Abstract
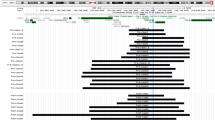
Both copy number losses and gains occur within subtelomeric 9q34 region without common breakpoints. The microdeletions cause Kleefstra syndrome (KS), whose responsible gene is EHMT1. A 9q34 duplication syndrome (9q34 DS) had been reported in literature, but it has never been characterized by a detailed molecular analysis of the gene content and endpoints. To the best of our knowledge, we report on the first patient carrying the smallest 9q34.3 duplication containing EHMT1 as the only relevant gene. We compared him with 21 reported patients described here as carrying 9q34.3 duplications encompassing the entire gene and extending within ~ 3 Mb. By surveying the available clinical and molecular cytogenetic data, we were able to discover that similar neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) were shared by patient carriers of even very differently sized duplications. Moreover, some facial features of the 9q34 DS were more represented than those of KS. However, an accurate in silico analysis of the genes mapped in all the duplications allowed us to support EHMT1 as being sufficient to cause a NDD phenotype. Wider patient cohorts are needed to ascertain whether the rearrangements have full causative role or simply confer the susceptibility to NDDs and possibly to identify the cognitive and behavioral profile associated with the increased dosage of EHMT1.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yatsenko SA, Hixson P, Roney EK, Scott DA, Schaaf CP, Ng YT, Palmer R, Fisher RB, Patel A, Cheung SW, Lupski JR (2012) Human subtelomeric copy number gains suggest a DNA replication mechanism for formation: beyond breakage-fusion-bridge for telomere stabilization. Hum Genet 131(12):1895–1910
Kleefstra T, Brunner HG, Amiel J, Oudakker AR, Nillesen WM, Magee A, Geneviève D, Cormier-Daire V, van Esch H, Fryns JP, Hamel BC, Sistermans EA, de Vries BB, van Bokhoven H (2006) Loss-of-function mutations in euchromatin histone methyl transferase 1 (EHMT1) cause the 9q34 subtelomeric deletion syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 79(2):370–377
Kleefstra T, van Zelst-Stams WA, Nillesen WM, Cormier-Daire V, Houge G, Foulds N, van Dooren M, Willemsen MH, Pfundt R, Turner A, Wilson M, McGaughran J, Rauch A, Zenker M, Adam MP, Innes M, Davies C, López AG, Casalone R, Weber A, Brueton LA, Navarro AD, Bralo MP, Venselaar H, Stegmann SP, Yntema HG, van Bokhoven H, Brunner HG (2009) Further clinical and molecular delineation of the 9q subtelomeric deletion syndrome supports a major contribution of EHMT1 haploinsufficiency to the core phenotype. J Med Genet 46(9):598–606
Yatsenko SA, Brundage EK, Roney EK, Cheung SW, Chinault AC, Lupski JR (2009) Molecular mechanisms for subtelomeric rearrangements associated with the 9q34.3 microdeletion syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 18(11):1924–1936
Betancur C (2011) Etiological heterogeneity in autism spectrum disorders: more than 100 genetic and genomic disorders and still counting. Brain Res 1380:42–77
Vermeulen K, Staal W, Janzing J, Buitelaar J, van Bokhoven H, Egger J, Kleefstra T (2015) From a single gene defect towards a cross species neurocognitive phenotype: the EHMT1 disruption example (Kleefstra syndrome). Austin J Autism Relat Disabil 1(2):1009
Schmidt S, Nag HE, Hunn BS, Houge G, Hoxmark LB (2016) A structured assessment of motor function and behavior in patients with Kleefstra syndrome. Eur J Med Genet 59(4):240–248
