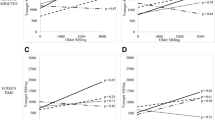
Abstract
This study aims to estimate sibling resemblance in metabolic syndrome (MS) markers, and to investigate the associations of biological and behavioral characteristics with MS. The sample comprises 679 biological siblings (363 females; 316 males) aged 9–20 years. MS markers included waist circumference (WC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglycerides (TRI), fasting glucose (GLU) and systolic blood pressure (SBP). Body mass index (BMI), biological maturation, muscular, and cardiorespiratory fitness were also assessed. Behavioral characteristics, including dietary intake and physical activity, were self-reported by questionnaire. Multilevel models were used, and sibling resemblance was estimated using the intraclass correlation (ρ). In general, same-sex siblings showed higher resemblance in MS markers than opposite-sex siblings. However, variability in sibling resemblance in MS markers was evident with the inclusion of covariates. Biological characteristics including age, BMI and maturity offset influenced all MS markers except for TRI. Importantly, behavioral characteristics diversely influenced MS markers: fruit and vegetables only influenced SBP, whereas physical activity affected HDL-C. Additionally, muscular fitness impacted significantly on MS Z-score, WC, SBP and GLU, whilst cardiorespiratory fitness only affected WC. In conclusion, biological and behavioral characteristics influenced the expression of MS markers. These results confirmed the importance of considering individual characteristics when designing individualized programs for diminishing the adverse effects of specific MS markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agirbasli M, Agaoglu NB, Orak N, Caglioz H, Ocek T, Poci N, Salaj A, Maya S (2009) Sex hormones and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Metabolism 58(9):1256–1262
Agirbasli M, Tanrikulu AM, Berenson GS (2016) Metabolic syndrome: bridging the gap from childhood to adulthood. Cardiovasc Ther 34(1):30–36
Alberga AS, Sigal RJ, Goldfield G, Prud’homme D, Kenny GP (2012) Overweight and obese teenagers: why is adolescence a critical period? Pediatr Obes 7(4):261–273
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J (2006) Metabolic syndrome—a new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the international diabetes federation. Diabet Med 23(5):469–480
Arora P, Newton-Cheh C (2010) Blood pressure and human genetic variation in the general population. Curr Opin Cardiol 25(3):229–237
Artero EG, Ruiz JR, Ortega FB, Espana-Romero V, Vicente-Rodriguez G, Molnar D, Gottrand F, Gonzalez-Gross M, Breidenassel C, Moreno LA, Gutierrez A (2011) Muscular and cardiorespiratory fitness are independently associated with metabolic risk in adolescents: the HELENA study. Pediatr Diabetes 12(8):704–712
Arya R, Puppala S, Farook VS, Chittoor G, Jenkinson CP, Blangero J, Hale DE, Duggirala R, Almasy L (2015) Mapping of susceptibility genes for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome in human populations. In: Duggirala R, Almasy L, Williams-Blangero S, Paul SFD, Kole C (eds) Genome mapping and genomics in human and non-human primates. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–245
Aydın B, Winters SJ (2016) Sex hormone-binding globulin in children and adolescents. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 8(1):1–12
Baecke JA, Burema J, Frijters JE (1982) A short questionnaire for the measurement of habitual physical activity in epidemiological studies. Am J Clin Nutr 36(5):936–942
Baxter AJ, Coyne T, McClintock C (2006) Dietary patterns and metabolic syndrome—a review of epidemiologic evidence. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 15(2):134–142
Bellia A, Giardina E, Lauro D, Tesauro M, Di Fede G, Cusumano G, Federici M, Rini GB, Novelli G, Lauro R, Sbraccia P (2009) “The Linosa Study”: epidemiological and heritability data of the metabolic syndrome in a Caucasian genetic isolate. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 19(7):455–461
