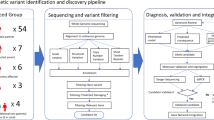
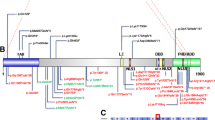
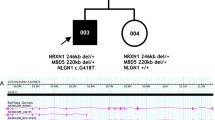
Abstract
Recent studies of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) have resulted in conflicting conclusions regarding the comorbidity of these disorders on phenotypic grounds. In a nuclear family with two dually affected and one unaffected offspring, whole-exome sequences were evaluated for single nucleotide and indel variants and CNVs. The affected siblings but not the unaffected sibling share a rare deleterious compound heterozygous mutation in WWOX, implicated both in ASD and motor control. In addition, one of the affected children carries a rare deleterious de novo mutation in the ASD candidate gene RIMS1. The two affected children but not their unaffected sibling inherited deleterious variants with relevance for ASD and/or CAS. WWOX, RIMS1, and several of the genes harboring the inherited variants are expressed in the brain during prenatal and early postnatal development. Results suggest compound heterozygosity as a cause of ASD and CAS, pleiotropic gene effects, and potentially additional, complex genetic effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Remaileh M, Joy-Dodson E, Schueler-Furman O, Aqeilan RI (2015) Pleiotropic functions of tumor suppressor WWOX in normal and cancer cells. J Biol Chem 290:30728–30735
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7:248–249
Aldrich J, Keats JJ, Christofferson A, Liang WS, Carpten JD, Baumbach-Reardon L, Craig D (2016) Optimization and detection of focal somatic copy number variants in whole genome, whole exome and panel sequencing for tumor/normal matched pairs and tumor only analysis. Paper presented at American Association for Cancer Research, New Orleans, 16–20 April, 2016
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Arlington
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Arlington
Asberg Johnels J, Gillberg C, Kopp S (2017) A hyperlexic-like reading style is associated with increased autistic features in girls with ADHD. J Atten Disord. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054716685838
ASHA (2007) American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Childhood Apraxia of Speech. Technical Report. http://www.asha.org/policy/TR2007-00278/
Baio J et al (2018) Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill Summ 67:1–23
Baker P, Piven J, Schwartz S, Patil S (1994) Brief report: duplication of chromosome 15q11-13 in two individuals with autistic disorder. J Autism Dev Disord 24:529–535
Becker EB, Stoodley CJ (2013) Autism spectrum disorder and the cerebellum. Int Rev Neurobiol 113:1–34
Bishop DV (2010) Overlaps between autism and language impairment: phenomimicry or shared etiology? Behav Genet 40:618–629
Bourgeron T (2016) Current knowledge on the genetics of autism and propositions for future research. C R Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2016.05.004
Boyar FZ et al (2001) A family with a grand-maternally derived interstitial duplication of proximal 15q. Clin Genet 60:421–430
Brady NC, Storkel HL, Bushnell P, Barker RM, Saunders K, Daniels D, Fleming K (2015) Investigating a multimodal intervention for children with limited expressive vocabularies associated with autism. Am J Speech-Lang Pathol 24:438–459
Breece E, Paciotti B, Nordahl CW, Ozonoff S, Van de Water JA, Rogers SJ, Amaral D, Ashwood P (2013) Myeloid dendritic cells frequencies are increased in children with autism spectrum disorder and associated with amygdala volume and repetitive behaviors. Brain Behav Immun 31:69–75
Button L, Peter B, Stoel-Gammon C, Raskind WH (2013) Associations among measures of sequential processing in motor and linguistics tasks in adults with and without a family history of childhood apraxia of speech: a replication study. Clin Linguist Phon 27:192–212
Casey JP et al (2012) A novel approach of homozygous haplotype sharing identifies candidate genes in autism spectrum disorder. Hum Genet 131:565–579
