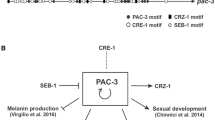
Abstract
A wealth of data is accumulating on the physiological functions of human Rac1, a member of the Rho GTPase family of molecular switches and substrate of botulinum toxin, which was first identified as a regulator of cell motility through its effect on the actin cytoskeleton. Later on, it was found to be involved in different diseases like cancers, cardiac function, neuronal disorders, and apoptotic cell death. Despite the presence of Rac1 homologues in most fungi investigated so far, including Rho5 in the genetically tractable model yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, knowledge on their physiological functions is still scarce, let alone the details of the molecular mechanisms of their actions and interactions. Nevertheless, all functions proposed for human Rac1 seem to be conserved in one or the other fungus. This includes the regulation of MAPK cascades, polarized growth, and actin dynamics. Moreover, both the production and response to reactive oxygen species, as well as the reaction to nutrient availability, can be affected. We here summarize the studies performed on fungal Rac1 homologues, with a special focus on S. cerevisiae Rho5, which may be of use in drug development in medicine and agriculture.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahren D, Tholander M, Fekete C, Rajashekar B, Friman E, Johansson T, Tunlid A (2005) Comparison of gene expression in trap cells and vegetative hyphae of the nematophagous fungus Monacrosporium haptotylum. Microbiology 151:789–803
Annan RB, Wu C, Waller DD, Whiteway M, Thomas DY (2008) Rho5p is involved in mediating the osmotic stress response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and its activity is regulated via Msi1p and Npr1p by phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Eukaryot Cell 7:1441–1449
Araujo-Palomares CL, Richthammer C, Seiler S, Castro-Longoria E (2011) Functional characterization and cellular dynamics of the CDC-42 - RAC - CDC-24 module in Neurospora crassa. PLoS One 6:e27148
Aspenstrom P (2018) Activated Rho GTPases in cancer - the beginning of a new paradigm. Int J Mol Sci 19 19:e3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123949
Ayscough KR, Drubin DG (1996) ACTIN: general principles from studies in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:129–160
Ballou ER, Selvig K, Narloch JL, Nichols CB, Alspaugh JA (2013) Two Rac paralogs regulate polarized growth in the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. Fungal Genet Biol 57:58–75
Blanda C, Hofken T (2013) Regulation of mating in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the zinc cluster proteins Sut1 and Sut2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 438:66–70
Boyce KJ, Hynes MJ, Andrianopoulos A (2003) Control of morphogenesis and actin localization by the Penicillium marneffei RAC homolog. J Cell Sci 116:1249–1260
Breitenbach M, Rinnerthaler M, Weber M, Breitenbach-Koller H, Karl T, Cullen P, Basu S, Haskova D, Hasek J (2018) The defense and signaling role of NADPH oxidases in eukaryotic cells: review. Wien Med Wochenschr 168:286–299
Cao L, Tang Y, Quan Z, Zhang Z, Oliver SG, Zhang N (2016) Chronological lifespan in yeast is dependent on the accumulation of storage carbohydrates mediated by Yak1, Mck1 and Rim15 Kinases. PLoS Genet 12:e1006458
Carbo N, Perez-Martin J (2008) Spa2 is required for morphogenesis but it is dispensable for pathogenicity in the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis. Fungal Genet Biol 45:1315–1327
Chen C, Dickman MB (2004) Dominant active Rac and dominant negative Rac revert the dominant active Ras phenotype in Colletotrichum trifolii by distinct signalling pathways. Mol Microbiol 51:1493–1507
Chen J, Zheng W, Zheng S, Zhang D, Sang W, Chen X, Li G, Lu G, Wang Z (2008) Rac1 is required for pathogenicity and Chm1-dependent conidiogenesis in rice fungal pathogen Magnaporthe grisea. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000202