Camhi SM, Katzmarzyk PT (2011) Prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factor clustering and body mass index in adolescents. J Pedriatr 159(2):303–307
Chang Y, Cheng Y, Yu H, Chuang L (2013) Molecular genetics of metabolic syndrome. eLS, Wiley, Chichester
Cholestech LDX (2003) The accuracy and reproducibility of a rapid, fingerstick method for measuring a complete lipid profile is comparable to a Reference Laboratory Method (b). Cholestech Corporation, Hayward
Cohen DD, Gomez-Arbelaez D, Camacho PA, Pinzon S, Hormiga C, Trejos-Suarez J, Duperly J, Lopez-Jaramillo P (2014) Low muscle strength is associated with metabolic risk factors in Colombian children: the ACFIES study. PLoS ONE 9(4):e93150
Collese TS, Nascimento-Ferreira MV, de Moraes ACF, Rendo-Urteaga T, Bel-Serrat S, Moreno LA, Carvalho HB (2017) Role of fruits and vegetables in adolescent cardiovascular health: a systematic review. Nutr Rev 75(5):339–349
Couch SC, Saelens BE, Levin L, Dart K, Falciglia G, Daniels SR (2008) The efficacy of a clinic-based behavioral nutrition intervention emphasizing a DASH-type diet for adolescents with elevated blood pressure. J Pedriatr 152(4):494–501
Currie C, Gabhainn SN, Godeau E, Roberts C, Smith R, Currie D, Pickett W, Richter M, Morgan A, Barnekow V (2008) Inequalities in Young People’s Health: HBSC International Report from the 2005/06 Survey. Health Policy for Children and Adolescents. WHO Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen
Demmer DL, Beilin LJ, Hands B, Burrows S, Cox KL, Straker LM, Mori TA (2016) Effects of muscle strength and endurance on blood pressure and related cardiometabolic risk factors from childhood to adolescence. J Hypertens 34(12):2365–2375
Duan H, Pang Z, Zhang D, Li S, Kruse TA, Kyvik KO, Christensen K, Tan Q (2011) Genetic and environmental dissections of sub-phenotypes of metabolic syndrome in the Chinese population: a twin-based heritability study. Obes Facts 4(2):99–104
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ (2005) The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 365(9468):1415–1428
Eisenmann JC (2008) On the use of a continuous metabolic syndrome score in pediatric research. Cardiovasc Diabetol 7:17
Eisenmann JC, Laurson KR, DuBose KD, Smith BK, Donnelly JE (2010) Construct validity of a continuous metabolic syndrome score in children.. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2:28
Fam B, Amouzegar A, Arzhan S, Ghanbariyan A, Delshad M, Hosseinpanah F, Azizi F (2013) Association between physical activity and metabolic risk factors in adolescents: Tehran lipid and glucose study. Int J Prev Med 4(9):1011–1017
Ford ES, Li C (2006) Physical activity or fitness and the metabolic syndrome. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 4(6):897–915
Friend A, Craig L, Turner S (2013) The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in children: a systematic review of the literature. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 11(2):71–80
Gomes TN, Dos Santos FK, Katzmarzyk PT, Maia J (2017) Active and strong: physical activity, muscular strength, and metabolic risk in children.. Am J Hum Biol 29(1)
Hedeker D, Mermelstein RJ, Demirtas H (2012) Modeling between-subject and within-subject variances in ecological momentary assessment data using mixed-effects location scale models. Stat Med 31(27):3328–3336
Helmerhorst HJ, Brage S, Warren J, Besson H, Ekelund U (2012) A systematic review of reliability and objective criterion-related validity of physical activity questionnaires. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 9:9103
Huang YC, Malina RM (2007) BMI and health-related physical fitness in Taiwanese youth 9–18 years. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(4):701–708
Johansen CT, Kathiresan S, Hegele RA (2011) Genetic determinants of plasma triglycerides. J Lipid Res 52(2):189–206
