Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to test the hypotheses that the joint distraction force changes the three-dimensional articulation between the femur and the tibia and that the presence of posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) affects the three-dimensional articulation during joint gap evaluation in total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Methods
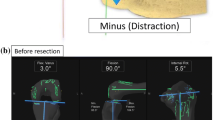
Cruciate-retaining TKA procedures were performed on 6 cadaveric knees using a navigation system. The joint center gap and varus ligament balance were measured using Offset Repo-Tensor® with the knee at 90° of flexion before and after PCL resection for joint distraction forces of 89, 178, and 266 N. The three-dimensional location of the tibia relative to the femur and the axial rotational angle of the tibia were also assessed.
Results
Regardless of PCL resection, the joint center gap became larger (p = 0.002, p = 0.020) and varus ligament balance became more varus (p = 0.002, p = 0.002) with increasing joint distraction force, whereas the tibia was more internally rotated (p = 0.015, p = 0.009) and more anteriorly located (p = 0.004, p = 0.009). The tibia was more internally rotated (p = 0.015) and more posteriorly located (p = 0.026) after PCL resection than before resection.
Conclusions
Joint distraction force changed three-dimensional articulation regardless of PCL preservation. PCL function was revealed as a factor restraining both tibial posterior translation and internal rotation. Surgeons should recognize that joint gap evaluation using a tensor device is subject to three-dimensional changes depending on the magnitude of the joint distraction force.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CR:
-
Cruciate retaining
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation
- LCL:
-
Lateral collateral ligament
- MCL:
-
Medial collateral ligament
- PCL:
-
Posterior cruciate ligament
- TKA:
-
Total knee arthroplasty
References
Ahmad CS, Cohen ZA, Levine WN, Gardner TR, Ateshian GA, Mow VC (2003) Codominance of the individual posterior cruciate ligament bundles. An analysis of bundle lengths and orientation. Am J Sports Med 31:221–225
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Asano H, Muneta T, Hoshino A (2008) Stiffness of soft tissue complex in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:51–55
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods 39:175–191
Gejo R, McGarry MH, Jun BJ, Hofer JK, Kimura T, Lee TQ (2010) Biomechanical effects of patellar positioning on intraoperative knee joint gap measurement in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 25:352–358
Ghosh KM, Merican AM, Iranpour F, Deehan DJ, Amis AA (2012) Length-change patterns of the collateral ligaments after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:1349–1356
Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Komatsu T, Nakagawa S, Yamano Y (2001) Effects of posterior cruciate ligament resection on the tibiofemoral joint gap. Clin Orthop Relat Res 391:210–217
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Lee JK, Lee S, Chun SH, Kim KT, Lee MC (2017) Rotational alignment of femoral component with different methods in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18:217
Matsui Y, Nakagawa S, Minoda Y, Mizokawa S, Tokuhara Y, Kadoya Y (2014) Joint gap measurement in total knee arthroplasty using a tensor device with the same articulating surface as the prosthesis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134:699–705
Matsumoto T, Mizuno K, Muratsu H, Tsumura N, Fukase N, Kubo S et al (2007) Influence of intra-operative joint gap on post-operative flexion angle in osteoarthritis patients undergoing posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:1013–1018
Matsumoto T, Muratsu H, Kawakami Y, Takayama K, Ishida K, Matsushita T et al (2014) Soft-tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty: cruciate-retaining versus posterior-stabilised, and measured-resection versus gap technique. Int Orthop 38:531–537
Matsumoto T, Muratsu H, Kubo S, Matsushita T, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2012) Intraoperative soft tissue balance reflects minimum 5-year midterm outcomes in cruciate-retaining and posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 27:1723–1730
Matsumoto T, Muratsu H, Tsumura N, Mizuno K, Kuroda R, Yoshiya S et al (2006) Joint gap kinematics in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty measured by a new tensor with the navigation system. J Biomech Eng 128:867–871
Meister BR, Michael SP, Moyer RA, Kelly JD, Schneck CD (2000) Anatomy and kinematics of the lateral collateral ligament of the knee. Am J Sports Med 28:869–878
Minoda Y, Nakagawa S, Sugama R, Ikawa T, Noguchi T, Hirakawa M (2018) Joint gap in mid-flexion is not a predictor of postoperative flexion angle after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 33:735–739
Moulton SG, Cram TR, James EW, Dornan GJ, Kennedy NI, LaPrade RF (2015) The supine internal rotation test: a pilot study evaluating tibial internal rotation in grade III posterior cruciate ligament tears. Orthop J Sports Med 3:2325967115572135
Muratsu H, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Maruo A, Miya H, Kurosaka M et al (2010) Femoral component placement changes soft tissue balance in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 25:926–930
Muratsu H, Tsumura N, Yamaguchi M, Kuroda R, Harada T, Yoshiya S, Kurosaka M (2003) Patellar eversion affects soft tissue balance in total knee arthroplasty. Trans Orthop Res Soc 28:242
Nagai K, Muratsu H, Kanda Y, Tsubosaka M, Kamenaga T, Miya H et al (2018) Intraoperative soft tissue balance using novel medial preserving gap technique in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty: comparison to measured resection technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26:3474–3481
Nagai K, Muratsu H, Matsumoto T, Miya H, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2014) Soft tissue balance changes depending on joint distraction force in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 29:520–524
Oka S, Muratsu H, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Maruo A, Miya H et al (2012) The influence of patellar position on soft tissue balance in minimal incision total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:1064–1068
Seo SS, Kim CW, Seo JH, Kim DH, Kim OG, Lee CR (2017) Effects of resection of posterior condyles of femur on extension gap of knee joint in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 32:1819–1823
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86:420–428
Takayama K, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Muratsu H, Ishida K, Matsushita T et al (2012) Influence of intra-operative joint gaps on post-operative flexion angle in posterior cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:532–537
Unitt L, Sambatakakis A, Johnstone D, Briggs TW, Balancer Study G (2008) Short-term outcome in total knee replacement after soft-tissue release and balancing. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:159–165
Winemaker MJ (2002) Perfect balance in total knee arthroplasty: the elusive compromise. J Arthroplasty 17:2–10
Wymenga AB, Kats JJ, Kooloos J, Hillen B (2006) Surgical anatomy of the medial collateral ligament and the posteromedial capsule of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14:229–234
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. Hiroshi Mikami, Vice-President of Yoshinogawa Medical Center, for his help in interpreting the significance of the results of this study. This research was not funded by any specific grants from public, commercial, or not-for-profit agencies.
Funding
No funding has been received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KW carried out the measurements, performed the statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. DH participated in the design of the study and performed the TKA surgery as the surgeon. TT and AN performed the TKA surgery and kinematic measurements as assistants. IT and YT participated in coordination of this study. TG and KS helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All performed procedures were approved by the institutional review board of Tokushima University Hospital (the ID number of approval was 2068) and done in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments for comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, K., Hamada, D., Takasago, T. et al. Joint distraction force changes the three-dimensional articulation of the femur and tibia in total knee arthroplasty: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28, 1488–1496 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05546-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05546-8