Centanni TM, Green JR, Iuzzini-Seigel J, Bartlett CW, Hogan TP (2015a) Evidence for the multiple hits genetic theory for inherited language impairment: a case study. Front Genet 6:272
Centanni TM, Sanmann JN, Green JR, Iuzzini-Seigel J, Bartlett C, Sanger WG, Hogan TP (2015b) The role of candidate-gene CNTNAP2 in childhood apraxia of speech and specific language impairment. Am J Med Genet B 168:536–543
Chang HT, Liu CC, Chen ST, Yap YV, Chang NS, Sze CI (2014) WW domain-containing oxidoreductase in neuronal injury and neurological diseases. Oncotarget 5:11792–11799
Chen X, Shen Y, Zhang F, Chiang C, Pillalamarri V, Blumenthal I, Talkowski M, Wu BL, Gusella JF (2013) Molecular analysis of a deletion hotspot in the NRXN1 region reveals the involvement of short inverted repeats in deletion CNVs. Am J Hum Genet 92:375–386
Cooper GM, Stone EA, Asimenos G, Program NCS, Green ED, Batzoglou S, Sidow A (2005) Distribution and intensity of constraint in mammalian genomic sequence. Genome Res 15:901–913
De Rubeis S et al (2014) Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature 515:209–215
DiStefano C, Gulsrud A, Huberty S, Kasari C, Cook E, Reiter LT, Thibert R, Jeste SS (2016) Identification of a distinct developmental and behavioral profile in children with Dup15q syndrome. J Neurodev Disord 8:19
Dong S et al (2014) De novo insertions and deletions of predominantly paternal origin are associated with autism spectrum disorder. Cell Rep 9:16–23
Eising E et al (2018) A set of regulatory genes co-expressed in embryonic human brain is implicated in disrupted speech development. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0020-x
Elsas LJ II, Langley S, Paulk EM, Hjelm LN, PP Dembure (1995) A molecular approach to galactosemia. Eur J Pediatr 154:S21–S27
Fedorenko E, Morgan A, Murray E, Cardinaux A, Mei C, Tager-Flusberg H, Fisher SE, Kanwisher N (2016) A highly penetrant form of childhood apraxia of speech due to deletion of 16p11.2. Eur J Hum Genet: EJHG 24:302–306
Fiori S, Guzzetta A, Mitra J, Pannek K, Pasquariello R, Cipriani P, Tosetti M, Cioni G, Rose SE, Chilosi A (2016) Neuroanatomical correlates of childhood apraxia of speech: a connectomic approach. Neuroimage Clin 12:894–901
Firth HV, Richards SM, Bevan AP, Clayton S, Corpas M, Rajan D, Van Vooren S, Moreau Y, Pettett RM, Carter NP (2009) DECIPHER: database of chromosomal imbalance and phenotype in humans using ensembl resources. Am J Hum Genet 84:524–533
Fisher SE, Vargha-Khadem F, Watkins KE, Monaco AP, Pembrey ME (1998) Localisation of a gene implicated in a severe speech and language disorder. Nat Genet 18:168–170
Fisher SE, Lai CS, Monaco AP (2003) Deciphering the genetic basis of speech and language disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:57–80
Fletcher SG (1972) Time-by-count measurement of diadochokinetic syllable rate. J Speech Hear Res 15:763–770
Gaugler T et al (2014) Most genetic risk for autism resides with common variation. Nat Genet 46:881–885
Genomes Project C et al (2015) A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526:68–74
Gialluisi A, Visconti A, Willcutt EG, Smith SD, Pennington BF, Falchi M, DeFries JC, Olson RK, Francks C, Fisher SE (2016) Investigating the effects of copy number variants on reading and language performance. J Neurodev Disord 8:17
Gilman SR, Iossifov I, Levy D, Ronemus M, Wigler M, Vitkup D (2011) Rare de novo variants associated with autism implicate a large functional network of genes involved in formation and function of synapses. Neuron 70:898–907
Girirajan S et al (2011) Relative burden of large CNVs on a range of neurodevelopmental phenotypes. PLoS Genet 7:e1002334
Girirajan S et al (2012) Phenotypic heterogeneity of genomic disorders and rare copy-number variants. N Engl J Med 367:1321–1331
Goldman R, Fristoe M (2000) Goldman-Fristoe test of articulation 2. American Guidance Service, Circle Pines
Gotts SJ, Ramot M, Jasmin K, Martin A (2018) Altered resting-state dynamics in autism spectrum disorder: causal to the social impairment? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 90:28–36