Katzmarzyk PT, Malina RM, Perusse L, Rice T, Province MA, Rao DC, Bouchard C (2000) Familial resemblance in fatness and fat distribution. Am J Hum Biol 12(3):395–404
LeBlanc AG, Janssen I (2010) Dose-response relationship between physical activity and dyslipidemia in youth. J Cardiol 26(6):201–205
Lin HF, Boden-Albala B, Juo SH, Park N, Rundek T, Sacco RL (2005) Heritabilities of the metabolic syndrome and its components in the Northern Manhattan Family Study. Diabetologia 48(10):2006–2012
Luo BF, Du L, Li JX, Pan BY, Xu JM, Chen J, Yin XY, Ren Y, Zhang F (2010) Heritability of metabolic syndrome traits among healthy younger adults: a population based study in China. J Med Genet 47(6):415–420
Lusis AJ, Attie AD, Reue K (2008) Metabolic syndrome: from epidemiology to systems biology. Nat Rev Genet 9(11):819–830
Malina RM, Bar-Or O, Bouchard C (2004) Growth, maturation, and physical activity. Human Kinetics, Champaign
McMurray RG, Bangdiwala SI, Harrell JS, Amorim LD (2008) Adolescents with metabolic syndrome have a history of low aerobic fitness and physical activity levels. Dyn Med 75:5
Mehairi AE, Khouri AA, Naqbi MM, Muhairi SJ, Maskari FA, Nagelkerke N, Shah SM (2013) Metabolic syndrome among Emirati adolescents: a school-based study. PLoS ONE 8(2):e56159
Miller DJ, Freedson PS, Kline GM (1994) Comparison of activity levels using the Caltrac accelerometer and five questionnaires. Med Sci Sports Exerc 26(3):376–382
Miranda-Lora AL, Vilchis-Gil J, Molina-Diaz M, Flores-Huerta S, Klunder-Klunder M (2017) Heritability, parental transmission and environment correlation of pediatric-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome-related traits.. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 126151–126159
Mirwald RL, Baxter-Jones AD, Bailey DA, Beunen GP (2002) An assessment of maturity from anthropometric measurements. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34(4):689–694
Mohlke KL, Boehnke M (2015) Recent advances in understanding the genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes. Hum Mol Genet 24(R1):R85–R92
Moschonis G, Mavrogianni C, Karatzi K, Iatridi V, Chrousos GP, Lionis C, Manios Y (2013) Increased physical activity combined with more eating occasions is beneficial against dyslipidemias in children. The Healthy Growth Study. Eur J Nutr 52(3):1135–1144
Nguyen TH, Tang HK, Kelly P, van der Ploeg HP, Dibley MJ (2010) Association between physical activity and metabolic syndrome: a cross sectional survey in adolescents in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. BMC Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-10-141
Ordovas JM, Shen J (2008) Gene–environment interactions and susceptibility to metabolic syndrome and other chronic diseases. J Periodontol 79(8 Suppl):1508–1513
Park HS, Park JY, Cho SI (2006) Familial aggregation of the metabolic syndrome in Korean families with adolescents. Atherosclerosis 186(1):215–221
Pereira MA, FitzerGerald SJ, Gregg EW, Joswiak ML, Ryan WJ, Suminski RR, Utter AC, Zmuda JM (1997) A collection of Physical Activity Questionnaires for health-related research. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29(6 Suppl):S1–S205
Pereira S, Katzmarzyk PT, Gomes TN, Souza M, Chaves RN, Dos Santos FK, Santos D, Hedeker D, Maia J (2017) A multilevel analysis of health-related physical fitness. The Portuguese sibling study on growth, fitness, lifestyle and health. PLoS ONE 12(2)
Pereira S, Katzmarzyk PT, Gomes TN, Souza M, Chaves RN, Santos FK, Santos D, Bustamante A, Barreira TV, Hedeker D, Maia JA (2018) Resemblance in physical activity levels: the Portuguese sibling study on growth, fitness, lifestyle, and health. Am J Hum Biol 30(1):e23061
Philippaerts RM, Westerterp KR, Lefevre J (1999) Doubly labelled water validation of three physical activity questionnaires. Int J Sports Med 20(5):284–289
Poulsen P, Vaag A, Kyvik K, Beck-Nielsen H (2001) Genetic versus environmental aetiology of the metabolic syndrome among male and female twins. Diabetologia 44(5):537–543