Bock I, Németh K, Pentelényi K, Balicza P, Balázs A, Molnár MJ, Román V, Nagy J, Lévay G, Kobolák J, Dinnyés A (2016) Targeted next generation sequencing of a panel of autism-related genes identifies an EHMT1 mutation in a Kleefstra syndrome patient with autism and normal intellectual performance. Gene 595(2):131–141
Benevento M, Iacono G, Selten M, Ba W, Oudakker A, Frega M, Keller J, Mancini R, Lewerissa E, Kleefstra T, Stunnenberg HG, Zhou H, van Bokhoven H, Nadif Kasri N (2016) Histone methylation by the Kleefstra syndrome protein EHMT1 mediates homeostatic synaptic scaling. Neuron 91(2):341–355
Allderdice PW, Eales B, Onyett H, Sprague W, Henderson K, Lefeuvre PA, Pal G (1983) Duplication 9q34 syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 35(5):1005–1019
Gawlik-Kuklinska K, Iliszko M, Wozniak A, Debiec-Rychter M, Kardas I, Wierzba J, Limon J (2007) A girl with duplication 9q34 syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 143A(17):2019–2023
Gijsbers AC, Bijlsma EK, Weiss MM, Bakker E, Breuning MH, Hoffer MJ, Ruivenkamp CA (2008) A 400kb duplication, 2.4Mb triplication and 130kb duplication of 9q34.3 in a patient with severe mental retardation. Eur J Med Genet 51(5):479–487
Singh S, Ashton F, Marquis-Nicholson R, Love JM, Lan CC, Aftimos S, George AM, Love DR (2012) A novel 2.3 mb microduplication of 9q34.3 inserted into 19q13.4 in a patient with learning disabilities. Case Rep Pediatr 2012:459602
Gadancheva VG, Casey JP, Russell JD, McDaid J, Betts DR, Lynch SA (2014) Vocal cord paralysis in association with 9q34 duplication. Clin Dysmorphol 23(3):105–108
Narahara K, Himoto Y, Yokoyama Y (1984) The critical monosomic segment involved in 4p- syndrome: a high resolution banding study on five inherited cases. Jpn J Hum Genet 29:403–413
Wellesley D, Young ID, Cooke P, Callen DF, Hockey A (1988) Simultaneous trisomy 9q3 and monosomy 5p in two children with der(5),t(5;9)(p15.1;q34.13): report of an extended family. J Med Genet 25(10):707–710
Krauss CM, Liptak KJ, Aggarwal A, Robinson D (1989) Inheritance and phenotypic expression of a t(7;9)(q36;q34)mat. Am J Med Genet 34(4):514–519
Houdou S, Yorifugi T, Tsuruta S, Hashida K, Ohta S, Ieshima A (1987) Distal 9q trisomy syndrome: report of the first oriental case and literature review. Acta Neonatal Jpn 23:347–352
Spinner NB, Lucas JN, Poggensee M, Jacquette M, Schneider A (1993) Duplication 9q34-->qter identified by chromosome painting. Am J Med Genet 45(5):609–613
Estop AM, Mowery-Rushton PA, Cieply KM, Kochmar SJ, Sherer CR, Clemens M, Surti U, McPherson E (1995) Identification of an unbalanced cryptic translocation t(9;17)(q34.3;p13.3) in a child with dysmorphic features. J Med Genet 32(10):819–822
Mattina T, Pierluigi M, Mazzone D, Scardilli S, Perfumo C, Mollica F (1997) Double partial trisomy 9q34.1-->qter and 21pter-->q22.11: FISH and clinical findings. J Med Genet 34(11):945–948
Shapira SK, Orr-Urtreger A, Gagos S, Shaffer LG (1997) Constitutional mosaicism for a chromosome 9 inversion resulting in recombinant aneusomy in an offspring. Am J Med Genet 69(4):360–364
Sanger TM, Olney AH, Zaleski D, Pickering D, Nelson M, Sanger WG, Dave BJ (2005) Cryptic duplication and deletion of 9q34.3 --> qter in a family with a t(9;22)(q34.3;p11.2). Am J Med Genet A 138(1):51–55
