Abstract
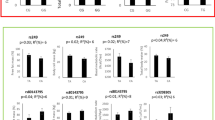
During the last decades, the prevalence of obesity has increased rapidly among young people. A polymorphism in the promoter region of the IL6 gene (-174G/C), has been previously reported to be involved in obesity and metabolic syndrome development. Therefore, the aim of the study was to examine whether the IL6-174G/C polymorphism influence the association of body fat with low-grade inflammatory markers and blood lipids and lipoproteins in Spanish adolescents. 504 Spanish adolescents participating in the AVENA study were genotyped for the-174G/C polymorphism of the IL6 gene. Anthropometric and body composition measurements were taken and blood samples were collected for plasma molecules determinations. No differences between genotypes were observed in anthropometric values, body composition measurements and plasma markers concentration. Physical activity level differ between genotypes with subjects carrying the C allele of the polymorphism being significantly (p<0.05) more active than GG subjects. The association between body fat mass and plasma glucose was influenced by the -174G/C polymorphism of the IL6 gene. Subjects carrying the C allele of the mutation seem to have higher values of lipoprotein (a) and C-reactive protein as their percentage of body fat mass increase. Our results suggest that this promoter polymorphism influences the association between adiposity and some plasma markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anuurad, E., Boffa, M.B., Koschinsky, M.L. and Berglund, L. (2006): Lipoprotein(a): a unique risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Clin Lab Med, 26, 751–772.
Buckley, D.I., Fu, R., Freeman, M., Rogers, K., et al. (2009): C-reactive protein as a risk factor for coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analyses for the U.S.Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med, 151, 483–495.
Clement, K., Boutin, P. and Froguel, P. (2002): Genetics of obesity. Am J Pharmacogenomics, 2, 177–187.
Cole, T.J., Bellizzi, M.C., Flegal, K.M. and Dietz, W.H. (2000): Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. Bmj, 320, 1240–1243.
Charakida, M., Tousoulis, D., Skoumas, I., Pitsavos, C., et al. (2009): Inflammatory and thrombotic processes are associated with vascular dysfunction in children with familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis, 204, 532–537.
Eyzaguirre, F. and Mericq, V. (2009): Insulin resistance markers in children. Horm Res, 71, 65–74.
Fernández-Real, J.M., Broch, M., Vendrell, J., Richart, C., et al. (2000): Interleukin-6 gene polymorphism and lipid abnormalities in healthy subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 85, 1334–1339.
GarcÍa-Artero, E., Ortega, F.B., Ruiz, J.R., Mesa, J.L., et al. (2007): Lipid and metabolic profiles in adolescents are affected more by physical fitness than physical activity (AVENA study). Rev Esp Cardiol, 60, 581–588.
González-Gross, M., Castillo, M.J., Moreno, L., Nova, E., et al. (2003): Feeding and assessment of nutritional status of spanish adolescents (AVENA study). Evaluation of risks and interventional proposal. Nutr Hosp, 18, 15–28.
Goyenechea, E., Parra, D. and MartÍnez, J.A. (2007): Impact of interleukin 6 -174GτC polymorphism on obesity-related metabolic disorders in people with excess in body weight. Metabolism, 56, 1643–1648.
Hamid, Y.H., Rose, C.S., Urhammer, S.A., Glumer, C., et al. (2005): Variations of the interleukin-6 promoter are associated with features of the metabolic syndrome in Caucasian Danes. Diabetologia, 48, 251–260.
Higuchi, R. (1989): Simple and rapid preparation of samples for PCR. In “PCR technology”, (Erlich, Ed.), Stockton Press, pp. 31–38.
Humphries, S.E., Luong, L.A., Ogg, M.S., Hawe, E., et al. (2001): The interleukin-6-174 G/C promoter polymorphism is associated with risk of coronary heart disease and systolic blood pressure in healthy men. Eur Heart J, 22, 2243–2252.
Illig, T., Bongardt, F., Schopfer, A., Muller-Scholze, S., et al. (2004): Significant association of the interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms C-174G and A-598G with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 89, 5053–5058.
Isnard, P., Michel, G., Frelut, M.L., Vila, G., et al. (2003): Binge eating and psychopathology in severely obese adolescents. Int J Eat Disord, 34, 235–243.
Knoflach, M., Kiechl, S., Penz, D., Zangerle, A., et al. (2009): Cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in young women: atherosclerosis risk factors in female youngsters (ARFY study). Stroke, 40, 1063–1069.
Kubaszek, A., Pihlajamaki, J., Punnonen, K., Karhapaa, P., et al. (2003): The C-174G promoter polymorphism of the IL-6 gene affects energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes, 52, 558–561.
Marti, A., MartÍnez-González, M.A. and MartÍnez, J.A. (2008): Interaction between genes and lifestyle factors on obesity. Proc Nutr Soc, 67, 1–8.
MartÍnez, J.A. (2000): Obesity in young Europeans: genetic and environmental influences. Eur J Clin Nutr, 54 Suppl 1, S56–60.
