Abstract
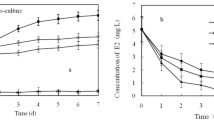
17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2), the active compound of the contraceptive pill, is a recalcitrant estrogen, which is encountered at ng/l levels in wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) effluents and rivers and can cause feminization of aquatic organisms. The aim of this study was to isolate micro-organisms that could remove such low EE2 concentrations. In this study, six bacterial strains were isolated from compost that cometabolize EE2 when metabolizing estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2) and estriol (E3). The strains belong to the α, β and γ-Proteobacteria. All six strains metabolize E2 over E1, at μg/l to ng/l concentrations. In 4 days, initial concentrations of 0.5 μg E2/l and 0.6 μg EE2/l were degraded to 1.8 ± 0.4 ng E2/l and 85 ± 16 ng EE2/l, respectively. No other metabolites besides E1, E2, E3 or EE2 were detected, suggesting that total degradation and cleavage of the aromatic ring occurred. This is the first study describing that bacteria able to metabolize E2, can subsequently cometabolize EE2 at low μg/l levels.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E1:
-
Estrone
- E2:
-
Estradiol
- E3:
-
Estriol
- EE2:
-
Ethinylestradiol
- HRT:
-
Hydraulic residence time
- SRT:
-
Sludge retention time
- WWTP:
-
Wastewater treatment plant
References
Adler P, Steger-Hartmann T, Kalbfus W (2001) Distribution of natural and synthetic estrogenic steroid hormones in water samples from Southern and Middle Germany. Acta Hydroch Hydrob 29:227–241
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Andersen H, Siegrist HR, Halling-Sørensen B et al (2003) Fate of estrogens in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 37(18):4021–4026
Cargouet M, Perdiz D, Mouatassim-Souali A et al (2003) Assessment of river contamination by estrogenic compounds in Paris area (France). Sci Total Environ 324:55–66
Clara M, Strenn B, Ausserleitner M et al (2004) Comparison of the behaviour of selected micropollutants in a membrane bioreactor and a conventional wastewater treatment plant. Water Sci Technol 50(5):29–36
Feisti CF, Hegeman GD (1969) Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol 100(2):869–877
Fujii K, Kikuchi S, Satomi M et al (2002) Degradation of 17β-estradiol by a gram-negative bacterium isolated from activated sludge in a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo, Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):2057–2060
Haiyan R, Shulan J, ud din Ahmad N et al (2007) Degradation characteristics and metabolic pathway of 17α-ethynylestradiol by Sphingobacterium sp. JCR5. Chemosphere 66(2):340–346
Holbrook RD, Love NG, Novak JT (2004). Sorption of 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol by colloidal organic carbon derived from biological wastewater treatment systems. Environ Sci Technol 38:3322–3329
Hollender J EAWAG, Dübendorf, Switzerland, personal communication, 27/02/2006
Johnson AC, Williams RJ (2004) A model to estimate influent and effluent concentrations of estradiol, estrone and ethinylestradiol at sewage treatment works. Environ Sci Technol 38(13):3649–3658
Johnson AC, Aerni HR, Gerritsen A et al (2005) Comparing steroid estrogen, and nonylphenol content across a range of European sewage plants with different treatment and management practices. Water Res 39:47–58
Joss A, Andersen H, Ternes TA et al (2004) Removal of estrogens in municipal wastewater treatment under aerobic and anaerobic conditions: consequences for plant optimisation. Environ Sci Technol 38:3047–3055
Kim MH, Hao OJ (1999) Cometabolic degradation of chlorophenols by Acinetobacter species. Water Res 33(2):562–574
Lee HB, Liu D (2002) Degradation of 17 beta-estradiol and its metabolites by sewage bacteria. Water Air Soil Pollut 134(1–4):353–368
Noppe H, De Wasch K, Poelmans S et al (2005) Development and validation of an analytical method for detection of estrogens in water. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:91–98
