lung Transplant 28:1119–1126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2009.05.038
He S, Liu P, Jian Z, Li J, Zhu Y, Feng Z, Xiao Y (2013) miR-138 protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis via MLK3/JNK/c-Jun pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441:763–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.151
He S, Liu S, Wu X, Xin M, Ding S, Xin D, Ouyang H, Zhang J (2016) Protective role of downregulated MLK3 in myocardial adaptation to chronic hypoxia. J Physiol Biochem 73:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0561-5
Jeong Y, You D, Kang HG, Yu J, Kim SW, Nam SJ, Lee JE, Kim S (2018) Berberine suppresses fibronectin expression through inhibition of c-Jun phosphorylation in breast cancer cells. J Breast Cancer 21:21–27. https://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2018.21.1.21
Johansson P, Svensson E, Alehagen U, Jaarsma T, Brostrom A (2015) The contribution of hypoxia to the association between sleep apnoea, insomnia, and cardiovascular mortality in community-dwelling elderly with and without cardiovascular disease. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 14:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1177/1474515114524072
Julian RJ (2007) The response of the heart and pulmonary arteries to hypoxia, pressure, and volume. A short review. Poult Sci 86:1006–1011. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/86.5.1006
Li G, Ying L, Wang H, Wei SS, Chen J, Chen YH, Xu WP, Jie QQ, Zhou Q, Li YG, Wei YD, Wang YP (2016) Rac1b enhances cell survival through activation of the JNK2/c-JUN/Cyclin-D1 and AKT2/MCL1 pathways. Oncotarget 7:17970–17985. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7602
Liu J, Lin A (2005) Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res 15:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7290262
Mitupatum T, Aree K, Kittisenachai S, Roytrakul S, Puthong S, Kangsadalampai S, Rojpibulstit P (2016) mRNA expression of Bax, Bcl-2, p53, cathepsin B, caspase-3 and caspase-9 in the HepG2 cell line following induction by a novel monoclonal ab Hep88 mAb: cross-talk for paraptosis and apoptosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17:703–712
Prinz E, Aviram S, Aronheim A (2018) WDR62 mediates TNFalpha-dependent JNK activation via TRAF2-MLK3 axis. Mol Biol Cell 29:2470–2480. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E17-08-0504
Rachakonda G, Vu T, Jin L, Samanta D, Datta PK (2016) Role of TGF-beta-induced Claudin-4 expression through c-Jun signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Signal 28:1537–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.07.006
Rivas S, Gomez-Oro C, Anton IM, Wandosell F (2018) Role of Akt isoforms controlling cancer stem cell survival, phenotype and self-renewal. Biomedicines 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010029
Salnikow K, Kluz T, Costa M, Piquemal D, Demidenko ZN, Xie K, Blagosklonny MV (2002) The regulation of hypoxic genes by calcium involves c-Jun/AP-1, which cooperates with hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in response to hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol 22:1734–1741
Savla JJ, Levine BD, Sadek HA (2018) The effect of hypoxia on cardiovascular disease: friend or foe? High Alt Med Biol 19:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1089/ham.2018.0044
Sousa Fialho MDL, Abd Jamil AH, Stannard GA, Heather LC (2018) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signalling, metabolism and its therapeutic potential in cardiovascular disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.09.024
Udayappan UK, Casey PJ (2017) c-Jun contributes to transcriptional control of GNA12 expression in prostate cancer cells. Molecules 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040612
van der Laan AM, Nahrendorf M, Piek JJ (2012) Healing and adverse remodelling after acute myocardial infarction: role of the cellular immune response. Heart 98:1384–1390. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2012-301623
Wei J, Wang W, Chopra I, Li HF, Dougherty CJ, Adi J, Adi N, Wang H, Webster KA (2011) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK-1) confers protection against brief but not extended ischemia during acute myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem 286:13995–14006. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.211334
Wisdom R, Johnson RS, Moore C (1999) c-Jun regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis by distinct mechanisms. EMBO J 18:188–197. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.1.188
Wu Z, Zhao S, Li C, Liu C (2018) LncRNA TUG1 serves an important role in hypoxia-induced myocardial cell injury by regulating the miR1455pBinp3 axis. Mol Med Rep 17:2422–2430. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8116
Youle RJ, Strasser A (2008) The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2308
Yu B, Miao ZH, Jiang Y, Li MH, Yang N, Li T, Ding J (2009) c-Jun protects hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha from degradation via its oxygen-dependent degradation domain in a nontranscriptional manner. Cancer Res 69:7704–7712. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0808
Zuo Q, Liu J, Huang L, Qin Y, Hawley T, Seo C, Merlino G, Yu Y (2018) AXL/AKT axis mediated-resistance to BRAF inhibitor depends on PTEN status in melanoma. Oncogene 37:3275–3289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0205-4
Funding
The present work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant Nos. 81270228 and 81700277.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Gao, F., He, S. et al. c-Jun promotes the survival of H9c2 cells under hypoxia via PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. J Physiol Biochem 75, 433–441 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00695-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00695-3