Ruiter EM, Koolen DA, Kleefstra T, Nillesen WM, Pfundt R, de Leeuw N, Hamel BC, Brunner HG, Sistermans EA, de Vries BB (2007) Pure subtelomeric microduplications as a cause of mental retardation. Clin Genet 72(4):362–368
Wu DJ, Wang NJ, Driscoll J, Dorrani N, Liu D, Sigman M, Schanen NC (2009) Autistic disorder associated with a paternally derived unbalanced translocation leading to duplication of chromosome 15pter-q13.2: a case report. Mol Cytogenet 2:27
Papadopoulou E, Sismani C, Christodoulou C, Ioannides M, Kalmanti M, Patsalis P (2010) Phenotype-genotype correlation of a patient with a "balanced" translocation 9;15 and cryptic 9q34 duplication and 15q21q25 deletion. Am J Med Genet A 152A(6):1515–1522
Youngs EL, McCord T, Hellings JA, Spinner NB, Schneider A, Butler MG (2010) An 18-year follow-up report on an infant with a duplication of 9q34. Am J Med Genet A 152A(1):230–233
Mizuno S, Fukushi D, Kimura R, Yamada K, Yamada Y, Kumagai T, Wakamatsu N (2011) Clinical and genomic characterization of siblings with a distal duplication of chromosome 9q (9q34.1-qter). Am J Med Genet A 155A(9):2274–2280
Mundhofir FE, Smeets D, Nillesen W, Winarni TI, Yntema HG, de Leeuw N, Hamel BC, Faradz SM, van Bon BW (2012) Monosomy 9pter and trisomy 9q34.11qter in two sisters due to a maternal pericentric inversion. Gene 511(2):451–454
Koolen DA, Pfundt R, de Leeuw N, Hehir-Kwa JY, Nillesen WM, Neefs I, Scheltinga I, Sistermans E, Smeets D, Brunner HG, van Kessel AG, Veltman JA, de Vries BB (2009) Genomic microarrays in mental retardation: a practical workflow for diagnostic applications. Hum Mutat 30(3):283–292
Miller DT, Adam MP, Aradhya S, Biesecker LG, Brothman AR, Carter NP, Church DM, Crolla JA, Eichler EE, Epstein CJ, Faucett WA, Feuk L, Friedman JM, Hamosh A, Jackson L, Kaminsky EB, Kok K, Krantz ID, Kuhn RM, Lee C, Ostell JM, Rosenberg C, Scherer SW, Spinner NB, Stavropoulos DJ, Tepperberg JH, Thorland EC, Vermeesch JR, Waggoner DJ, Watson MS, Martin CL, Ledbetter DH (2010) Consensus statement: chromosomal microarray is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with developmental disabilities or congenital anomalies. Am J Hum Genet 86(5):749–764
Kearney HM, Thorland EC, Brown KK, Quintero-Rivera F, South ST, Working Group of the American College of Medical Genetics Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee (2011) American College of Medical Genetics standards and guidelines for interpretation and reporting of postnatal constitutional copy number variants. Genet Med 13(7):680–685
Lichter P, Ledbetter SA, Ledbetter DH, Ward DC (1990) Fluorescence in situ hybridization with Alu and L1 polymerase chain reaction probes for rapid characterization of human chromosomes in hybrid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(17):6634–6638
Lichter P, Cremer T (1992) Chromosome analysis by non-isotopic in situ hybridisation. In: Rooney DE, Czepulkowski BH (eds) Human cytogenetics - a practical approach. IRL Press, New York, pp 157–192
Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV, Samocha KE, Banks E, Fennell T, O’Donnell-Luria AH, Ware JS, Hill AJ, Cummings BB, Tukiainen T, Birnbaum DP, Kosmicki JA, Duncan LE, Estrada K, Zhao F, Zou J, Pierce-Hoffman E, Berghout J, Cooper DN, Deflaux N, DePristo M, Do R, Flannick J, Fromer M, Gauthier L, Goldstein J, Gupta N, Howrigan D, Kiezun A, Kurki MI, Moonshine AL, Natarajan P, Orozco L, Peloso GM, Poplin R, Rivas MA, Ruano-Rubio V, Rose SA, Ruderfer DM, Shakir K, Stenson PD, Stevens C, Thomas BP, Tiao G, Tusie-Luna MT, Weisburd B, Won HH, Yu D, Altshuler DM, Ardissino D, Boehnke M, Danesh J, Donnelly S, Elosua R, Florez JC, Gabriel SB, Getz G, Glatt SJ, Hultman CM, Kathiresan S, Laakso M, McCarroll S, McCarthy MI, McGovern D, McPherson R, Neale BM, Palotie A, Purcell SM, Saleheen D, Scharf JM, Sklar P, Sullivan PF, Tuomilehto J, Tsuang MT, Watkins HC, Wilson JG, Daly MJ, MacArthur DG, Exome Aggregation Consortium (2016) Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 536(7616):285–291