Randall JC, Winkler TW, Kutalik Z, Berndt SI, Jackson AU, Monda KL, Kilpeläinen TO, Esko T, Mägi R, Li S, Workalemahu T, Feitosa MF, Croteau-Chonka DC, Day FR, Fall T, Ferreira T, Gustafsson S, Locke AE, Mathieson I, Scherag A, Vedantam S, Wood AR, Liang L, Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Dermitzakis ET, Dimas AS, Karpe F, Min JL, Nicholson G, Clegg DJ, Person T, Krohn JP, Bauer S, Buechler C, Eisinger K, Consortium D, Bonnefond A, Froguel P, Investigators M, Hottenga J-J, Prokopenko I, Waite LL, Harris TB, Smith AV, Shuldiner AR, McArdle WL, Caulfield MJ, Munroe PB, Grönberg H, Chen Y-D, Li G, Beckmann JS, Johnson T, Thorsteinsdottir U, Teder-Laving M, Khaw K-T, Wareham NJ, Zhao JH, Amin N, Oostra BA, Kraja AT, Province MA, Cupples LA, Heard-Costa NL, Kaprio J, Ripatti S, Surakka I, Collins FS, Saramies J, Tuomilehto J, Jula A, Salomaa V, Erdmann J, Hengstenberg C, Loley C, Schunkert H, Lamina C, Wichmann HE, Albrecht E, Gieger C, Hicks AA, Johansson Å, Pramstaller PP, Kathiresan S, Speliotes EK, Penninx B, Hartikainen A-L, Jarvelin M-R, Gyllensten U, Boomsma DI, Campbell H, Wilson JF, Chanock SJ, Farrall M, Goel A, Medina-Gomez C, Rivadeneira F, Estrada K, Uitterlinden AG, Hofman A, Zillikens MC, den Heijer M, Kiemeney LA, Maschio A, Hall P, Tyrer J, Teumer A, Völzke H, Kovacs P, Tönjes A, Mangino M, Spector TD, Hayward C, Rudan I, Hall AS, Samani NJ, Attwood AP, Sambrook JG, Hung J, Palmer LJ, Lokki M-L, Sinisalo J, Boucher G, Huikuri H, Lorentzon M, Ohlsson C, Eklund N, Eriksson JG, Barlassina C, Rivolta C, Nolte IM, Snieder H, Van der Klauw MM, Van Vliet-Ostaptchouk JV, Gejman PV, Shi J, Jacobs KB, Wang Z, Bakker SJL, Mateo LI, Navis G, van der Harst P, Martin NG, Medland SE, Montgomery GW, Yang J, Chasman DI, Ridker PM, Rose LM, Lehtimäki T, Raitakari O, Absher D, Iribarren C, Basart H, Hovingh KG, Hyppönen E, Power C, Anderson D, Beilby JP, Hui J, Jolley J, Sager H, Bornstein SR, Schwarz PEH, Kristiansson K, Perola M, Lindström J, Swift AJ, Uusitupa M, Atalay M, Lakka TA, Rauramaa R, Bolton JL, Fowkes G, Fraser RM, Price JF, Fischer K, KrjutÅ¡kov K, Metspalu A, Mihailov E, Langenberg C, Luan JA, Ong KK, Chines PS, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi SM, Saaristo TE, Edkins S, Franks PW, Hallmans G, Shungin D, Morris AD, Palmer CNA, Erbel R, Moebus S, Nöthen MM, Pechlivanis S, Hveem K, Narisu N, Hamsten A, Humphries SE, Strawbridge RJ, Tremoli E, Grallert H, Thorand B, Illig T, Koenig W, Müller-Nurasyid M, Peters A, Boehm BO, Kleber ME, März W, Winkelmann BR, Kuusisto J, Laakso M, Arveiler D, Cesana G, Kuulasmaa K, Virtamo J, Yarnell JWG, Kuh D, Wong A, Lind L, de Faire U, Gigante B, Magnusson PKE, Pedersen NL, Dedoussis G, Dimitriou M, Kolovou G, Kanoni S, Stirrups K, Bonnycastle LL, Njølstad I, Wilsgaard T, Ganna A, Rehnberg E, Hingorani A, Kivimaki M, Kumari M, Assimes TL, Barroso I, Boehnke M, Borecki IB, Deloukas P, Fox CS, Frayling T, Groop LC, Haritunians T, Hunter D, Ingelsson E, Kaplan R, Mohlke KL, O’Connell JR, Schlessinger D, Strachan DP, Stefansson K, van Duijn CM, Abecasis GR, McCarthy MI, Hirschhorn JN, Qi L, Loos RJF, Lindgren CM, North KE, Heid IM (2013) Sex-stratified Genome-wide Association Studies Including 270,000 Individuals Show Sexual Dimorphism in Genetic Loci for Anthropometric Traits. PLoS Genet 9(6):e1003500
Rioux BV, Kuwornu P, Sharma A, Tremblay MS, McGavock JM, Senechal M (2017) Association between handgrip muscle strength and cardiometabolic z-score in children 6 to 19 years of age: results from the canadian health measures survey. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 15(7):379–384
Santos DM, Katzmarzyk PT, Tregouet DA, Gomes TN, Santos FK, Maia JA (2013) Familial aggregation of metabolic syndrome indicators in Portuguese families. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/314823
Santos DM, Katzmarzyk PT, Diego VP, Blangero J, Souza MC, Freitas DL, Chaves RN, Gomes TN, Santos FK, Maia JA (2014) Genotype by sex and genotype by age interactions with sedentary behavior: the Portuguese Healthy Family Study. PloS ONE 9(10):e110025