Øvreas L, Forney L, Daae FL et al (1997) Distribution of bacterioplankton in meromictic lake Saelevannet, as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3367–3373
Panter GH, Thompson RS, Beresford N et al (1999) Transformation of non-estrogenic steroid metabolite to an oestrogenically active substance by minimal bacterial activity. Chemosphere 38:3579–3596
Pruneda-Paz JL, Linares M, Cabrera JA et al (2004) Identification of a novel steroid inducible gene associated with the βhsd locus of Comamonas testosteroni. J Steroid Biochem 88:91–100
Seurinck S, Verstraete W, Siciliano SD (2003) Use of 16S–23S rRNA intergenic spacer region PCR and repetitive extragenic palindromic PCR analyses of Escherichia coli isolates to identify nonpoint fecal sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(8):4942–4950
Shi JH, Suzuki Y, Lee BD et al (2002) Isolation and characterization of the ethinylestradiol-biodegrading micro-organism Fusarium proliferatum strain HNS-1. Water Sci Technol 45:175–179
Shi JH, Fujisawa S, Nakai S et al (2004a) Biodegradation of natural and synthetic estrogens by nitrifying activated sludge and ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Water Res 38(9):2322–2329
Shi JH, Suzuki Y, Nakai S et al (2004b) Mimbial degradation of estrogens using activated sludge and night soil-composting microorganisms. Water Sci Technol 50(8):153–159
Stanier RY, Palleroni NJ, Douderoff M (1966) The aerobic Pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol 43:159–271
Ternes TA, Stumpf M, Mueller J et al (1999a) Behavior and occurence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants—I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Sci Total Environ 225:81–90
Ternes TA, Kreckel P, Mueller J (1999b) Behaviour and occurence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plans—II. Aerobic batch experiments with activated sludge. Sci Total Environ 228(1):91–99
Thomas KV, Hurst MR, Matthiessen P (2001) Characterization of estrogenic compounds in water samples collected from United Kingdom estuaries. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(10):2165–2170
Vader JS, van Ginkel CG, Sperling FMGM et al (2000) Degradation of ethinyl estradiol by nitrifying activated sludge. Chemosphere 41:1239–1243
Verstraete W, Vandewerf H, Kucnerowicz F et al (1983) Specific measurement of soil microbial ATP. Soil Biol Biochem 15(4):391–396
Vethaak AD, Lahr J, Kuiper RV (2002) Estrogenic effects in fish in the Netherlands: some preliminary results. Toxicology 181:147–150
Weber S, Leuschner P, Kämpfer P et al (2005) Degradation of estradiol and ethinylestradiol by activated sludge and by a defined mixed culture. Appl Microbiol Biotech 67:106–112
Yoshimoto T, Nagai F, Fujimoto J et al (2004) Degradation of estrogens by Rhodococcus zopfii and Rhodococcus equi isolates from activated sludge in wastewater treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5283–5289
Yi T, Harper WF (2005) Mechanisms for removal of 17α-ethinylestradiol in bioreactors. Proceedings of the 78th annual water environment federation technical exposition and conference (WEFTEC). Washington DC, pp 5140–5153
Yi T, Harper WF (2007) The link between nitrification and biotransformation of 17α-ethinylestradiol. Environ Sci Technol 41(12):4311–4316
Yi T, Harper WF Jr, Holbrook RD et al (2006) The role of particle size and nitrification in removal of 17α-ethinylestradiol in bioreactors. ASCE J Environ Eng 132(11):1527–1529
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank IWT Vlaanderen to support this research with a Ph.D. funding (Grant Number IWT-33298). Petra Vandamme is greatly acknowledged for performing the molecular analyses. The authors wish to thank Ilse Forrez and Lynn Vanhaecke for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pauwels, B., Wille, K., Noppe, H. et al. 17α-ethinylestradiol cometabolism by bacteria degrading estrone, 17β-estradiol and estriol. Biodegradation 19, 683–693 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-007-9173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-007-9173-z