Lord C, Risi S, Lambrecht L, Cook EH Jr, Leventhal BL, DiLavore PC, Pickles A, Rutter M (2000) The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: a standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. J Autism Dev Disord 30(3):205–223
Rosenfeld JA, Ballif BC, Torchia BS, Sahoo T, Ravnan JB, Schultz R, Lamb A, Bejjani BA, Shaffer LG (2010) Copy number variations associated with autism spectrum disorders contribute to a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders. Genet Med 12(11):694–702
Girirajan S, Rosenfeld JA, Coe BP, Parikh S, Friedman N, Goldstein A, Filipink RA, McConnell JS, Angle B, Meschino WS, Nezarati MM, Asamoah A, Jackson KE, Gowans GC, Martin JA, Carmany EP, Stockton DW, Schnur RE, Penney LS, Martin DM, Raskin S, Leppig K, Thiese H, Smith R, Aberg E, Niyazov DM, Escobar LF, El-Khechen D, Johnson KD, Lebel RR, Siefkas K, Ball S, Shur N, McGuire M, Brasington CK, Spence JE, Martin LS, Clericuzio C, Ballif BC, Shaffer LG, Eichler EE (2012) Phenotypic heterogeneity of genomic disorders and rare copy-number variants. N Engl J Med 367(14):1321–1331
Coe BP, Witherspoon K, Rosenfeld JA, van Bon BW, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Bosco P, Friend KL, Baker C, Buono S, Vissers LE, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers JH, Hoischen A, Pfundt R, Krumm N, Carvill GL, Li D, Amaral D, Brown N, Lockhart PJ, Scheffer IE, Alberti A, Shaw M, Pettinato R, Tervo R, de Leeuw N, Reijnders MR, Torchia BS, Peeters H, O’Roak BJ, Fichera M, Hehir-Kwa JY, Shendure J, Mefford HC, Haan E, Gécz J, de Vries BB, Romano C, Eichler EE (2014) Refining analyses of copy number variation identifies specific genes associated with developmental delay. Nat Genet 46(10):1063–1071
Yatsenko SA, Cheung SW, Scott DA, Nowaczyk MJ, Tarnopolsky M, Naidu S, Bibat G, Patel A, Leroy JG, Scaglia F, Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR (2005) Deletion 9q34.3 syndrome: genotype-phenotype correlations and an extended deletion in a patient with features of Opitz C trigonocephaly. J Med Genet 42(4):328–335
Kim C, Jun K, Lee T, Kim SS, McEnery MW, Chin H, Kim HL, Park JM, Kim DK, Jung SJ, Kim J, Shin HS (2001) Altered nociceptive response in mice deficient in the alpha(1B) subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel. Mol Cell Neurosci 18(2):235–245
Kleefstra T, Kramer JM, Neveling K, Willemsen MH, Koemans TS, Vissers LE, Wissink-Lindhout W, Fenckova M, van den Akker WM, Kasri NN, Nillesen WM, Prescott T, Clark RD, Devriendt K, van Reeuwijk J, de Brouwer AP, Gilissen C, Zhou H, Brunner HG, Veltman JA, Schenck A, van Bokhoven H (2012) Disruption of an EHMT1-associated chromatin-modification module causes intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet 91(1):73–82
Kramer JM, Kochinke K, Oortveld MA, Marks H, Kramer D, de Jong EK, Asztalos Z, Westwood JT, Stunnenberg HG, Sokolowski MB, Keleman K, Zhou H, van Bokhoven H, Schenck A (2011) Epigenetic regulation of learning and memory by Drosophila EHMT/G9a. PLoS Biol 9(1):e1000569
