Abstract
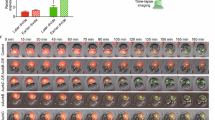
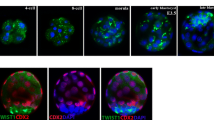
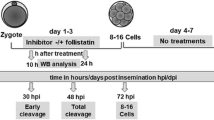
The first cell lineage differentiation occurs during the development of mouse 8-cell embryo to blastocyst. Akt is a potent kinase whose role during blastocyst formation has not been elucidated. In the present study, immunofluorescence results showed that the Akt protein was specifically localized to the outer cells of the morula. Akt-specific inhibitor MK2206 significantly inhibited mouse blastocyst formation and resulted in decreased expression of the trophectoderm marker Cdx2 and led to granular distribution of ERα in the cytoplasm. Furthermore, knockdown of ERα by siRNA microinjection can also lead to a decrease in the development rate of mouse blastocysts, accompanied by a decrease in the expression level of Yap protein. We conclude that Akt may be indispensable for the first cell lineage differentiation of mouse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baran V, Fabian D, Rehak P (2013) Akt/PKB plays role of apoptosis relay on entry into first mitosis of mouse embryo. Zygote 21(4):406–416
Britschgi A, Duss S, Kim S, Couto JP, Brinkhaus H, Koren S, De Silva D, Mertz KD, Kaup D, Varga Z, Voshol H, Vissieres A, Leroy C, Roloff T, Stadler MB, Scheel CH, Miraglia LJ, Orth AP, Bonamy GM, Reddy VA, Bentires-Alj M (2017) The Hippo kinases LATS1 and 2 control human breast cell fate via crosstalk with ERalpha. Nature 541(7638):541–545
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276(13):9817–9824
Chen J, Lian X, Du J, Xu S, Wei J, Pang L, Song C, He L, Wang S (2016) Inhibition of phosphorylated Ser473-Akt from translocating into the nucleus contributes to 2-cell arrest and defective zygotic genome activation in mouse preimplantation embryogenesis. Dev Growth Differ 58(3):280–292
Cheng X, Xu S, Song C, He L, Lian X, Liu Y, Wei J, Pang L, Wang S (2016) Roles of ERalpha during mouse trophectoderm lineage differentiation: revealed by antagonist and agonist of ERalpha. Dev Growth Differ 58(3):327–338
Fayard E, Xue G, Parcellier A, Bozulic L, Hemmings BA (2010) Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), a key mediator of the PI3 K signaling pathway. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 346:31–56
Feng C, Yu A, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zong Z, Su W, Zhang Z, Yu D, Sun QY, Yu B (2007) Involvement of protein kinase B/AKT in early development of mouse fertilized eggs. Biol Reprod 77(3):560–568
Frum T, Ralston A (2015) Cell signaling and transcription factors regulating cell fate during formation of the mouse blastocyst. Trends Genet 31(7):402–410
Jin XL, Chandrakanthan V, Morgan HD, O’Neill C (2009) Preimplantation embryo development in the mouse requires the latency of TRP53 expression, which is induced by a ligand-activated PI3 kinase/AKT/MDM2-mediated signaling pathway. Biol Reprod 80(2):286–294
Liu Y, Xu S, Lian X, Su Y, Zhong Y, Lv R, Mo K, Zhu H, Wang X, Xu L, Wang S (2019) Atypical GATA protein TRPS1 plays indispensable roles in mouse two-cell embryo. Cell Cycle 18(4):437–451
O’Neill C (2008) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in mammalian preimplantation embryo development. Reproduction 136(2):147–156
Park S, Song J, Joe CO, Shin I (2008) Akt stabilizes estrogen receptor alpha with the concomitant reduction in its transcriptional activity. Cell Signal 20(7):1368–1374
Rayon T, Menchero S, Nieto A, Xenopoulos P, Crespo M, Cockburn K, Canon S, Sasaki H, Hadjantonakis AK, de la Pompa JL, Rossant J, Manzanares M (2014) Notch and hippo converge on Cdx2 to specify the trophectoderm lineage in the mouse blastocyst. Dev Cell 30(4):410–422
Sasaki H (2015) Position- and polarity-dependent Hippo signaling regulates cell fates in preimplantation mouse embryos. Semin Cell Dev Biol 47–48:80–87
Strumpf D, Mao CA, Yamanaka Y, Ralston A, Chawengsaksophak K, Beck F, Rossant J (2005) Cdx2 is required for correct cell fate specification and differentiation of trophectoderm in the mouse blastocyst. Development 132(9):2093–2102
Tsukamoto S, Hara T, Yamamoto A, Ohta Y, Wada A, Ishida Y, Kito S, Nishikawa T, Minami N, Sato K, Kokubo T (2013) Functional analysis of lysosomes during mouse preimplantation embryo development. J Reprod Dev 59(1):33–39
Tufail R, Jorda M, Zhao W, Reis I, Nawaz Z (2012) Loss of Yes-associated protein (YAP) expression is associated with estrogen and progesterone receptors negativity in invasive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131(3):743–750
Wicklow E, Blij S, Frum T, Hirate Y, Lang RA, Sasaki H, Ralston A (2014) HIPPO pathway members restrict SOX2 to the inner cell mass where it promotes ICM fates in the mouse blastocyst. PLoS Genet 10(10):e1004618
Wu DD, Feng C, Xu XY, Xiao JY, Liu C, Meng J, Wang EH, Yu BZ (2011) Protein kinase B/Akt may regulate G2/M transition in the fertilized mouse egg by changing the localization of p21(Cip1/WAF1). Cell Biochem Funct 29(4):265–271
Xu S, Lian X, Cheng X, Song C, He L, Liu Y, Chen J, Du J, Pang L, Wang S (2016) Dynamic subcellular localization of estrogen receptor alpha during the first two cleavages of mouse preimplantation embryos. Acta Histochem 118(3):317–321
Yasar P, Ayaz G, User SD, Gupur G, Muyan M (2017) Molecular mechanism of estrogen-estrogen receptor signaling. Reprod Med Biol 16(1):4–20
Zheng W, Gorre N, Shen Y, Noda T, Ogawa W, Lundin E, Liu K (2010) Maternal phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signalling is crucial for embryonic genome activation and preimplantation embryogenesis. EMBO Rep 11(11):890–895
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671526), Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Joint Fund Project (2017Y9114), Fujian Provincial Project of Education and Science for Young and Middle-aged Teachers (JAT170212), Fujian Provincial Health and Family Planning Research Talents Training Project (2017-1-67) and Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Fujian Province University (2018B028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., Pang, L., Liu, Y. et al. Akt plays indispensable roles during the first cell lineage differentiation of mouse. J Mol Hist 50, 369–374 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09833-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09833-z