Abstract
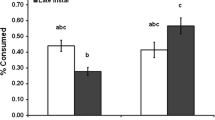
Surplus or ‘wasteful’ killing of uneaten prey has been documented in the fourth larval instar of various species of the mosquito genus Toxorhynchites that occur in treeholes and other phytotelmata. Here we document surplus killing by the predatory midge Corethrella appendiculata, which in Florida cohabits treeholes and artificial containers with larvae of Toxorhynchites rutilus. Provided with a surfeit of larval mosquito prey, surplus killing was observed only in the fourth instar of C. appendiculata, peaking in intensity in the final 24 h prior to pupation, as observed for Toxorhynchites spp. Attack sites identified from videotaped encounters with mosquito prey were divided among head, thorax, abdomen, and siphon. Consumed mosquito larvae (n = 70) were attacked primarily on the head (46%) or siphon (34%), but surplus-killed prey (n = 30) were attacked predominantly on the thorax (83%). Despite its independent evolution among different insect species in aquatic container habitats, the functional significance of prepupal surplus killing remains unclear.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradshaw WE, Holzapfel CM (1983) Predator-mediated, non-equilibrium coexistence of tree-hole mosquitoes in southeastern North America. Oecologia 57:239–256
Chan KL (1968) Observations on Toxorhynchites splendens (Wiedemann) (Diptera:Culicidae) in Singapore. Mosq News 28:91–95
Corbet PS (1985) Prepupal killing behavior in Toxorhynchites brevipalpis: a status report. In: Lounibos LP, Rey JR, Frank JH (eds) Ecology of mosquitoes: proceedings of a workshop. Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory, Vero Beach, pp 407–417
Corbet PS (1999) Dragonflies. Behavior and ecology of Odonata. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Corbet PS, Griffiths A (1963) Observations on the aquatic stages of two species of Toxorhynchites (Diptera:Culicidae) in Uganda. Proc R Ent Soc Lond 38:125–135
Fincke OM (1994) Population regulation of a tropical damselfly in the larval stage by food limitation, cannibalism, intraguild predation and habitat drying. Oecologia 100:118–127
Griswold MW, Lounibos LP (2005a) Competitive outcomes of aquatic container Diptera depend on predation and resource levels. Ann Entomol Soc Am 98:673–681
Griswold MW, Lounibos LP (2005b) Does differential predation permit invasive and native mosquito larvae to coexist in Florida? Ecol Entomol 30:122–127
Griswold MW, Lounibos LP (2006) Predator identity and additive effects in a treehole community. Ecology 87:987–995
Hamilton WD (1970) Selfish and spiteful behaviour in an evolutionary model. Nature 228:1218–1220
Johnson DM, Akre BG, Crowley PH (1975) Modeling arthropod predation—wasteful killing by damselfly naiads. Ecology 56:1081–1093
Kesavaraju B, Juliano SA (2004) Differential behavioral responses to water-borne cues to predation in two container-dwelling mosquitoes. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:194–201
Kesavaraju B, Alto BW, Lounibos LP, Juliano SA (2007) Behavioural responses of larval container mosquitoes to a size-selective predator. Ecol Entomol 32:262–272
Kitching RL (2000) Food webs and container habitats. The natural history and ecology of phytotelmata. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kruuk H (1972) Surplus killing by carnivores. J Zool 166:233–244
Linley JR (1990) The predatory behavior of Toxorhynchites amboinensis and Tx. brevipalpis larvae (Diptera: Culicidae) in response to subsurface prey. Fla Entomol 73:9–50
Lounibos LP (1979) Temporal and spatial distribution, growth and predatory behaviour of Toxorhynchites brevipalpis (Diptera: Culicidae) on the Kenya coast. J Anim Ecol 48:213–236
Lounibos LP (1985) Interactions influencing production of treehole mosquitoes in south Florida. In: Lounibos LP, Rey JR, Frank JH (eds) Ecology of mosquitoes: proceedings of a workshop. Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory, Vero Beach, pp 65–77
Lounibos LP, Martin EA, Duzak D, Escher RL (1998) Daylength and temperature control of predation, body size, and rate of increase in Toxorhynchites rutilus (Diptera: Culicidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 91:308–314
Lounibos LP, O, Meara GF, Escher RL, Nishimura N, Cutwa MM, Nelson T, Campos RE, Juliano SA (2001) Testing predictions of displacement of native Aedes by the invasive Asian Tiger Mosquito Aedes albopictus in Florida, USA. Biol Invas 3:151–166
McKeever S (1986) Mouthparts of the four North American Corethrella species (Diptera: Chaoboridae), with detailed study of Corethrella appendiculata. J Med Entomol 23:502–512
McKeever S, French FE (1991a) Corethrella (Diptera: Corethrellidae) of eastern North-America: laboratory life history and field responses to anuran calls. Ann Entomol Soc Am 84:493–497
McKeever S, French FE (1991b) Corethrella (Diptera: Corethrellidae) of North America north of Mexico—distribution and morphology of immature stages. Ann Entomol Soc Am 84:522–530
Marti GA, Micieli MV, Maciá A, Lounibos LP, Garcia JJ (2007) Seasonality and abundance of the mosquito Isostomyia paraensis from phytotelmata in temperate Argentina. J Am Mosq Cont Assoc 23:252–258
Russo R (1986) Comparison of predatory behavior in five species of Toxorhynchites (Diptera: Culicidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 79:715–722
SAS Institute (1989) SAS/STAT User’s Guide. SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA
Steffan WA, Evenhuis NL (1981) Biology of Toxorhynchites. Ann Rev Entomol 26:159–181
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by NIH grant AI-044793 to LPL and NSF doctoral dissertation improvement grants to BWA (DEB-0407689) and BK (DEB-0507015). We thank R. Escher and N. Nishimura for technical support, A. Borkent for sharing his knowledge of the Corethrellidae, and M. Griswold and S. Yanoviak for critical comments on a previous draft of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lounibos, L.P., Makhni, S., Alto, B.W. et al. Surplus Killing by Predatory Larvae of Corethrella appendiculata: Prepupal Timing and Site-Specific Attack on Mosquito Prey. J Insect Behav 21, 47–54 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-007-9103-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-007-9103-2