Graham SA, Fisher SE (2013) Decoding the genetics of speech and language. Curr Opin Neurobiol 23:43–51
Graham SA, Fisher SE (2015) Understanding language from a genomic perspective. Annu Rev Genet. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092236
Grigorenko EL, Klin A, Volkmar F (2003) Annotation: hyperlexia: disability or superability? J Child Psychol Psychiatry 44:1079–1091
Griswold AJ et al (2012) Evaluation of copy number variations reveals novel candidate genes in autism spectrum disorder-associated pathways. Hum Mol Genet 21:3513–3523
Haag N, Schwintzer L, Ahuja R, Koch N, Grimm J, Heuer H, Qualmann B, Kessels MM (2012) The actin nucleator Cobl is crucial for Purkinje cell development and works in close conjunction with the F-actin binding protein Abp1. J Neurosci 32:17842–17856
Hanson E, Nasir RH, Fong A, Lian A, Hundley R, Shen Y, Wu BL, Holm IA, Miller DT, p11.2 Study Group C (2010) Cognitive and behavioral characterization of 16p11.2 deletion syndrome. J Dev Behav Pediatr 31:649–657
Huang DW et al (2007) DAVID bioinformatics resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W169–W175
Hussman JP et al (2011) A noise-reduction GWAS analysis implicates altered regulation of neurite outgrowth and guidance in autism. Mol Autism 2:1
Hwang BJ, Mohamed MA, Brasic JR (2017) Molecular imaging of autism spectrum disorder. Int Rev Psychiatry 29:530–554
Iafrate AJ, Feuk L, Rivera MN, Listewnik ML, Donahoe PK, Qi Y, Scherer SW, Lee C (2004) Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat Genet 36:949–951
Iossifov I et al (2012) De novo gene disruptions in children on the autistic spectrum. Neuron 74:285–299
Isaksson J, Pettersson E, Kostrzewa E, Diaz Heijtz R, Bolte S (2017) Brief report: association between autism spectrum disorder, gastrointestinal problems and perinatal risk factors within sibling pairs. J Autism Dev Disord 47:2621–2627
Jimenez-Barron LT, O’Rawe JA, Wu Y, Yoon M, Fang H, Iossifov I, Lyon GJ (2015) Genome-wide variant analysis of simplex autism families with an integrative clinical-bioinformatics pipeline. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 1:a000422
Kircher M, Witten DM, Jain P, O’Roak BJ, Cooper GM, Shendure J (2014) A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat Genet 46:310–315
Krumm N et al (2015) Excess of rare, inherited truncating mutations in autism. Nat Genet 47:582–588
Laffin JJ, Raca G, Jackson CA, Strand EA, Jakielski KJ, Shriberg LD (2012) Novel candidate genes and regions for childhood apraxia of speech identified by array comparative genomic hybridization. Genet Med: Off J Am Coll Med Genet 14:928–936
Lai CS, Fisher SE, Hurst JA, Vargha-Khadem F, Monaco AP (2001) A forkhead-domain gene is mutated in a severe speech and language disorder. Nature 413:519–523
Leblond CS et al (2012) Genetic and functional analyses of SHANK2 mutations suggest a multiple hit model of autism spectrum disorders. PLoS Genet 8:e1002521
Lek M et al (2016) Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 536:285–291
Leppa VM et al (2016) Rare inherited and de novo CNVs reveal complex contributions to ASD risk in multiplex families. Am J Hum Genet. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.06.036
Lewis BA, Freebairn LA, Hansen AJ, Iyengar SK, Taylor HG (2004) School-age follow-up of children with childhood apraxia of speech. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch 35:122–140
Lewis BA, Freebairn LA, Hansen AJ, Stein CM, Shriberg LD, Iyengar SK, Gerry Taylor H (2006) Dimensions of early speech sound disorders: a factor analytic study. J Commun Disord 39:139–157
Li Q, Han Y, Dy ABC, Hagerman RJ (2017) The gut microbiota and autism spectrum disorders. Front Cell Neurosci 11:120
Liegeois FJ, Morgan AT (2012) Neural bases of childhood speech disorders: lateralization and plasticity for speech functions during development. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:439–458