Sardinha LB, Santos DA, Silva AM, Grontved A, Andersen LB, Ekelund U (2016) A comparison between BMI, waist circumference, and waist-to-height ratio for identifying cardio-metabolic risk in children and adolescents. PLoS ONE 11(2):e0149351
Sekokotla MA, Goswami N, Sewani-Rusike CR, Iputo JE, Nkeh-Chungag BN (2017) Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adolescents living in Mthatha, South Africa. Ther Clin Risk Manag 13:131–137
Shi L, Krupp D, Remer T (2013) Salt, fruit and vegetable consumption and blood pressure development: a longitudinal investigation in healthy children. Br J Nutr 111(4):662–671
Stabelini NA, Sasaki JE, Mascarenhas LP, Boguszewski MC, Bozza R, Ulbrich AZ, da Silva SG, de Campos W (2011) Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and metabolic syndrome in adolescents: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health11:11674
Stabelini NA, de Campos W, Dos Santos GC, Mazzardo JO (2014) Metabolic syndrome risk score and time expended in moderate to vigorous physical activity in adolescents.. BMC Pediatr 14:1442
Steene-Johannessen J, Anderssen SA, Kolle E, Andersen LB (2009) Low muscle fitness is associated with metabolic risk in youth. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(7):1361–1367
Sung J, Lee K, Song YM (2009) Heritabilities of the metabolic syndrome phenotypes and related factors in Korean twins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(12):4946–4952
van Dongen J, Willemsen G, Chen W-M, de Geus EJC, Boomsma DI (2013) Heritability of metabolic syndrome traits in a large population-based sample. J Lipid Res 54(10):2914–2923
Warburton DE, Nicol CW, Bredin SS (2006) Health benefits of physical activity: the evidence. CMAJ 174(6):801–809
Weissglas-Volkov D, Pajukanta P (2010) Genetic causes of high and low serum HDL-cholesterol. J Lipid Res 51(8):2032–2057
Werneck AO, Silva DR, Collings PJ, Fernandes RA, Ronque ER, Barbosa DS, Cyrino ES (2016) Biological maturation, central adiposity, and metabolic risk in adolescents: a mediation analysis. Child Obes 12(5):377–383
WHO (1995) Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry: Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organization, Geneva
Widen E, Silventoinen K, Sovio U, Ripatti S, Cousminer DL, Hartikainen AL, Laitinen J, Pouta A, Kaprio J, Jarvelin MR, Peltonen L, Palotie A (2012) Pubertal timing and growth influences cardiometabolic risk factors in adult males and females. Diabetes care 35(4):850–856
Zaqout M, Michels N, Bammann K, Ahrens W, Sprengeler O, Molnar D, Hadjigeorgiou C, Eiben G, Konstabel K, Russo P, Jimenez-Pavon D, Moreno LA, De Henauw S (2016) Influence of physical fitness on cardio-metabolic risk factors in European children. The IDEFICS study. Int J Obes 40(7):1119–1125
Zarkesh M, Hosseinpanah F, Barzin M, Hosseinzadeh N, Guity K, Daneshpour MS, Azizi F (2014) Recurrence risk ratio of siblings and familial aggregation of the metabolic syndrome among Tehranian population. Arch Iran Med 17(6):411–416
Funding
This study was funded by FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology Portugal (Grant Reference: SFRH/BD/116374/2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Sara Pereira, Peter T. Katzmarzyk, Thayse Natacha Gomes, Rojapon Buranarugsa, Marcos A. Moura-Dos-Santos, Donald Hedeker, José Maia declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from legal guardians, and the project was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Porto and school authorities (CEFADE 09.2015).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Handling Editor: Meike Bartels.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, S., Katzmarzyk, P.T., Gomes, T.N. et al. Sibling Similarity in Metabolic Syndrome: The Portuguese Sibling Study on Growth, Fitness, Lifestyle and Health. Behav Genet 49, 299–309 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-019-09953-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-019-09953-y