Willemsen MH, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Nillesen WM, Wissink-Lindhout WM, van Bokhoven H, Philip N, Berry-Kravis EM, Kini U, van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, Delle Chiaie B, Innes AM, Houge G, Kosonen T, Cremer K, Fannemel M, Stray-Pedersen A, Reardon W, Ignatius J, Lachlan K, Mircher C, Helderman van den Enden PT, Mastebroek M, Cohn-Hokke PE, Yntema HG, Drunat S, Kleefstra T (2012) Update on Kleefstra Syndrome. Mol Syndromol 2(3–5):202–212
Männik K, Mägi R, Macé A, Cole B, Guyatt AL, Shihab HA, Maillard AM, Alavere H, Kolk A, Reigo A, Mihailov E, Leitsalu L, Ferreira AM, Nõukas M, Teumer A, Salvi E, Cusi D, McGue M, Iacono WG, Gaunt TR, Beckmann JS, Jacquemont S, Kutalik Z, Pankratz N, Timpson N, Metspalu A, Reymond A (2015) Copy number variations and cognitive phenotypes in unselected populations. JAMA 313:2044–2054
Adamo A, Atashpaz S, Germain PL, Zanella M, D’Agostino G, Albertin V, Chenoweth J, Micale L, Fusco C, Unger C, Augello B, Palumbo O, Hamilton B, Carella M, Donti E, Pruneri G, Selicorni A, Biamino E, Prontera P, McKay R, Merla G, Testa G (2015) 7q11.23 dosage-dependent dysregulation in human pluripotent stem cells affects transcriptional programs in disease-relevant lineages. Nat Genet 47(2):132–141
Cook EH Jr, Scherer SW (2008) Copy-number variations associated with neuropsychiatric conditions. Nature 455(7215):919–923
Acknowledgments
This study makes use of data generated by the DECIPHER community. A full list of centers who contributed to the generation of the data is available from http://decipher.sanger.ac.uk and via email from decipher@sanger.ac.uk. Funding for the project was provided by the Wellcome Trust.
Funding
This study was funded by Ministry of Health “Ricerca Corrente” (grant numbers 08C607_2006, 08C602_2006, and 08C204_2012) to IRCCS Istituto Auxologico Italiano.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
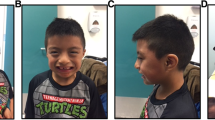
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study or their legal guardians. Signed informed consent for publication of patient 1’s photographs was obtained from his mother. The study was approved by the Ethical Clinical Research Committee of IRCCS Istituto Auxologico Italiano.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
Array-CGH analysis identifies two rare inherited CNVs: a paternal 399 kb duplication at 1p36.11 (chr1:25320307–25,719,620, hg19) (upper panel), and a maternal 24 kb gain at Xq22.3 (chrX:104155507–104,179,536, hg19) (lower panel) (PNG 1163 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Scatter plots, obtained using TaqMan probes, show increased SYF2 expression in P1 (Pt) and his father (F) (circular dot) compared to 10 normal individuals (Ctrls, circular dots). The horizontal dotted bars in the control expression indicate the range between mean ± 2 standard deviation values (PNG 14 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Supplementary Table 2a
(DOCX 25 kb)
Supplementary Table 2b
(DOCX 20 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(XLSX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonati, M.T., Castronovo, C., Sironi, A. et al. 9q34.3 microduplications lead to neurodevelopmental disorders through EHMT1 overexpression. Neurogenetics 20, 145–154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-019-00581-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-019-00581-6