Liegeois F, Baldeweg T, Connelly A, Gadian DG, Mishkin M, Vargha-Khadem F (2003) Language fMRI abnormalities associated with FOXP2 gene mutation. Nat Neurosci 6:1230–1237
MacArthur DG et al (2014) Guidelines for investigating causality of sequence variants in human disease. Nature 508:469–476
MacDonald JR, Ziman R, Yuen RK, Feuk L, Scherer SW (2014) The database of genomic variants: a curated collection of structural variation in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D986–D992
Mallaret M et al (2014) The tumour suppressor gene WWOX is mutated in autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia with epilepsy and mental retardation. Brain: A J Neurol 137:411–419
Marshall CR et al (2008) Structural variation of chromosomes in autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet 82:477–488
McKenna A et al (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Mei C, Fedorenko E, Amor DJ, Boys A, Hoeflin C, Carew P, Burgess T, Fisher SE, Morgan AT (2018) Deep phenotyping of speech and language skills in individuals with 16p11.2 deletion. Eur J Hum Genet: EJHG 26:676–686
Miller M, Chukoskie L, Zinni M, Townsend J, Trauner D (2014) Dyspraxia, motor function and visual-motor integration in autism. Behav Brain Res 269:95–102
Miscimarra L et al (2007) Further evidence of pleiotropy influencing speech and language: analysis of the DYX8 region. Hum Hered 63:47–58
Murray E, McCabe P, Heard R, Ballard KJ (2015) Differential diagnosis of children with suspected childhood apraxia of speech. J Speech, Lang Hear Res: JSLHR 58:43–60
Nation K, Clarke P, Wright B, Williams C (2006) Patterns of reading ability in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord 36:911–919
Neef NE, Hoang TN, Neef A, Paulus W, Sommer M (2015) Speech dynamics are coded in the left motor cortex in fluent speakers but not in adults who stutter. Brain: A J Neurol 138:712–725
Newbury DF, Mari F, Sadighi Akha E, Macdermot KD, Canitano R, Monaco AP, Taylor JC, Renieri A, Fisher SE, Knight SJ (2013) Dual copy number variants involving 16p11 and 6q22 in a case of childhood apraxia of speech and pervasive developmental disorder. Eur J Hum Genet: EJHG 21:361–365
Ng PC, Henikoff S (2003) SIFT: predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3812–3814
Onore C, Careaga M, Ashwood P (2012) The role of immune dysfunction in the pathophysiology of autism. Brain Behav Immun 26:383–392
Pal DK, Li W, Clarke T, Lieberman P, Strug LJ (2010) Pleiotropic effects of the 11p13 locus on developmental verbal dyspraxia and EEG centrotemporal sharp waves. Genes Brain Behav 9:1004–1012
Peter B, Raskind WH (2011) A multigenerational family study of oral and hand motor sequencing ability provides evidence for a familial speech sound disorder subtype. Top Lang Disord 31:145–167
Peter B, Matsushita M, Raskind WH (2012) Motor sequencing deficit as an endophenotype of speech sound disorder: a genome-wide linkage analysis in a multigenerational family. Psychiatr Genet 22:226–234
Peter B, Button L, Stoel-Gammon C, Chapman K, Raskind WH (2013) Deficits in sequential processing manifest in motor and linguistic tasks in a multigenerational family with childhood apraxia of speech. Clin Linguist Phon 27:163–191
Peter B, Matsushita M, Oda K, Raskind W (2014) De novo microdeletion of BCL11A is associated with severe speech sound disorder. Am J Med Genet A 164A:2091–2096
Peter B et al (2016) Genetic candidate variants in two multigenerational families with childhood apraxia of speech. PLoS ONE 11:e0153864
Peter B, Lancaster H, Vose C, Fares A, Schrauwen I, Huentelman M (2017) Two unrelated children with overlapping 6q25.3 deletions, motor speech disorders, and language delays. Am J Med Genet A. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.38385
Pettigrew KA et al (2015) Copy number variation screen identifies a rare De novo deletion at chromosome 15q13.1-13.3 in a child with language impairment. PLoS ONE 10:e0134997
Rabin M, Wen XL, Hepburn M, Lubs HA, Feldman E, Duara R (1993) Suggestive linkage of developmental dyslexia to chromosome 1p34-p36. Lancet 342:178