Cherfils J, Zeghouf M (2013) Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol Rev 93:269–309
Davis RL, Zhong Y (2017) The biology of forgetting - a perspective. Neuron 95:490–503
Delley PA, Hall MN (1999) Cell wall stress depolarizes cell growth via hyperactivation of Rho1. J Cell Biol 147:163–174
Doi A, Kita A, Kanda Y, Uno T, Asami K, Satoh R, Nakano K, Sugiura R (2015) Geranylgeranyltransferase Cwg2-Rho4/Rho5 module is implicated in the Pmk1 MAP kinase-mediated cell wall integrity pathway in fission yeast. Genes Cells 20:310–323
Dumortier JG, David NB (2015) The TORC2 component, Sin1, controls migration of anterior mesendoderm during zebrafish gastrulation. PLoS One 10:e0118474
Egan MJ, Wang ZY, Jones MA, Smirnoff N, Talbot NJ (2007) Generation of reactive oxygen species by fungal NADPH oxidases is required for rice blast disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:11772–11777
Elias M, Klimes V (2012) Rho GTPases: deciphering the evolutionary history of a complex protein family. Methods Mol Biol 827:13–34
Frieser SH, Hlubek A, Sandrock B, Bolker M (2011) Cla4 kinase triggers destruction of the Rac1-GEF Cdc24 during polarized growth in Ustilago maydis. Mol Biol Cell 22:3253–3262
Fu C, Iyer P, Herkal A, Abdullah J, Stout A, Free SJ (2011) Identification and characterization of genes required for cell-to-cell fusion in Neurospora crassa. Eukaryot Cell 10:1100–1109
Gorfer M, Tarkka MT, Hanif M, Pardo AG, Laitiainen E, Raudaskoski M (2001) Characterization of small GTPases Cdc42 and Rac and the relationship between Cdc42 and actin cytoskeleton in vegetative and ectomycorrhizal hyphae of Suillus bovinus. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:135–144
Gujar MR, Sundararajan L, Stricker A, Lundquist EA (2018) Control of growth cone polarity, microtubule accumulation, and protrusion by UNC-6/Netrin and its receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 210:235–255
Harris SD (2011) Cdc42/Rho GTPases in fungi: variations on a common theme. Mol Microbiol 79:1123–1127
Heinisch JJ, Rodicio R (2017) Stress response in wine yeast. In: König H, Unden G, Fröhlich J (eds) Biology of microorganisms on grapes, in must and wine. Springer Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 377–395
Heinisch JJ, Rodicio R (2018) Protein kinase C in fungi - more than just cell wall integrity. FEMS Microbiol Rev 42
Hohmann S (2002) Osmotic stress signaling and osmoadaptation in yeasts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:300–372
Hope H, Schmauch C, Arkowitz RA, Bassilana M (2010) The Candida albicans ELMO homologue functions together with Rac1 and Dck1, upstream of the MAP Kinase Cek1, in invasive filamentous growth. Mol Microbiol 76:1572–1590
Howard SC, Deminoff SJ, Herman PK (2006) Increased phosphoglucomutase activity suppresses the galactose growth defect associated with elevated levels of Ras signaling in S. cerevisiae. Curr Genet 49:1–6
Hudson LG, Gillette JM, Kang H, Rivera MR, Wandinger-Ness A (2018) Ovarian tumor microenvironment signaling: convergence on the Rac1 GTPase. Cancers (Basel) 10:e358
Hurtado CA, Beckerich JM, Gaillardin C, Rachubinski RA (2000) A rac homolog is required for induction of hyphal growth in the dimorphic yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J Bacteriol 182:2376–2386
Jiang SS, Yin YP, Song ZY, Zhou GL, Wang ZK (2014) RacA and Cdc42 regulate polarized growth and microsclerotium formation in the dimorphic fungus Nomuraea rileyi. Res Microbiol 165:233–242
Johnston SD, Enomoto S, Schneper L, McClellan MC, Twu F, Montgomery ND, Haney SA, Broach JR, Berman J (2001) CAC3(MSI1) suppression of RAS2(G19V) is independent of chromatin assembly factor I and mediated by NPR1. Mol Cell Biol 21:1784–1794
