Abstract.
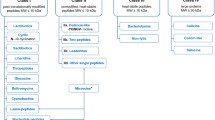
Bacteriocins are ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides produced by microorganisms belonging to different eubacterial taxonomic branches. Most of them are small cationic membrane-active compounds that form pores in the target cells, disrupting membrane potentials and causing cell death. The production of small cationic peptides with antibacterial activity is a defense strategy found not only in bacteria, but also in plants and animals. Bacteriocins are classified according to different criteria by different authors; in this review, we will summarize the principal bacteriocin classifications, highlight their main physical and chemical characteristics, and describe the mechanism of some selected bacteriocins that act at the membrane level.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oscáriz, J.C., Pisabarro, A.G. Classification and mode of action of membrane-active bacteriocins produced by gram-positive bacteria. Int Microbiol 4, 13–19 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s101230100003
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s101230100003