Raca G, Baas BS, Kirmani S, Laffin JJ, Jackson CA, Strand EA, Jakielski KJ, Shriberg LD (2013) Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) in two patients with 16p11.2 microdeletion syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet: EJHG 21:455–459
Ram Venkataraman G, O’Connell C, Egawa F, Kashef-Haghighi D, Wall DP (2016) De novo mutations in autism implicate the synaptic elimination network. Pac Symp Biocomput 22:521–532
Reuter MS et al (2017) FOXP2 variants in 14 individuals with developmental speech and language disorders broaden the mutational and clinical spectrum. J Med Genet 54:64–72
Reynolds CR, Kamphaus RW (2003) RIAS, Reynolds intellectual assessment scales. Psychological Assessment Resources, Missoula
Richards S et al (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med: Off J Am Coll Med Genet 17:405–424
Roberts JL, Hovanes K, Dasouki M, Manzardo AM, Butler MG (2014) Chromosomal microarray analysis of consecutive individuals with autism spectrum disorders or learning disability presenting for genetic services. Gene 535:70–78
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdottir H, Winckler W, Guttman M, Lander ES, Getz G, Mesirov JP (2011) Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol 29:24–26
Shriberg LD, Aram DM, Kwiatkowski J (1997) Developmental apraxia of speech: I. Descriptive and theoretical perspectives. J Speech, Lang Hear Res: JSLHR 40:273–285
Shriberg LD, Lewis BA, Tomblin JB, McSweeny JL, Karlsson HB, Scheer AR (2005) Toward diagnostic and phenotype markers for genetically transmitted speech delay. J Speech Lang Hear Res: JSLHR 48:834–852
Shriberg LD, Paul R, Black LM, van Santen JP (2011a) The hypothesis of apraxia of speech in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord 41:405–426
Shriberg LD, Potter NL, Strand EA (2011b) Prevalence and phenotype of childhood apraxia of speech in youth with galactosemia. J Speech Lang Hear Res: JSLHR 54:487–519
Shyr C, Tarailo-Graovac M, Gottlieb M, Lee JJ, van Karnebeek C, Wasserman WW (2014) FLAGS, frequently mutated genes in public exomes. BMC Med Genom 7:64
Stefansson H et al (2014) CNVs conferring risk of autism or schizophrenia affect cognition in controls. Nature 505:361–366
Steinberg J, Webber C (2013) The roles of FMRP-regulated genes in autism spectrum disorder: single- and multiple-hit genetic etiologies. Am J Hum Genet 93:825–839
Steinman KJ et al (2016) 16p11.2 deletion and duplication: characterizing neurologic phenotypes in a large clinically ascertained cohort. Am J Med Genet A. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.37820
Stevenson CL, Krantz PJ, McClannahan LE (2000) Social interaction skills for children with autism: a script-fading procedure for nonreaders. Behav Interv 15:1–20
Strand EA, McCauley RJ, Weigand SD, Stoeckel RE, Baas BS (2013) A motor speech assessment for children with severe speech disorders: reliability and validity evidence. J Speech Lang Hear Res: JSLHR 56:505–520
Subramanian K, Brandenburg C, Orsati F, Soghomonian JJ, Hussman JP, Blatt GJ (2017) Basal ganglia and autism—a translational perspective. Autism Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1837
Szymanska K, Szczaluba K, Lugowska A, Obersztyn E, Radkowski M, Nowakowska BA, Kusmierska K, Tryfon J, Demkow U (2014) The analysis of genetic aberrations in children with inherited neurometabolic and neurodevelopmental disorders. Biomed Res Int 2014:424796
Terband H, Maassen B, van Lieshout P, Nijland L (2011) Stability and composition of functional synergies for speech movements in children with developmental speech disorders. J Commun Disord 44:59–74
Thevenon J et al (2013) 12p13.33 microdeletion including ELKS/ERC1, a new locus associated with childhood apraxia of speech. Eur J Hum Genet: EJHG 21:82–88
Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP (2013) Integrative genomics viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 14:178–192