Karabiyik C, Fernandes R, Figueiredo FR, Socodato R, Brakebusch C, Lambertsen KL, Relvas JB, Santos SD (2018) Neuronal Rho GTPase Rac1 elimination confers neuroprotection in a mouse model of permanent ischemic stroke. Brain Pathol 28:569–580
Kowluru A (2017) Role of G-proteins in islet function in health and diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 19(Suppl 1):63–75
Kwon MJ, Nitsche BM, Arentshorst M, Jorgensen TR, Ram AF, Meyer V (2013) The transcriptomic signature of RacA activation and inactivation provides new insights into the morphogenetic network of Aspergillus niger. PLoS One 8:e68946
Li H, Barker BM, Grahl N, Puttikamonkul S, Bell JD, Craven KD, Cramer RA, Jr. (2011) The small GTPase RacA mediates intracellular reactive oxygen species production, polarized growth, and virulence in the human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot Cell 10: 174-186
Lichius A, Goryachev AB, Fricker MD, Obara B, Castro-Longoria E, Read ND (2014) CDC-42 and RAC-1 regulate opposite chemotropisms in Neurospora crassa. J Cell Sci 127:1953–1965
Liu M, Bi F, Zhou X, Zheng Y (2012) Rho GTPase regulation by miRNAs and covalent modifications. Trends Cell Biol 22:365–373
Marei H, Malliri A (2017) Rac1 in human diseases: the therapeutic potential of targeting Rac1 signaling regulatory mechanisms. Small GTPases 8:139–163
Merzendorfer H, Heinisch JJ (2013) Microcompartments within the yeast plasma membrane. Biol Chem 394:189–202
Michaelson D, Abidi W, Guardavaccaro D, Zhou M, Ahearn I, Pagano M, Philips MR (2008) Rac1 accumulates in the nucleus during the G2 phase of the cell cycle and promotes cell division. J Cell Biol 181:485–496
Minz Dub A, Kokkelink L, Tudzynski B, Tudzynski P, Sharon A (2013) Involvement of Botrytis cinerea small GTPases BcRAS1 and BcRAC in differentiation, virulence, and the cell cycle. Eukaryot Cell 12:1609–1618
Nesher I, Minz A, Kokkelink L, Tudzynski P, Sharon A (2011) Regulation of pathogenic spore germination by CgRac1 in the fungal plant pathogen Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Eukaryot Cell 10:1122–1130
Nordmann D, Lickfeld M, Warnsmann V, Wiechert J, Jendretzki A, Schmitz HP (2014) The small GTP-binding proteins AgRho2 and AgRho5 regulate tip-branching, maintenance of the growth axis and actin-ring-integrity in the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii. PLoS One 9:e106236
Pai SY, Kim C, Williams DA (2010) Rac GTPases in human diseases. Dis Markers 29:177–187
Raudaskoski M, Kothe E, Fowler TJ, Jung EM, Horton JS (2012) Ras and Rho small G proteins: insights from the Schizophyllum commune genome sequence and comparisons to other fungi. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 28:61–100
Rincon SA, Santos B, Perez P (2006) Fission yeast Rho5p GTPase is a functional paralogue of Rho1p that plays a role in survival of spores and stationary-phase cells. Eukaryot Cell 5:435–446
Rolke Y, Tudzynski P (2008) The small GTPase Rac and the p21-activated kinase Cla4 in Claviceps purpurea: interaction and impact on polarity, development and pathogenicity. Mol Microbiol 68:405–423
Schmitz HP, Philippsen P (2011) Evolution of multinucleated Ashbya gossypii hyphae from a budding yeast-like ancestor. Fungal Biol 115:557–568
Schmitz HP, Huppert S, Lorberg A, Heinisch JJ (2002) Rho5p downregulates the yeast cell integrity pathway. J Cell Sci 115:3139–3148
Schmitz HP, Jendretzki A, Wittland J, Wiechert J, Heinisch JJ (2015) Identification of Dck1 and Lmo1 as upstream regulators of the small GTPase Rho5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 96:306–324
Schmitz HP, Jendretzki A, Sterk C, Heinisch JJ (2018) The small yeast GTPase Rho5 and its dimeric GEF Dck1/Lmo1 respond to glucose starvation. Int J Mol Sci 19:e2186
Singh K, Kang PJ, Park HO (2008) The Rho5 GTPase is necessary for oxidant-induced cell death in budding yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1522–1527