MartÍnez, J.A., Moreno, M.J., Marques-Lopes, I. and Marti, A. (2002): Causes of obesity. An Sist Sanit Navar, 25 Suppl 1, 17–27.
McKenzie, J.A., Weiss, E.P., Ghiu, I.A., Kulaputana, O., et al. (2004): Influence of the interleukin-6-174 G/C gene polymorphism on exercise training-induced changes in glucose tolerance indexes. J Appl Physiol, 97, 1338–1342.
Mohlig, M., Boeing, H., Spranger, J., Osterhoff, M., et al. (2004): Body mass index and C-174G interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism interact in predicting type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 89, 1885–1890.
Moreno-Aliaga, M.J., Campión, J., Milagro, F.I. and Berjón, A. (2005): Adiposity and proinflammatory state: The chicken or the egg. Adipocytes, 1, 1–9.
Moreno, L.A., Joyanes, M., Mesana, M.I., González-Gross, M., et al. (2003): Harmonization of anthropometric measurements for a multicenter nutrition survey in Spanish adolescents. Nutrition, 19, 481–486.
Moreno, L.A., Mesana, M.I., Fleta, J., Ruiz, J.R., et al. (2005): Overweight, obesity and body fat composition in spanish adolescents. The AVENA Study. Ann Nutr Metab, 49, 71–76.
Moreno, L.A., Mesana, M.I., González-Gross, M., Gil, C.M., et al. (2007): Body fat distribution reference standards in Spanish adolescents: the AVENA Study. Int J Obes (Lond), 31, 1798–1805.
Ortega, F.B., Tresaco, B., Ruiz, J.R., Moreno, L.A., et al. (2007): Cardiorespiratory fitness and sedentary activities are associated with adiposity in adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring), 15, 1589–1599.
Panoulas, V.F., Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A., Metsios, G.S., Smith, J.P., et al. (2009): Association of interleukin-6 (IL-6)-174G/C gene polymorphism with cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the role of obesity and smoking. Atherosclerosis, 204, 178–183.
Puchau, B., Zulet, M.A., Gonzalez de Echavarri, A., Navarro-Blasco, I., et al. (2009): Selenium intake reduces serum C3, an early marker of metabolic syndrome manifestations, in healthy young adults. Eur J Clin Nutr, 63, 858–864.
Qureshi, M.M., Singer, M.R. and Moore, L.L. (2009): A cross-sectional study of food group intake and C-reactive protein among children. Nutr Metab (Lond), 6, 40.
Razquin, C., Martinez, J.A., Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A., Fernandez-Crehuet, J., et al. (2009): A Mediterranean diet rich in virgin oil may reverse the effects of the -174G/C IL6 gene variant on 3-year body weight change. Mol Nutr & Food Res, (In press)
Ruiz, J.R., Buxens, A., Artieda, M., Arteta, D., et al. (2009): The -174 G/C polymorphism of the IL6 gene is associated with elite power performance. J Sci Med Sport,
Ruiz, J.R., Ortega, F.B., Warnberg, J., Moreno, L.A., et al. (2008): Inflammatory proteins and muscle strength in adolescents: the Avena study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, 162, 462–468.
Santos, M.G., Pegoraro, M., Sandrini, F. and Macuco, E.C. (2008): Risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis in childhood and adolescence. Arq Bras Cardiol, 90, 276–283.
Slaughter, M.H., Lohman, T.G., Boileau, R.A., Horswill, C.A., et al. (1988): Skinfold equations for estimation of body fatness in children and youth. Hum Biol, 60, 709–723.
Sorensen, K.E., Celermajer, D.S., Georgakopoulos, D., Hatcher, G., et al. (1994): Impairment of endothelium-dependent dilation is an early event in children with familial hypercholesterolemia and is related to the lipoprotein(a) level. J Clin Invest, 93, 50–55.
Vozarova, B., Weyer, C., Hanson, K., Tataranni, P.A., et al. (2001): Circulating interleukin-6 in relation to adiposity, insulin action, and insulin secretion. Obes Res, 9, 414–417.
Warnberg, J. and Marcos, A. (2008): Low-grade inflammation and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Curr Opin Lipidol, 19, 11–15.
Warnberg, J., Moreno, L.A., Mesana, M.I. and Marcos, A. (2004): Inflammatory mediators in overweight and obese Spanish adolescents. The AVENA Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 28 Suppl 3, S59-S63.
Warnberg, J., Nova, E., Moreno, L.A., Romeo, J., et al. (2006): Inflammatory proteins are related to total and abdominal adiposity in a healthy adolescent population: the AVENA Study. Am J Clin Nutr, 84, 505–512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moleres, A., Rendo-Urteaga, T., Azcona, C. et al. Il6 gene promoter polymorphism (-174G/C) influences the association between fat mass and cardiovascular risk factors. J Physiol Biochem 65, 405–413 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185936
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185936