Tierney C, Mayes S, Lohs SR, Black A, Gisin E, Veglia M (2015) How valid is the checklist for autism spectrum disorder when a child has apraxia of speech? J Dev Behav Pediatr 36:569–574
Tonne E et al (2015) Syndromic X-linked intellectual disability segregating with a missense variant in RLIM. Eur J Hum Genet: EJHG 23:1652–1656
Torgesen JK, Wagner RK, Rashotte CA (2012) Test of word reading efficiency, 2nd edn. Pro-Ed, Austin
Toro R, Konyukh M, Delorme R, Leblond C, Chaste P, Fauchereau F, Coleman M, Leboyer M, Gillberg C, Bourgeron T (2010) Key role for gene dosage and synaptic homeostasis in autism spectrum disorders. Trends Genet 26:363–372
Urraca N et al (2016) A rare inherited 15q11.2-q13.1 interstitial duplication with maternal somatic mosaicism, renal carcinoma, and autism. Front Genet 7:205
van der Merwe A (2009) A theoretical framework for the characterization of pathological speech sensorimotor control. In: McNeil MR (ed) Clinical management of sensorimotor speech disorders, 2nd edn, pp 3–18. Thieme Medical Publishers, New York
Velayos-Baeza A, Vettori A, Copley RR, Dobson-Stone C, Monaco AP (2004) Analysis of the human VPS13 gene family. Genomics 84:536–549
Vick JC, Campbell TF, Shriberg LD, Green JR, Truemper K, Rusiewicz HL, Moore CA (2014) Data-driven subclassification of speech sound disorders in preschool children. J Speech, Lang, Hear Res: JSLHR 57:2033–2050
Wang T et al (2016) De novo genic mutations among a Chinese autism spectrum disorder cohort. Nat Commun 7:13316
Wei X, Christiano ER, Yu JW, Wagner M, Spiker D (2015) Reading and math achievement profiles and longitudinal growth trajectories of children with an autism spectrum disorder. Autism 19:200–210
Weiss LA et al (2008) Association between microdeletion and microduplication at 16p11.2 and autism. N Engl J Med 358:667–675
Whiffin N et al (2017) Using high-resolution variant frequencies to empower clinical genome interpretation. Genet Med: Off J Am Coll Med Genet 19:1151–1158
Winchester L, Newbury DF, Monaco AP, Ragoussis J (2008) Detection, breakpoint identification and detailed characterisation of a CNV at the FRA16D site using SNP assays. Cytogenet Genome Res 123:322–332
Woodcock R (2011) Woodcock reading mastery test, 3rd edn. Pearson, Bloomington
Zarrei M, MacDonald JR, Merico D, Scherer SW (2015) A copy number variation map of the human genome. Nat Rev Genet 16:172–183
Funding
This research was supported by Arizona State University New Faculty Startup Funding (B. Peter).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BP and IS conceived the study. BP oversaw and participated in the behavioral data collection and analysis, participated in the variant analysis, and drafted the manuscript; all authors provided comments and revisions. VD and LL provided guidance and participation regarding bioinformatic procedures. HL assisted with the behavioral data collection. CV assisted with analyzing the behavioral test data. IS, MH, and MN managed the variant annotations, validated the variants in IGV, and provided interpretation of genomic results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Beate Peter, Valentin Dinu, Li Liu, Matthew Huentelman, Marcus Naymik, Hope Lancaster, Caitlin Vose, and Isabelle Schrauwen declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted with the approval of the University of Washington’s institutional review board acting on behalf of Arizona State University. All procedures were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
The adults gave written consent to participate and the children participated with their parents’ written permission.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by Gene Fisch.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peter, B., Dinu, V., Liu, L. et al. Exome Sequencing of Two Siblings with Sporadic Autism Spectrum Disorder and Severe Speech Sound Disorder Suggests Pleiotropic and Complex Effects. Behav Genet 49, 399–414 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-019-09957-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-019-09957-8