Singh K, Lee ME, Entezari M, Jung CH, Kim Y, Park Y, Fioretti JD, Huh WK, Park HO, Kang PJ (2019) Genome-wide studies of Rho5-interacting proteins that are involved in oxidant-induced cell death in budding yeast. G3 (Bethesda): e-published ahead of print. doi: https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.118.200887
Sollier K, Gaude HM, Chartier FJ, Laprise P (2015) Rac1 controls epithelial tube length through the apical secretion and polarity pathways. Biol Open 5:49–54
Stankiewicz TR, Linseman DA (2014) Rho family GTPases: key players in neuronal development, neuronal survival, and neurodegeneration. Front Cell Neurosci 8:e314
Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T (2001) Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol Rev 81:153–208
Tanaka A, Takemoto D, Hyon GS, Park P, Scott B (2008) NoxA activation by the small GTPase RacA is required to maintain a mutualistic symbiotic association between Epichloe festucae and perennial ryegrass. Mol Microbiol 68:1165–1178
Tian H, Zhou L, Guo W, Wang X (2015) Small GTPase Rac1 and its interaction partner Cla4 regulate polarized growth and pathogenicity in Verticillium dahliae. Fungal Genet Biol 74:21–31
Tiedje C, Sakwa I, Just U, Hofken T (2008) The Rho GDI Rdi1 regulates Rho GTPases by distinct mechanisms. Mol Biol Cell 19:2885–2896
Tolbert CE, Beck MV, Kilmer CE, Srougi MC (2019) Loss of ATM positively regulates Rac1 activity and cellular migration through oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:1155–1161
Vallim MA, Nichols CB, Fernandes L, Cramer KL, Alspaugh JA (2005) A Rac homolog functions downstream of Ras1 to control hyphal differentiation and high-temperature growth in the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. Eukaryot Cell 4:1066–1078
Vauchelles R, Stalder D, Botton T, Arkowitz RA, Bassilana M (2010) Rac1 dynamics in the human opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida albicans. PLoS One 5:e15400
Virag A, Lee MP, Si H, Harris SD (2007) Regulation of hyphal morphogenesis by cdc42 and rac1 homologues in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 66:1579–1596
Wei W, Zhu W, Cheng J, Xie J, Jiang D, Li G, Chen W, Fu Y (2016) Nox complex signal and MAPK cascade pathway are cross-linked and essential for pathogenicity and conidiation of mycoparasite Coniothyrium minitans. Sci Rep 6:24325
Wennerberg K, Der CJ (2004) Rho-family GTPases: it’s not only Rac and Rho (and I like it). J Cell Sci 117:1301–1312
Wennerberg K, Rossman KL, Der CJ (2005) The Ras superfamily at a glance. J Cell Sci 118:843–846
Yamaguchi Y, Katsuki Y, Tanaka S, Kawaguchi R, Denda H, Ikeda T, Funato K, Tani M (2018) Protective role of the HOG pathway against the growth defect caused by impaired biosynthesis of complex sphingolipids in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 107:363–386
Yeh CW, Hsu LS (2016) Zebrafish diras1 promoted neurite outgrowth in neuro-2a cells and maintained trigeminal ganglion neurons in vivo via Rac1-dependent pathway. Mol Neurobiol 53:6594–6607
Zhang C, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhai Z, Zhang L, Zheng W, Yu W, Zhou J, Lu G, Shim WB, Wang Z (2013) Functional characterization of Rho family small GTPases in Fusarium graminearum. Fungal Genet Biol 61:90–99
Zhao X, Carnevale KA, Cathcart MK (2003) Human monocytes use Rac1, not Rac2, in the NADPH oxidase complex. J Biol Chem 278:40788–40792
Acknowledgements
We thank Rosaura Rodicio for critical reading of the manuscript and many fruitful discussions.
Funding
Work in our laboratory related to this review has been financed by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG; grant HE 1880/6-1) to J.J.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hühn, J., Musielak, M., Schmitz, HP. et al. Fungal homologues of human Rac1 as emerging players in signal transduction and morphogenesis. Int Microbiol 23, 43–53 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-019-00077-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-019-00077-1